Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2764 - Efficacy of Prophylactic Stent Placement to Prevent Esophageal Stricture After Esophageal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SY
Saira Yousuf, MD
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Nashville, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Tayyab Mushtaq, MD4, Haseeb Ali, MD5, Sultan Mahmood, MD6, Nilay Bhatt, MD7, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Umar Hayat, MD8, Nasir Saleem, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3King Edward Medical University, Chattanooga, TN; 4Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Services Hospital Lahore, Albany, NY; 6University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 7HCA Houston Clear Lake, Houston, TX; 8Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 9Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 10Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Esophageal stricture is a major concern after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in patients with esophageal lesions. Different prophylactic methods to prevent stricture formation have been explored. In this meta-analysis, we have evaluated the efficacy of prophylactic fully covered metal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after esophageal ESD
Methods: We reviewed several databases from inception to May 10, 2025, to identify studies
that evaluated the efficacy and safety of prophylactic esophageal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after ESD. Our outcomes of interest were rates of esophageal strictures and need for balloon dilation after esophageal stent placement. We also compared rates of stricture and mean number of balloon dilation sessions after stent alone vs. polyglycolic acid (PGA) sheet + stent. We calculated pooled rates with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for our outcomes of interest. For comparatives outcomes, we calculated odds ratios (95% CI) for categorical data and mean difference (95% CI) for continuous data. Data was analyzed using a random effect model. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistic.
Results: We included 5 studies (2 randomized controlled trials and 3 observational ) in final analysis. The mean age of the patients was 64.5(3.05) years. Pooled rates (95% CI) of esophageal stricture after prophylactic stent placement were 20.9% (13.8%, 30.8%), p=0.48, I² =0% (Figure 1). Comparative analysis of PGA plus stent vs. stent alone showed that PGA+stent was associated with lower rates of strictures, OR 0.41 (0.23, 0.74), p=0.003, I² =0%, and lower number of endoscopic balloon dilatation sessions, MD -1.65 (-2.40, 0.90), p< 0.0001, I² =0%.
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy of prophylactic esophageal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after ESD. PGA plus stents were associated with lower rates of esophageal strictures compared to stents alone. More studies with larger sample sizes are needed to further evaluate these findings.
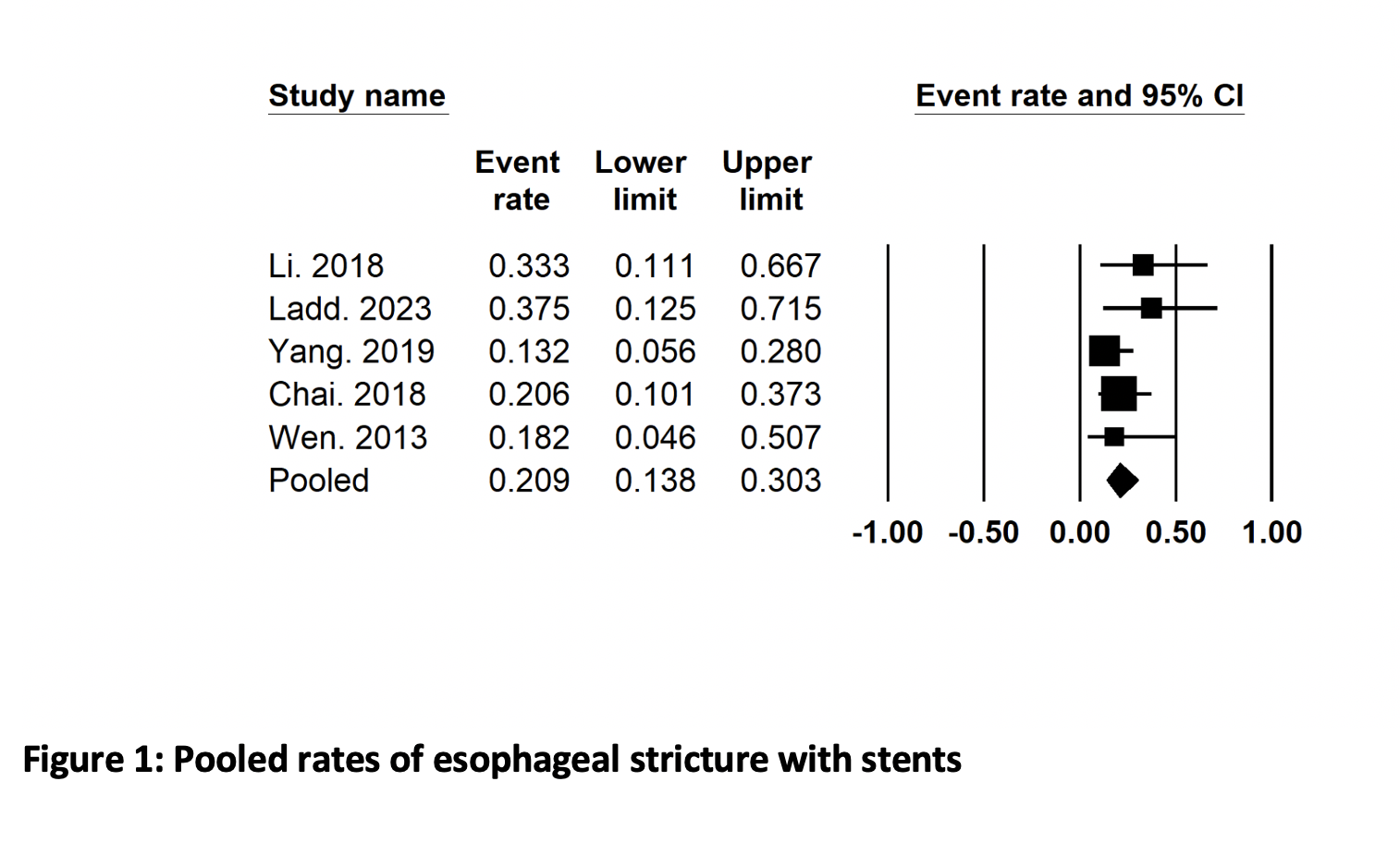
Figure: Figure 1: Pooled rates of esophageal stricture with stents
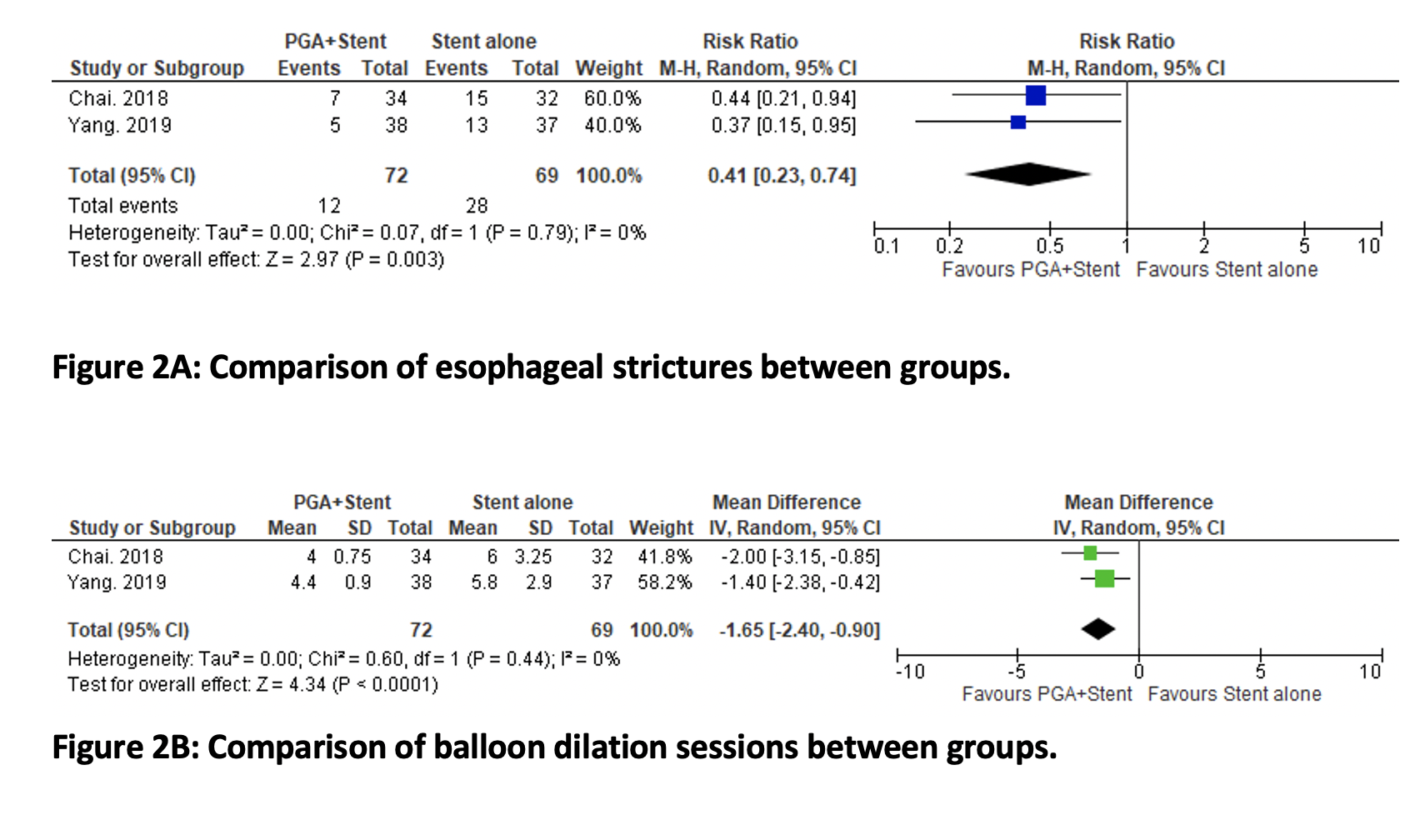
Figure: Figure 2: Comparison of esophageal strictures and number of balloon dilation sessions between groups
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Yousuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hina Akbar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tayyab Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sultan Mahmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilay Bhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Radlinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nasir Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Tayyab Mushtaq, MD4, Haseeb Ali, MD5, Sultan Mahmood, MD6, Nilay Bhatt, MD7, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Umar Hayat, MD8, Nasir Saleem, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10. P2764 - Efficacy of Prophylactic Stent Placement to Prevent Esophageal Stricture After Esophageal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3King Edward Medical University, Chattanooga, TN; 4Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Services Hospital Lahore, Albany, NY; 6University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 7HCA Houston Clear Lake, Houston, TX; 8Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 9Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 10Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Esophageal stricture is a major concern after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) in patients with esophageal lesions. Different prophylactic methods to prevent stricture formation have been explored. In this meta-analysis, we have evaluated the efficacy of prophylactic fully covered metal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after esophageal ESD
Methods: We reviewed several databases from inception to May 10, 2025, to identify studies
that evaluated the efficacy and safety of prophylactic esophageal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after ESD. Our outcomes of interest were rates of esophageal strictures and need for balloon dilation after esophageal stent placement. We also compared rates of stricture and mean number of balloon dilation sessions after stent alone vs. polyglycolic acid (PGA) sheet + stent. We calculated pooled rates with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for our outcomes of interest. For comparatives outcomes, we calculated odds ratios (95% CI) for categorical data and mean difference (95% CI) for continuous data. Data was analyzed using a random effect model. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistic.
Results: We included 5 studies (2 randomized controlled trials and 3 observational ) in final analysis. The mean age of the patients was 64.5(3.05) years. Pooled rates (95% CI) of esophageal stricture after prophylactic stent placement were 20.9% (13.8%, 30.8%), p=0.48, I² =0% (Figure 1). Comparative analysis of PGA plus stent vs. stent alone showed that PGA+stent was associated with lower rates of strictures, OR 0.41 (0.23, 0.74), p=0.003, I² =0%, and lower number of endoscopic balloon dilatation sessions, MD -1.65 (-2.40, 0.90), p< 0.0001, I² =0%.
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy of prophylactic esophageal stent placement to prevent esophageal strictures after ESD. PGA plus stents were associated with lower rates of esophageal strictures compared to stents alone. More studies with larger sample sizes are needed to further evaluate these findings.

Figure: Figure 1: Pooled rates of esophageal stricture with stents

Figure: Figure 2: Comparison of esophageal strictures and number of balloon dilation sessions between groups
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Yousuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hina Akbar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tayyab Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haseeb Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sultan Mahmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilay Bhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Radlinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nasir Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MBBS2, Hina Akbar, MD3, Tayyab Mushtaq, MD4, Haseeb Ali, MD5, Sultan Mahmood, MD6, Nilay Bhatt, MD7, Mark Radlinski, MD1, Umar Hayat, MD8, Nasir Saleem, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10. P2764 - Efficacy of Prophylactic Stent Placement to Prevent Esophageal Stricture After Esophageal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
