Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P2444 - System-Based and Culturally Responsive Interventions to Enhance CRC Screening Uptake in a Safety Net Clinic

Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Farmington, CT
Presenting Author(s)
1University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT; 2University of Connecticut Health Center, Hartford, CT; 3University of Connecticut Health, Farmington, CT; 4Hartford Hospital, Hartford, CT; 5Connecticut GI, Farmington, CT
Introduction:
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. Despite recommendations for screening at age 45, only 68.8% of eligible adults complete CRC screening, with lower rates among racial/ethnic minorities, low-income patients, and those with limited health literacy. At Hartford Healthcare Adult Primary Care Clinic, serving a Hispanic/Latino population with 65% on Medicaid or self-pay, only 113 multitarget stool DNA (mt-sDNA) orders and 254 screening colonoscopy referrals (SCR) were recorded from September 2022 through August 2023. The goal was to increase mt-sDNA orders by 50% (from 113 to 170) and SCR by 50% (from 254 to 381) by August 2024, with a focus on improving screening engagement among Spanish-speaking patients.
Methods: We conducted a prospective quality improvement initiative. Pre-intervention data were collected from September 2022 to August 2023 (baseline), and post-intervention data from September 2023 to August 2024 (intervention). Starting September 1, 2023, our multifaceted intervention included: (1) biweekly educational sessions for all resident and attending physicians on CRC screening guidelines, mt-sDNA order workflows, and cultural competence; (2) integration of a mt-sDNA prompt into the electronic medical record’s Best Practice Advisory; and (3) distribution of bilingual (English/Spanish) patient education pamphlets and QR-linked instructional videos. Outcomes—mt-sDNA orders and SCR referrals were aggregated into eight consecutive three-month periods, and pre- versus post-intervention proportions were compared using chi-square tests (α = 0.05) and Poisson log-linear model.
Results: After adjusting for quarterly clinic volume in a Poisson log‐linear model, the rate of mt-sDNA orders increased by 70% following the intervention (incidence-rate ratio [IRR] = 1.70; 95% CI 1.35–2.14; p < 0.001), and overall screening actions rose by 27% (IRR = 1.27; 95% CI 1.11–1.46; p = 0.0005). Combined screening actions increased significantly more among Spanish-speaking patients (χ²₁ = 4.53; p = 0.03) and Hispanic patients (χ²₁ = 4.80; p = 0.028) than among their counterparts.
Discussion: Embedding mt-sDNA orders into EMR workflows and reinforcing its use through targeted provider education and culturally tailored patient materials significantly improved CRC screening uptake, among underserved Spanish-speaking patients. Future work will evaluate mt-sDNA completion rates and integrate patient navigation to optimize follow-through after positive test results.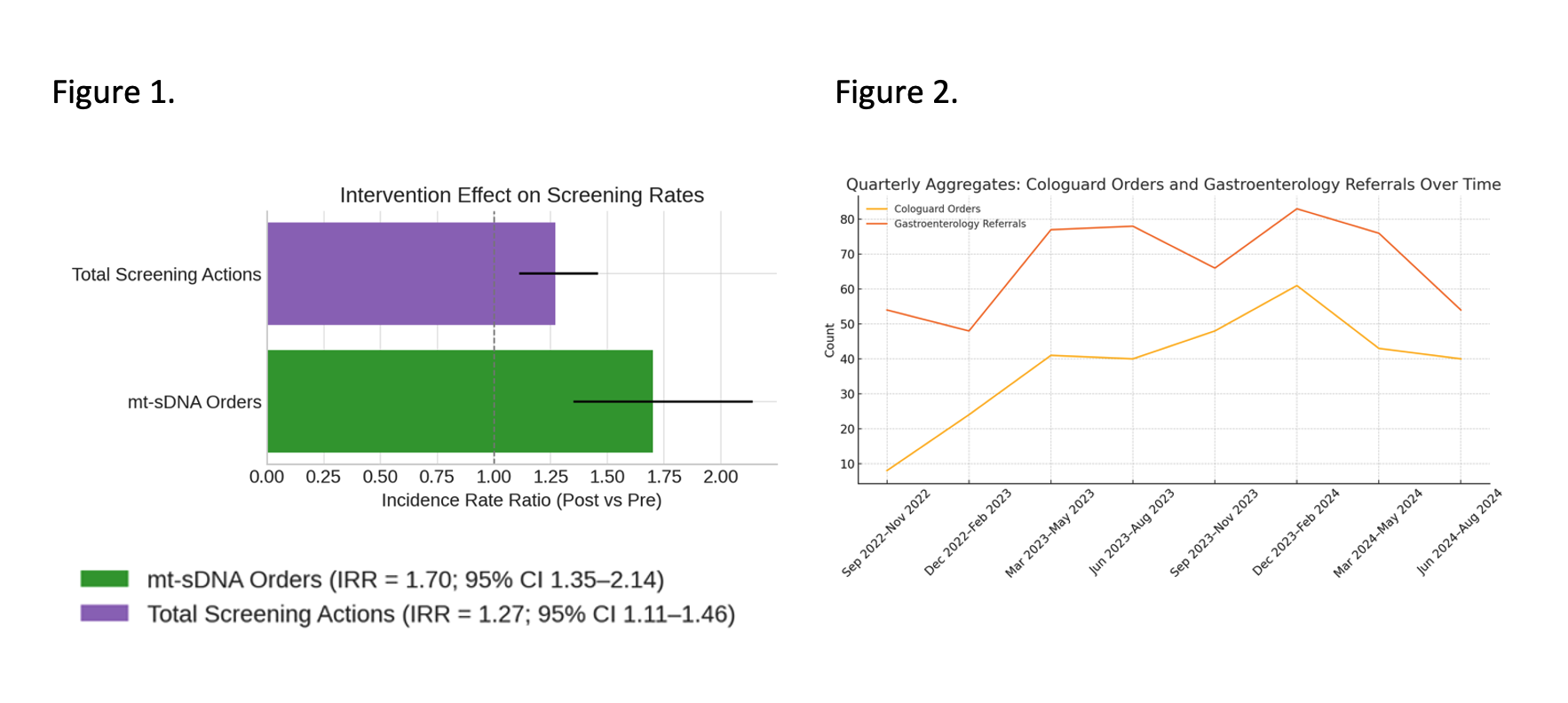
Figure: Table 1. Comparison of colorectal cancer screening uptake before and after implementation of the QI intervention (Sep 2022–Aug 2023 vs. Sep 2023–Aug 2024), stratified by patient subgroup.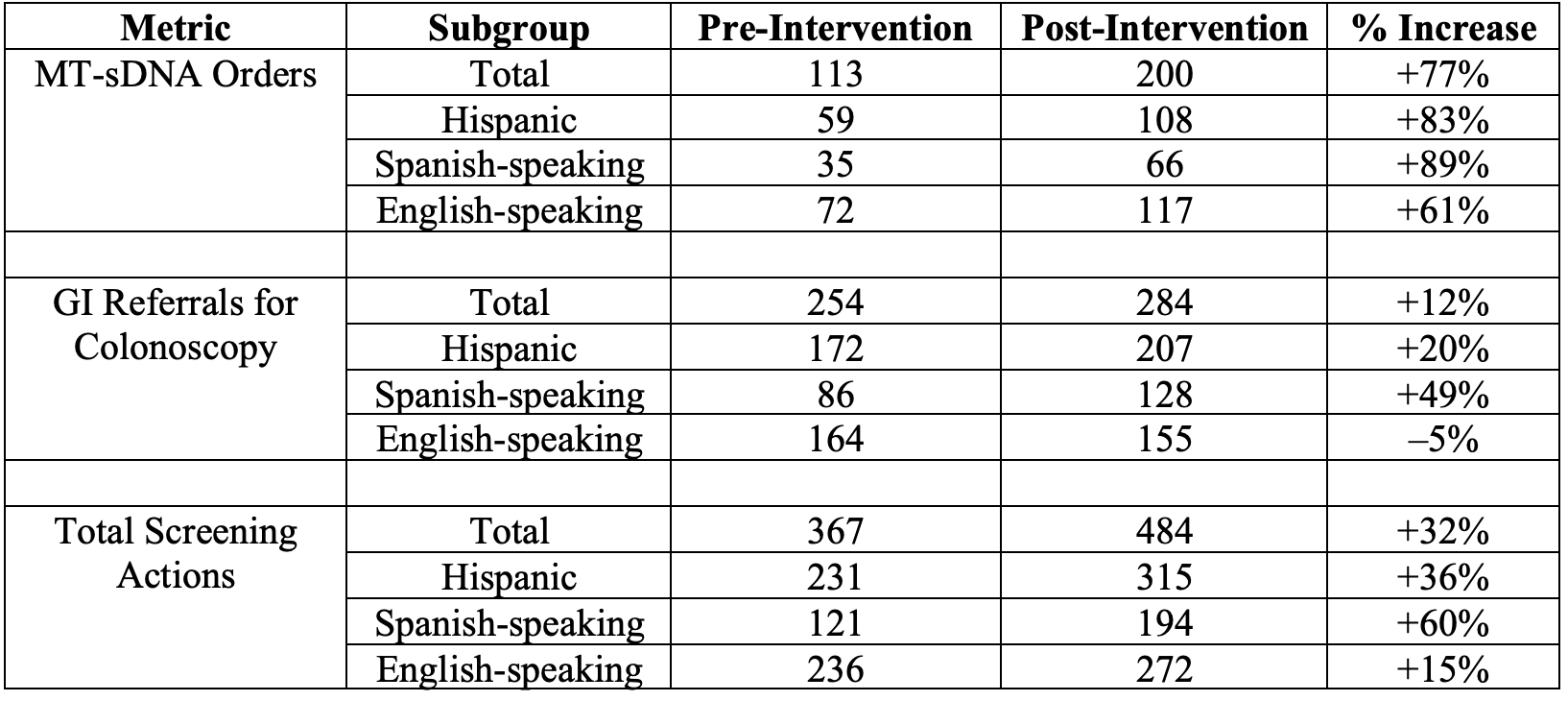
Figure: Figure 1. Horizontal bar chart depicting incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for mt-sDNA orders and total screening actions post- versus pre-intervention, with 95% confidence intervals. The dashed vertical line at IRR=1 denotes no change; bars to the right indicate significant increases.
Figure 2. Three-month aggregates of Cologuard orders (yellow line) and gastroenterology referrals (orange line) over eight consecutive periods from September 2022 to August 2024.
Disclosures:
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arup Ganguly indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karmen Brar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cunegundo Vergara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Parikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya, MBBS1, Arup Ganguly, MBBS2, Karmen Brar, MD3, Cunegundo Vergara, MD4, Neil Parikh, MD5. P2444 - System-Based and Culturally Responsive Interventions to Enhance CRC Screening Uptake in a Safety Net Clinic, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
