Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2783 - Pooled Diagnostic Accuracy of Methylated DNA Biomarker Panels from Nonendoscopic Cell Collection Devices for Barrett’s Esophagus and Neoplasia Detection
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Nouman Shafique, MD (he/him/his)
AdventHealth Orlando
Orlando, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Nihal I. Khan, MD1, Tareq Alsaleh, MD2, Abdullah Javed, MBBS3, Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO4, Shahzad Zafar, MD5, Sheraz Ahmad Tariq, MBBS6, Atta Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Ali Haider, MBBS7, Adeena Shafique, MBBS8, Iqra Shafique, MBBS9, Abu Hurairah, MD10, John George, MD11
1AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2Department of Internal Medicine, Adventhealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 5Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 6Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 9CMH Institute of Medical Sciences, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 10AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 11Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a known precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), a cancer with rising incidence and poor survival. Despite guideline recommendations, screening uptake remains low due to reliance on endoscopy, an invasive and resource-intensive procedure. Minimally invasive, nonendoscopic methods that use esophageal cell collection devices in combination with methylated DNA biomarkers (MDMs) have emerged as promising alternatives for detecting BE and associated neoplastic lesions. We evaluated the pooled diagnostic performance of MDM panels applied to cytologic samples collected via various capsule sponge-based devices for detection of non-dysplastic BE, indefinite for dysplasia (IND), high-grade dysplasia (HGD), and EAC.
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Scopus from inception through May 2025 for studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of MDM assays for BE and related lesions. Multiple studies used genome-wide methylation profiling to identify and validate hypermethylated genes that differentiate BE from normal epithelium. Candidate MDMs—including CCNA1, VIM, TFPI2, TWIST1, and others—were analyzed via quantitative PCR or next-generation sequencing from cytologic samples collected using swallowable devices such as Cytosponge, EsophaCap, and EsoCheck. The most discriminative panels included combinations such as TFPI2, TWIST1, ZNF345, ZNF569; CCNA1 + VIM; and USP44, TBC1D30, NELL1. Cases included patients with BE or neoplasia confirmed on endoscopy; controls had no evidence of BE or dysplasia.
Results: Eight studies were included, encompassing 853 cases and 713 controls. The pooled sensitivity for detecting any lesion (BE, IND, HGD, or EAC) amongst cases was 83.8%, and the pooled specificity for excluding these conditions in controls was 90.0%. Detailed study characteristics are summarized in Table 1, and diagnostic accuracy is illustrated in Figure 1.
Discussion: Nonendoscopic esophageal cell collection paired with methylated DNA biomarker assays demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity for detecting BE and associated neoplasia. These approaches offer a scalable, patient-friendly alternative to traditional endoscopic screening and may improve early detection and risk stratification. Widespread implementation could address current gaps in screening uptake and aligns with ACG and AGA guideline priorities for EAC prevention.
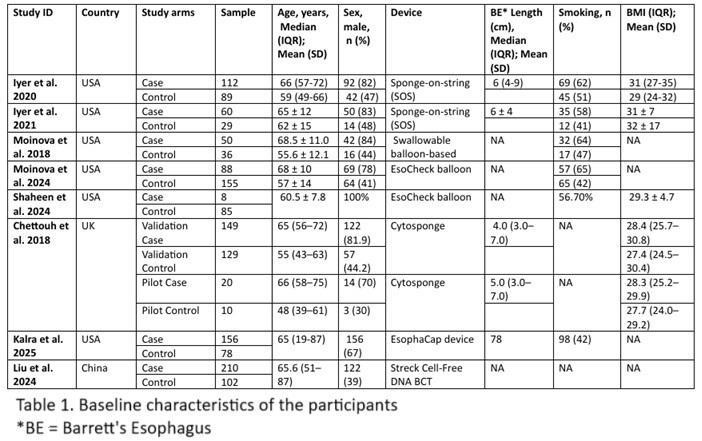
Figure: Table 1 showing baseline characteristics of all studies included
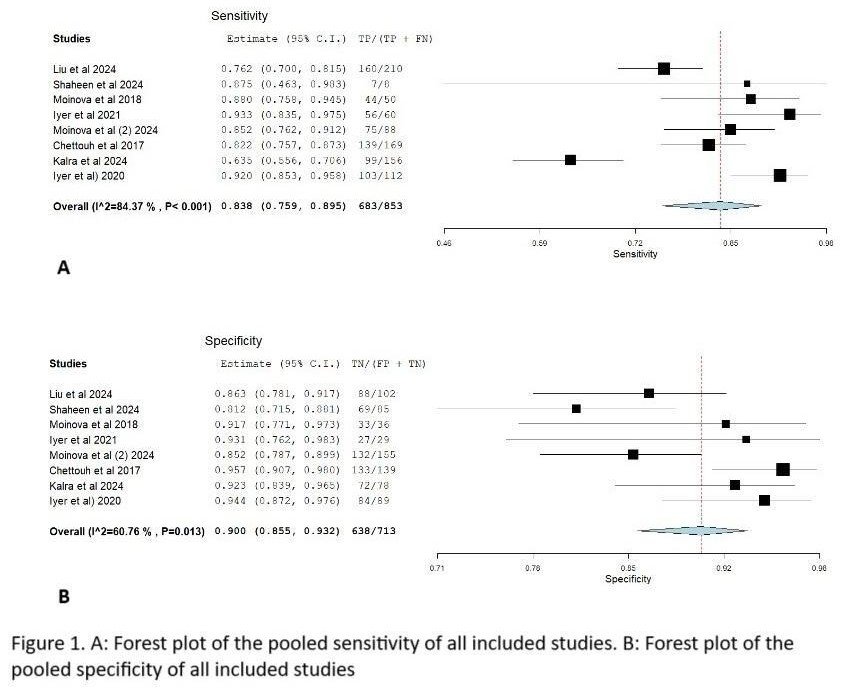
Figure: Forest plots for pooled sensitivity and specificity
Disclosures:
Nouman Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tareq Alsaleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Hamaad Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahzad Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sheraz Ahmad Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atta Ur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adeena Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abu Hurairah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John George indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Nihal I. Khan, MD1, Tareq Alsaleh, MD2, Abdullah Javed, MBBS3, Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO4, Shahzad Zafar, MD5, Sheraz Ahmad Tariq, MBBS6, Atta Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Ali Haider, MBBS7, Adeena Shafique, MBBS8, Iqra Shafique, MBBS9, Abu Hurairah, MD10, John George, MD11. P2783 - Pooled Diagnostic Accuracy of Methylated DNA Biomarker Panels from Nonendoscopic Cell Collection Devices for Barrett’s Esophagus and Neoplasia Detection, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 2Department of Internal Medicine, Adventhealth Orlando, Orlando, FL; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 5Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 6Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Nishtar Medical University, Multan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Aga Khan University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 9CMH Institute of Medical Sciences, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 10AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 11Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, AdventHealth Orlando, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is a known precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), a cancer with rising incidence and poor survival. Despite guideline recommendations, screening uptake remains low due to reliance on endoscopy, an invasive and resource-intensive procedure. Minimally invasive, nonendoscopic methods that use esophageal cell collection devices in combination with methylated DNA biomarkers (MDMs) have emerged as promising alternatives for detecting BE and associated neoplastic lesions. We evaluated the pooled diagnostic performance of MDM panels applied to cytologic samples collected via various capsule sponge-based devices for detection of non-dysplastic BE, indefinite for dysplasia (IND), high-grade dysplasia (HGD), and EAC.
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Scopus from inception through May 2025 for studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of MDM assays for BE and related lesions. Multiple studies used genome-wide methylation profiling to identify and validate hypermethylated genes that differentiate BE from normal epithelium. Candidate MDMs—including CCNA1, VIM, TFPI2, TWIST1, and others—were analyzed via quantitative PCR or next-generation sequencing from cytologic samples collected using swallowable devices such as Cytosponge, EsophaCap, and EsoCheck. The most discriminative panels included combinations such as TFPI2, TWIST1, ZNF345, ZNF569; CCNA1 + VIM; and USP44, TBC1D30, NELL1. Cases included patients with BE or neoplasia confirmed on endoscopy; controls had no evidence of BE or dysplasia.
Results: Eight studies were included, encompassing 853 cases and 713 controls. The pooled sensitivity for detecting any lesion (BE, IND, HGD, or EAC) amongst cases was 83.8%, and the pooled specificity for excluding these conditions in controls was 90.0%. Detailed study characteristics are summarized in Table 1, and diagnostic accuracy is illustrated in Figure 1.
Discussion: Nonendoscopic esophageal cell collection paired with methylated DNA biomarker assays demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity for detecting BE and associated neoplasia. These approaches offer a scalable, patient-friendly alternative to traditional endoscopic screening and may improve early detection and risk stratification. Widespread implementation could address current gaps in screening uptake and aligns with ACG and AGA guideline priorities for EAC prevention.

Figure: Table 1 showing baseline characteristics of all studies included

Figure: Forest plots for pooled sensitivity and specificity
Disclosures:
Nouman Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tareq Alsaleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Hamaad Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahzad Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sheraz Ahmad Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Atta Ur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adeena Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Shafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abu Hurairah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John George indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nouman Shafique, MD1, Nihal I. Khan, MD1, Tareq Alsaleh, MD2, Abdullah Javed, MBBS3, Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO4, Shahzad Zafar, MD5, Sheraz Ahmad Tariq, MBBS6, Atta Ur Rehman, MBBS6, Ali Haider, MBBS7, Adeena Shafique, MBBS8, Iqra Shafique, MBBS9, Abu Hurairah, MD10, John George, MD11. P2783 - Pooled Diagnostic Accuracy of Methylated DNA Biomarker Panels from Nonendoscopic Cell Collection Devices for Barrett’s Esophagus and Neoplasia Detection, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
