Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4630 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of T3 MSI-high Colorectal Cancer Treated With Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Anni Chowdhury Arellanes, DO
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes, DO1, Montserrat Guraieb Trueba, MD1, Van Karlyle II Morris, MD1, Phillip S.. Ge, MD2, Emmanuel Coronel, MD2
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immunotherapy (ICI) with programmed death 1 blockade such as pembrolizumab has been efficacious in treating early-stage deficient DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) and microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) colorectal tumors. Interestingly, this therapy has been reported to cause significant regression of colorectal cancer. Here we report a case of an elderly patient with locally invasive colon cancer (T3N0M0), that was treated with pembrolizumab and endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Case Description/
Methods: 88M with medical history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation with pacemaker and multiple colonic polyps since index colonoscopy at age 58. Surveillance colonoscopy on 6/6/24 found a 3cm friable ascending colon mass with pathology confirming invasive moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, MSI-H with loss of MLH1 and PMS2. He started on first line treatment with single agent pembrolizumab on 8/7/2024. Within 2 months, there was a decrease in size of the lesion from 3cm to 1.9 cm and no increase in size or evidence of metastasis at 8 months. Colonoscopy performed to assess treatment response showed a polypoid non-obstructing 3 cm ascending colon mass with an adjacent tattoo. Biopsies revealed sessile serrated lesion with high grade dysplasia and no malignancy noted. The case was discussed at multidisciplinary tumor board and since he was not a surgical candidate, the decision was made to attempt endoscopic resection. The residual mass was then resected successfully with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). A 4 cm by 4 cm resection specimen was obtained; the specimen was removed en-bloc. (Figure 2). The margins were free of polypoid tissue. Pathology showed minute focus of invasive adenocarcinoma without evidence of lymphovascular invasion.
Discussion: dMMR & MSI-H tumors account for 15% of all colorectal cancers. Immunotherapy has the potential to change the standard of care for localized dMMR tumors as it has shown high rates of pathologic, radiographic, and endoscopic response. As a result, organ-sparing strategies including endoscopic resection with ESD are becoming feasible management options for these lesions that previously required invasive surgical resection.
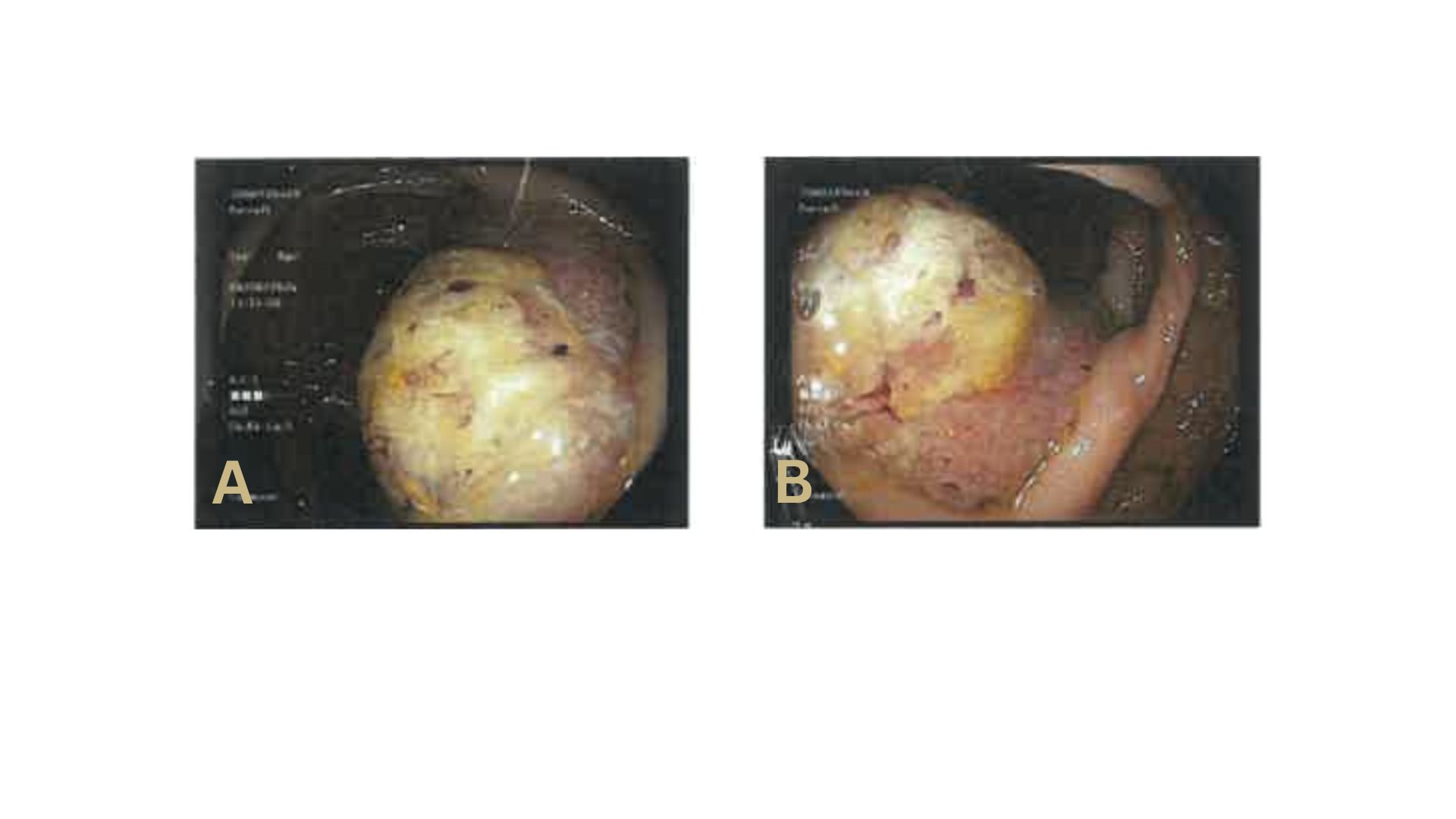
Figure: Figure 1. 3cm Right Colon Mass, prior to Pembrolizumab Therapy
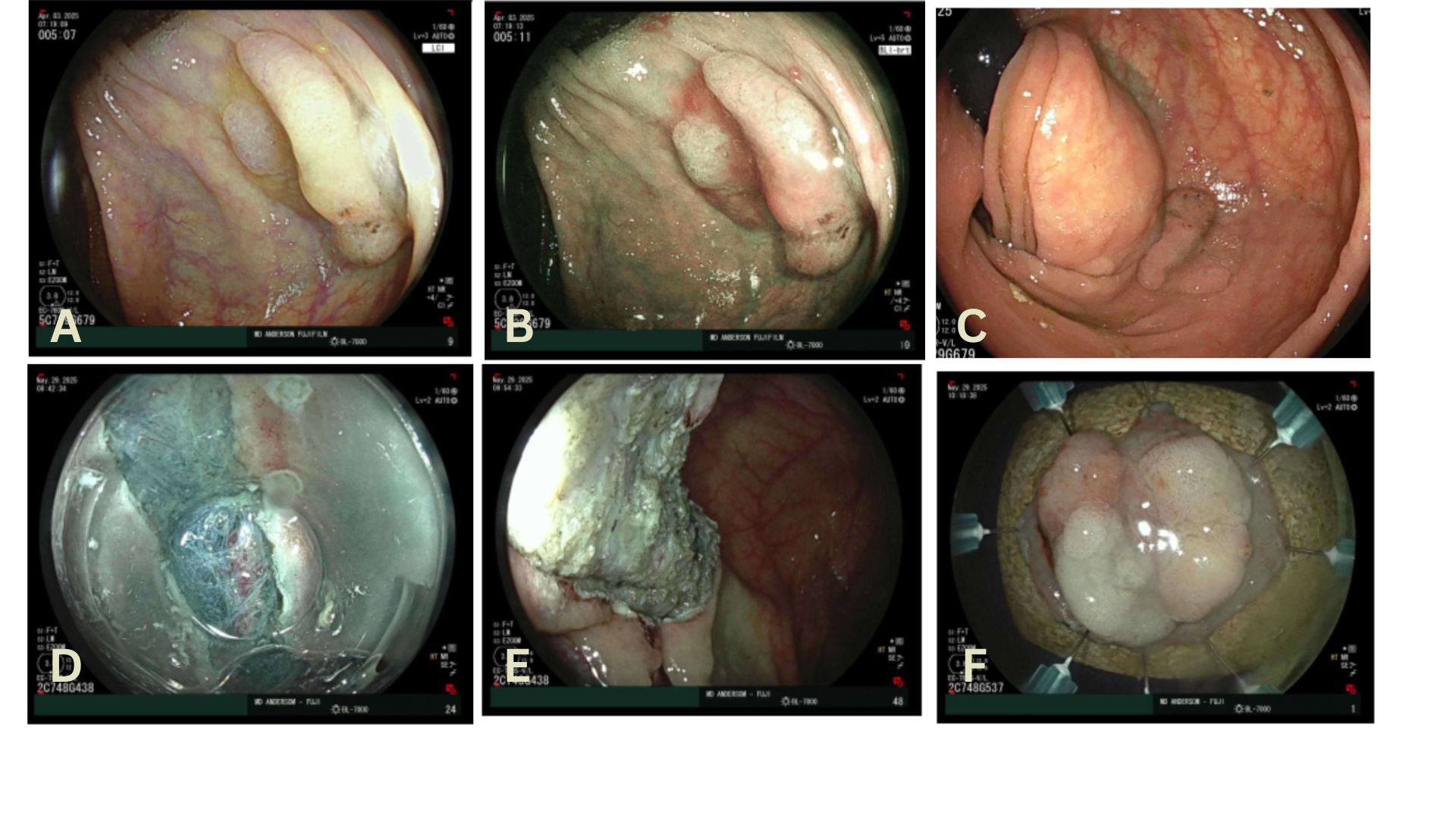
Figure: Figure 2: Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Residual Colonic Mass. Image A, B – 3cm mass (Paris Classification mixed IIa + IIc) in forward view. C – Mass in retroflexed view. D – ESD of lesion. E – Post Resection Site. F – Resected Specimen
Disclosures:
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Montserrat Guraieb Trueba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Van Karlyle II Morris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phillip Ge: Aspero Medical – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fujifilm Medical Systems – Consultant. Neptune Medical – Consultant. Ovesco Endoscopy USA – Consultant. UpToDate – Royalties.
Emmanuel Coronel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes, DO1, Montserrat Guraieb Trueba, MD1, Van Karlyle II Morris, MD1, Phillip S.. Ge, MD2, Emmanuel Coronel, MD2. P4630 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of T3 MSI-high Colorectal Cancer Treated With Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes, DO1, Montserrat Guraieb Trueba, MD1, Van Karlyle II Morris, MD1, Phillip S.. Ge, MD2, Emmanuel Coronel, MD2
1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 2The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Immunotherapy (ICI) with programmed death 1 blockade such as pembrolizumab has been efficacious in treating early-stage deficient DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) and microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) colorectal tumors. Interestingly, this therapy has been reported to cause significant regression of colorectal cancer. Here we report a case of an elderly patient with locally invasive colon cancer (T3N0M0), that was treated with pembrolizumab and endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Case Description/
Methods: 88M with medical history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation with pacemaker and multiple colonic polyps since index colonoscopy at age 58. Surveillance colonoscopy on 6/6/24 found a 3cm friable ascending colon mass with pathology confirming invasive moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, MSI-H with loss of MLH1 and PMS2. He started on first line treatment with single agent pembrolizumab on 8/7/2024. Within 2 months, there was a decrease in size of the lesion from 3cm to 1.9 cm and no increase in size or evidence of metastasis at 8 months. Colonoscopy performed to assess treatment response showed a polypoid non-obstructing 3 cm ascending colon mass with an adjacent tattoo. Biopsies revealed sessile serrated lesion with high grade dysplasia and no malignancy noted. The case was discussed at multidisciplinary tumor board and since he was not a surgical candidate, the decision was made to attempt endoscopic resection. The residual mass was then resected successfully with endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). A 4 cm by 4 cm resection specimen was obtained; the specimen was removed en-bloc. (Figure 2). The margins were free of polypoid tissue. Pathology showed minute focus of invasive adenocarcinoma without evidence of lymphovascular invasion.
Discussion: dMMR & MSI-H tumors account for 15% of all colorectal cancers. Immunotherapy has the potential to change the standard of care for localized dMMR tumors as it has shown high rates of pathologic, radiographic, and endoscopic response. As a result, organ-sparing strategies including endoscopic resection with ESD are becoming feasible management options for these lesions that previously required invasive surgical resection.

Figure: Figure 1. 3cm Right Colon Mass, prior to Pembrolizumab Therapy

Figure: Figure 2: Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Residual Colonic Mass. Image A, B – 3cm mass (Paris Classification mixed IIa + IIc) in forward view. C – Mass in retroflexed view. D – ESD of lesion. E – Post Resection Site. F – Resected Specimen
Disclosures:
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Montserrat Guraieb Trueba indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Van Karlyle II Morris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phillip Ge: Aspero Medical – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fujifilm Medical Systems – Consultant. Neptune Medical – Consultant. Ovesco Endoscopy USA – Consultant. UpToDate – Royalties.
Emmanuel Coronel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anni Chowdhury Arellanes, DO1, Montserrat Guraieb Trueba, MD1, Van Karlyle II Morris, MD1, Phillip S.. Ge, MD2, Emmanuel Coronel, MD2. P4630 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of T3 MSI-high Colorectal Cancer Treated With Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

