Monday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P2947 - Off-Label Use of the Oral NK-1 Antagonist Aprepitant Is Beneficial in GI Disorders of Nausea and Vomiting: Prescription Profiles and Patient Characteristics
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SR
Stacey Rolak, MD, MPH
Mayo Clinic Arizona
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Stacey Rolak, MD, MPH1, William L.. Hasler, MD2, Lucinda Harris, MD3, Tisha N. Lunsford, MD, FACG3, Alejandro Diaz Arumir Vergara, MD1, Mitsuko Sato, MD4, Rosita Frazier, MD3
1Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, AZ; 3Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 4Beneficencia Española, Veracruz, Veracruz-Llave, Mexico
Introduction: The oral neurokinin-1 (NK1) antagonist aprepitant is approved for chemotherapy-induced and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Benefits of off-label aprepitant are described for GI disorders of nausea and vomiting (N/V) such as gastroparesis and cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS). In our health system, 29% of aprepitant prescriptions from 2021-23 were for such off-label GI indications. However, aprepitant prescription profiles, use of other N/V therapies, symptom reductions, and adverse events on aprepitant in specialized motility clinics caring for chronic N/V are poorly defined.
Methods: A medical record search from a tertiary motility center identified adults who received aprepitant from 7/1/2021-6/30/2023 for GI disorders of N/V. GI diagnoses, aprepitant doses and duration of use, use of other N/V therapies, and outcomes on aprepitant were examined.
Results: Fifty-seven patients (74% female; age 40±16 yr) were prescribed aprepitant including 20 with gastroparesis (35%), 12 with CVS (21%), 6 with both conditions (11%), and 19 with other disorders (33%). Forty-three patients (75%) successfully obtained the drug; 34 (79%) filled prescriptions >3 months. Aprepitant dose packs (125 mg once/wk+80 mg twice/wk) were most often taken (17/43 patients [40%])(Table 1). Daily dosing was uncommon (6/43 patients [14%]). On average, patients used 5.0+2.3 other N/V therapies. Prior antiemetic use was universal—most often 5-HT3 antagonists (95%), dopamine D2 antagonists (79%), and histamine H1 antagonists (74%). Prokinetic agents and neuromodulators were taken by 61% and 72%, respectively. Cannabis was used by 45%. Reductions in N/V on aprepitant were noted by 29/43 patients (67%) similarly in gastroparesis vs. CVS (p=0.67). N/V decreased in 5/6 cases (83%) with daily dosing vs. 24/37 (65%) with less frequent use (p=0.65)(Table 1). Adverse effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue) were noted by 7 patients (16%).
Discussion: Aprepitant was commonly prescribed in a specialty motility center for disorders such as gastroparesis and CVS. Daily dosing was rare likely due to cost and insurance restrictions. Patients had already tried 5 other N/V therapies on average, reflecting their symptom burden. Nevertheless, two thirds of gastroparesis and CVS patients reported reduced N/V with infrequent side effects on aprepitant. These results support off-label inclusion of the NK1 antagonist aprepitant for treatment of these challenging conditions with chronic N/V.
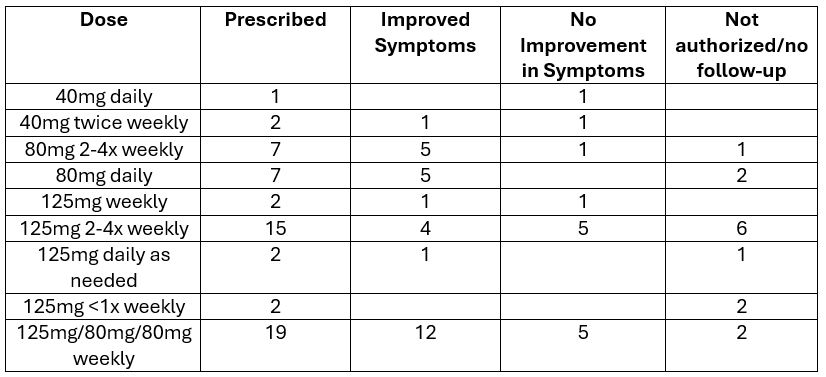
Figure: Table 1. Aprepitant dose schedule and response to treatment.
Disclosures:
Stacey Rolak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William Hasler: Alimetry Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Atmo Biosciences – Grant/Research Support. Enterra Medical – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Lucinda Harris: Anyx – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Consultant, Educational video. Gemelli Biotech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GI Health Foundation – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Rome – Member. Salix Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Tisha Lunsford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Diaz Arumir Vergara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mitsuko Sato indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rosita Frazier indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacey Rolak, MD, MPH1, William L.. Hasler, MD2, Lucinda Harris, MD3, Tisha N. Lunsford, MD, FACG3, Alejandro Diaz Arumir Vergara, MD1, Mitsuko Sato, MD4, Rosita Frazier, MD3. P2947 - Off-Label Use of the Oral NK-1 Antagonist Aprepitant Is Beneficial in GI Disorders of Nausea and Vomiting: Prescription Profiles and Patient Characteristics, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix, AZ; 2Mayo Clinic Arizona, Scottsdale, AZ; 3Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ; 4Beneficencia Española, Veracruz, Veracruz-Llave, Mexico
Introduction: The oral neurokinin-1 (NK1) antagonist aprepitant is approved for chemotherapy-induced and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Benefits of off-label aprepitant are described for GI disorders of nausea and vomiting (N/V) such as gastroparesis and cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS). In our health system, 29% of aprepitant prescriptions from 2021-23 were for such off-label GI indications. However, aprepitant prescription profiles, use of other N/V therapies, symptom reductions, and adverse events on aprepitant in specialized motility clinics caring for chronic N/V are poorly defined.
Methods: A medical record search from a tertiary motility center identified adults who received aprepitant from 7/1/2021-6/30/2023 for GI disorders of N/V. GI diagnoses, aprepitant doses and duration of use, use of other N/V therapies, and outcomes on aprepitant were examined.
Results: Fifty-seven patients (74% female; age 40±16 yr) were prescribed aprepitant including 20 with gastroparesis (35%), 12 with CVS (21%), 6 with both conditions (11%), and 19 with other disorders (33%). Forty-three patients (75%) successfully obtained the drug; 34 (79%) filled prescriptions >3 months. Aprepitant dose packs (125 mg once/wk+80 mg twice/wk) were most often taken (17/43 patients [40%])(Table 1). Daily dosing was uncommon (6/43 patients [14%]). On average, patients used 5.0+2.3 other N/V therapies. Prior antiemetic use was universal—most often 5-HT3 antagonists (95%), dopamine D2 antagonists (79%), and histamine H1 antagonists (74%). Prokinetic agents and neuromodulators were taken by 61% and 72%, respectively. Cannabis was used by 45%. Reductions in N/V on aprepitant were noted by 29/43 patients (67%) similarly in gastroparesis vs. CVS (p=0.67). N/V decreased in 5/6 cases (83%) with daily dosing vs. 24/37 (65%) with less frequent use (p=0.65)(Table 1). Adverse effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue) were noted by 7 patients (16%).
Discussion: Aprepitant was commonly prescribed in a specialty motility center for disorders such as gastroparesis and CVS. Daily dosing was rare likely due to cost and insurance restrictions. Patients had already tried 5 other N/V therapies on average, reflecting their symptom burden. Nevertheless, two thirds of gastroparesis and CVS patients reported reduced N/V with infrequent side effects on aprepitant. These results support off-label inclusion of the NK1 antagonist aprepitant for treatment of these challenging conditions with chronic N/V.

Figure: Table 1. Aprepitant dose schedule and response to treatment.
Disclosures:
Stacey Rolak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William Hasler: Alimetry Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Atmo Biosciences – Grant/Research Support. Enterra Medical – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Lucinda Harris: Anyx – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Consultant, Educational video. Gemelli Biotech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GI Health Foundation – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Rome – Member. Salix Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Tisha Lunsford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Diaz Arumir Vergara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mitsuko Sato indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rosita Frazier indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacey Rolak, MD, MPH1, William L.. Hasler, MD2, Lucinda Harris, MD3, Tisha N. Lunsford, MD, FACG3, Alejandro Diaz Arumir Vergara, MD1, Mitsuko Sato, MD4, Rosita Frazier, MD3. P2947 - Off-Label Use of the Oral NK-1 Antagonist Aprepitant Is Beneficial in GI Disorders of Nausea and Vomiting: Prescription Profiles and Patient Characteristics, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
