Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2790 - Dupilumab Outperforms Swallowed Steroids in PPI Refractory EoE: Insights From a Real-World Cohort
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

James O. McKnight, III, BS (he/him/his)
Henry Ford Health
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
James O. McKnight, BS1, Suraj Suresh, MD1, Abdulmalik Saleem, MD2
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Henry Ford Hospital, Flushing, MI
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated condition often treated with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). However, a subset of patients exhibit persistent symptoms and inflammation despite PPI therapy and are considered to have PPI-refractory EoE. In such cases, swallowed topical corticosteroids (STC) and dupilumab—a monoclonal antibody recently approved for EoE—are therapeutic options. Real-world comparative data between these treatments remain limited. This study evaluated the effectiveness of dupilumab versus STC in patients with PPI-refractory EoE, using clinical, endoscopic, and histologic outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients with PPI-refractory EoE treated with either dupilumab or STC at a large tertiary care center. Data collected included demographics, medical history, endoscopic findings, and clinical dysphagia scores. Outcomes assessed were changes in peak eosinophil counts per high-power field, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Scores (EREFS), and clinical dysphagia scores. Comparative analyses were performed using t-tests for continuous variables and chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests for categorical variables. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Thirty-five patients were included (dupilumab n=18; STC n=17). Baseline characteristics were similar between groups in age (39.6 ± 16.0 vs. 45.6 ± 13.2 years, p=0.227), sex (72% vs. 65% male, p=0.725), and race (p=0.212). Pre-treatment eosinophil counts, EREFS, and dysphagia scores were comparable. Post-treatment, patients on dupilumab showed significantly greater reductions in peak eosinophil counts compared to those on STC (−83.1 ± 52.9 vs. −43.4 ± 32.3, p=0.012). Dupilumab was also associated with lower EREFS (-1.1 ± 1.9 vs. -0.47 ± 1.2, p=0.279) and improved dysphagia scores (0.7 ± 0.5 vs. 0.6 ± 0.5, p=0.490), though these did not reach statistical significance.
Discussion: In this real-world cohort, dupilumab was associated with significantly greater histologic improvement compared to STC in patients with PPI-refractory EoE. Although endoscopic and clinical symptom scores did not show statistically significant differences, observed trends suggest potential clinical benefit. These findings support dupilumab as a promising treatment option for patients with persistent eosinophilic inflammation despite standard therapies. Prospective studies are warranted to confirm these results and assess long-term outcomes.
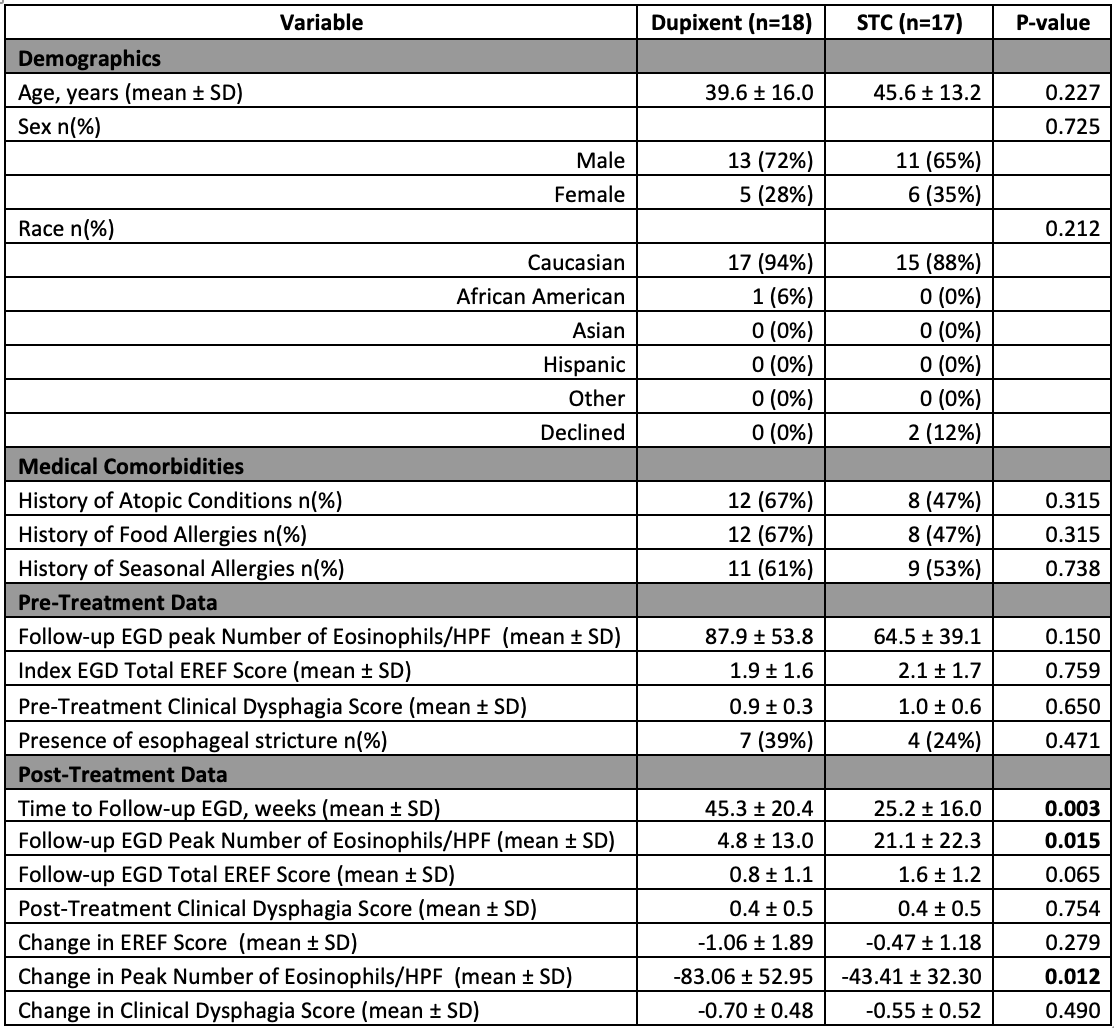
Figure: Table 1: Baseline Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Patients with PPI-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis Treated with Dupilumab vs. Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids
Disclosures:
James McKnight indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suraj Suresh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdulmalik Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James O. McKnight, BS1, Suraj Suresh, MD1, Abdulmalik Saleem, MD2. P2790 - Dupilumab Outperforms Swallowed Steroids in PPI Refractory EoE: Insights From a Real-World Cohort, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 2Henry Ford Hospital, Flushing, MI
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated condition often treated with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). However, a subset of patients exhibit persistent symptoms and inflammation despite PPI therapy and are considered to have PPI-refractory EoE. In such cases, swallowed topical corticosteroids (STC) and dupilumab—a monoclonal antibody recently approved for EoE—are therapeutic options. Real-world comparative data between these treatments remain limited. This study evaluated the effectiveness of dupilumab versus STC in patients with PPI-refractory EoE, using clinical, endoscopic, and histologic outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients with PPI-refractory EoE treated with either dupilumab or STC at a large tertiary care center. Data collected included demographics, medical history, endoscopic findings, and clinical dysphagia scores. Outcomes assessed were changes in peak eosinophil counts per high-power field, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Scores (EREFS), and clinical dysphagia scores. Comparative analyses were performed using t-tests for continuous variables and chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests for categorical variables. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Thirty-five patients were included (dupilumab n=18; STC n=17). Baseline characteristics were similar between groups in age (39.6 ± 16.0 vs. 45.6 ± 13.2 years, p=0.227), sex (72% vs. 65% male, p=0.725), and race (p=0.212). Pre-treatment eosinophil counts, EREFS, and dysphagia scores were comparable. Post-treatment, patients on dupilumab showed significantly greater reductions in peak eosinophil counts compared to those on STC (−83.1 ± 52.9 vs. −43.4 ± 32.3, p=0.012). Dupilumab was also associated with lower EREFS (-1.1 ± 1.9 vs. -0.47 ± 1.2, p=0.279) and improved dysphagia scores (0.7 ± 0.5 vs. 0.6 ± 0.5, p=0.490), though these did not reach statistical significance.
Discussion: In this real-world cohort, dupilumab was associated with significantly greater histologic improvement compared to STC in patients with PPI-refractory EoE. Although endoscopic and clinical symptom scores did not show statistically significant differences, observed trends suggest potential clinical benefit. These findings support dupilumab as a promising treatment option for patients with persistent eosinophilic inflammation despite standard therapies. Prospective studies are warranted to confirm these results and assess long-term outcomes.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Patients with PPI-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis Treated with Dupilumab vs. Swallowed Topical Corticosteroids
Disclosures:
James McKnight indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suraj Suresh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdulmalik Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James O. McKnight, BS1, Suraj Suresh, MD1, Abdulmalik Saleem, MD2. P2790 - Dupilumab Outperforms Swallowed Steroids in PPI Refractory EoE: Insights From a Real-World Cohort, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

