Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2872 - A Triple Hit: Multifocal Gastrointestinal Involvement of Metastatic Melanoma
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Dimitri Melki, MD (he/him/his)
University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health
Windsor, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3
1University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Windsor, CT; 2University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, East Windsor, CT; 3University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Springfield, MA
Introduction: Melanoma frequently metastasizes, but clinically apparent gastrointestinal (GI) involvement is rare, occurring in only 1–5% of cases despite being found in up to 60% at autopsy (Blecker et al. and Das Gupta et al.). Among GI sites, the small intestine is most commonly affected, while gastric and colonic involvement is less frequent. We present a rare case of multifocal GI metastatic melanoma involving the stomach, duodenum, and sigmoid colon.
Case Description/
Methods: A 59-year-old male presented with chest pain, dysphagia, and weight loss. CT imaging revealed bilateral pulmonary nodules, mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy, and metastases to the liver, spleen, adrenal glands, peritoneum, and retroperitoneum. CT-guided biopsy of a mediastinal mass confirmed metastatic melanoma.
EGD and colonoscopy were performed for further evaluation of his dysphagia and weight loss. EGD showed an 8mm gastric body ulcer and a 6mm duodenal ulcer. Colonoscopy revealed a 30mm ulcerated, infiltrative sigmoid mass with stigmata of recent bleeding . All three lesions were biopsied and confirmed to be metastatic melanoma. The patient began combination immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab, followed by maintenance nivolumab.
Discussion: Multifocal GI involvement by melanoma is exceptionally rare. This case underscores the importance of considering GI metastases in melanoma patients presenting with new symptoms such as dysphagia, bleeding, or weight loss. Endoscopic evaluation remains essential in identifying and managing metastatic lesions, especially in instances of bleeding. Simultaneous upper and lower GI involvement highlights the aggressive nature of the disease.
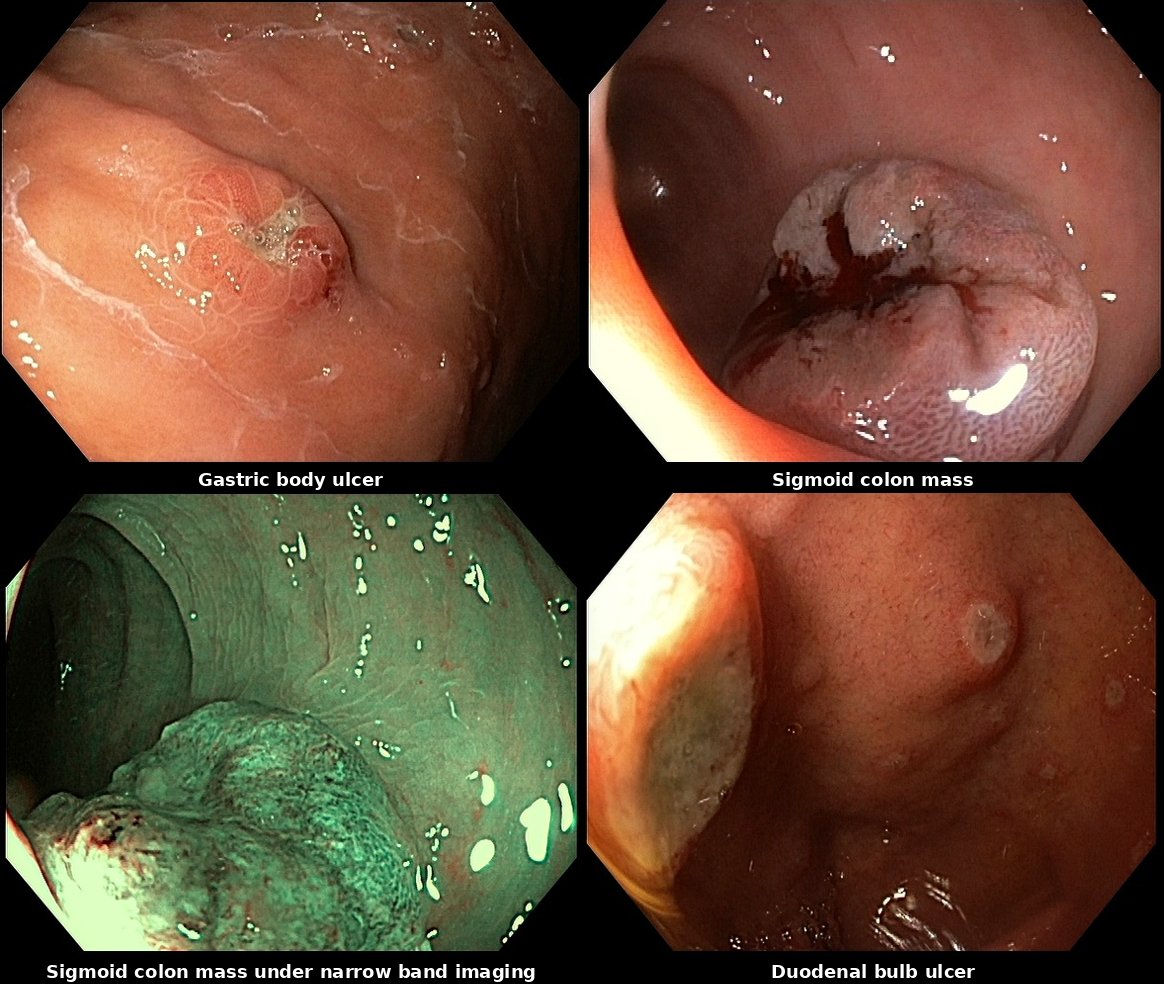
Figure: multifocal GI involvement seen on EGD and Colonoscopy
Disclosures:
Dimitri Melki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Groudan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nha Duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3. P2872 - A Triple Hit: Multifocal Gastrointestinal Involvement of Metastatic Melanoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Windsor, CT; 2University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, East Windsor, CT; 3University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School - Baystate Health, Springfield, MA
Introduction: Melanoma frequently metastasizes, but clinically apparent gastrointestinal (GI) involvement is rare, occurring in only 1–5% of cases despite being found in up to 60% at autopsy (Blecker et al. and Das Gupta et al.). Among GI sites, the small intestine is most commonly affected, while gastric and colonic involvement is less frequent. We present a rare case of multifocal GI metastatic melanoma involving the stomach, duodenum, and sigmoid colon.
Case Description/
Methods: A 59-year-old male presented with chest pain, dysphagia, and weight loss. CT imaging revealed bilateral pulmonary nodules, mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy, and metastases to the liver, spleen, adrenal glands, peritoneum, and retroperitoneum. CT-guided biopsy of a mediastinal mass confirmed metastatic melanoma.
EGD and colonoscopy were performed for further evaluation of his dysphagia and weight loss. EGD showed an 8mm gastric body ulcer and a 6mm duodenal ulcer. Colonoscopy revealed a 30mm ulcerated, infiltrative sigmoid mass with stigmata of recent bleeding . All three lesions were biopsied and confirmed to be metastatic melanoma. The patient began combination immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab, followed by maintenance nivolumab.
Discussion: Multifocal GI involvement by melanoma is exceptionally rare. This case underscores the importance of considering GI metastases in melanoma patients presenting with new symptoms such as dysphagia, bleeding, or weight loss. Endoscopic evaluation remains essential in identifying and managing metastatic lesions, especially in instances of bleeding. Simultaneous upper and lower GI involvement highlights the aggressive nature of the disease.

Figure: multifocal GI involvement seen on EGD and Colonoscopy
Disclosures:
Dimitri Melki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Groudan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nha Duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dimitri Melki, MD1, Kevin Groudan, MD2, Nha Duong, DO3. P2872 - A Triple Hit: Multifocal Gastrointestinal Involvement of Metastatic Melanoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

