Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4581 - Crystal Clear: NAC and Simethicone for Improved Colonoscopy Visualization: A Pilot Study
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- MA
Monica Arora, DO (she/her/hers)
Mather Hospital, Northwell Health
Port Jefferson, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Monica Arora, DO, Toby Bradford, MD, Karina Fatakhova, MD, Ramona Rajapakse, MD, FACG
Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY
Introduction: Colonoscopy is the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening, and high-quality bowel preparation is essential to ensure an effective and thorough examination. Adding adjunctive agents, N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and simethicone (SIM), have been shown to improve mucosal visibility and cleanliness compared to water or no intervention and reduce the need for endoscopic flushing during esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In contrast, there is limited data on adjunctive use of NAC and oral SIM to improve bowel cleanliness for colonoscopy.
To objectively assess bowel cleanliness and effectiveness of preparation regimens, the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS), which scores the colon in three segments, scale of 0 to 3 per segment, poor to best visualization (total score 0-9), and the Colon Endoscopic Bubble Scale (CEBuS) which evaluates bubbles, scale of 0 to 2 per segment, no bubbles to greater than 50% of the surface, (total score 0-6) were used.
This quality improvement project aimed to evaluate the efficacy of bowel cleansing and endoscopic visualization by adding SIM and NAC to bowel preparation prior to colonoscopy, using both the BBPS and CEBuS scores.
Methods: Patients at a single-center academic hospital completing routine colonoscopies between April 30, 2025, and May 31, 2025, were evaluated. Two groups of patients were analyzed: patients taking the standard bowel regimen of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate and then those who took the standard regimen in addition to the 600 mg of oral NAC and 250 mg of oral SIM. Primary outcomes were assessed using the CEBuS and the BBPS. Colonoscopy outcomes were analyzed using mean differences assessed by two-sample t-testing and Wilcoxon signed-rank non-parametric testing.
Results: We analyzed 53 eligible patients. Bubble scores assessed by CEBuS were improved in the combined standard bowel regimen and adjunct oral NAC and oral SIM group compared to the solo standard bowel regimen group (x̄ = 0.93 vs 3.5, p < 0.01). Bowel preparation scores assessed by BBPS were also improved in the combination standard bowel regimen and adjunct oral NAC and oral SIM group but not at a statistically significant level (7.64 vs 7.43, p = 0.37).
Discussion: Pretreatment with NAC and SIM significantly reduced intraluminal bubbles and improved endoscopic colonic visualization but did not significantly improve bowel preparation. Pre-procedure supplementation with oral SIM during colonoscopy preparation should be considered for routine colonoscopies.
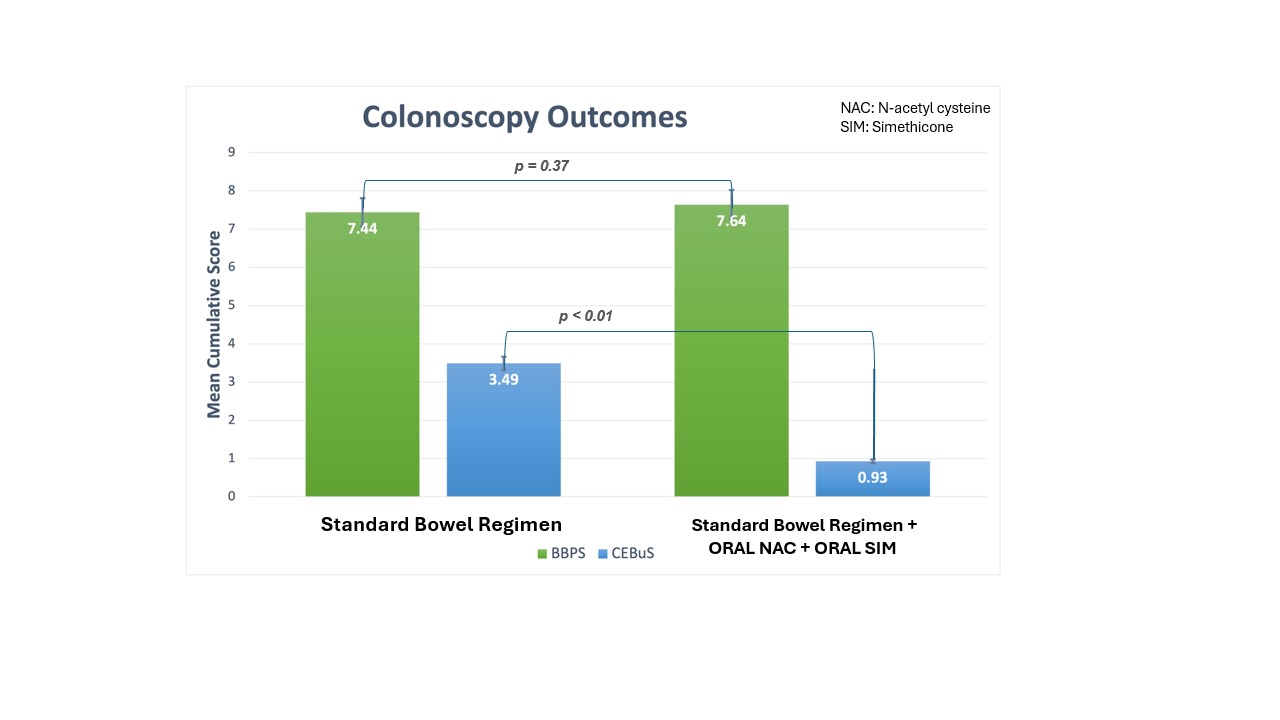
Figure: Table 1: Boston Bowel Preparation Scale and Colon Endoscopic Bubble Scale Mean Score in the Standard Bowel Regimen in comparison to the Standard Bowel Regimen and Oral NAC and Oral Simethicone
Disclosures:
Monica Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Toby Bradford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karina Fatakhova indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramona Rajapakse indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Arora, DO, Toby Bradford, MD, Karina Fatakhova, MD, Ramona Rajapakse, MD, FACG. P4581 - Crystal Clear: NAC and Simethicone for Improved Colonoscopy Visualization: A Pilot Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY
Introduction: Colonoscopy is the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening, and high-quality bowel preparation is essential to ensure an effective and thorough examination. Adding adjunctive agents, N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and simethicone (SIM), have been shown to improve mucosal visibility and cleanliness compared to water or no intervention and reduce the need for endoscopic flushing during esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In contrast, there is limited data on adjunctive use of NAC and oral SIM to improve bowel cleanliness for colonoscopy.
To objectively assess bowel cleanliness and effectiveness of preparation regimens, the Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS), which scores the colon in three segments, scale of 0 to 3 per segment, poor to best visualization (total score 0-9), and the Colon Endoscopic Bubble Scale (CEBuS) which evaluates bubbles, scale of 0 to 2 per segment, no bubbles to greater than 50% of the surface, (total score 0-6) were used.
This quality improvement project aimed to evaluate the efficacy of bowel cleansing and endoscopic visualization by adding SIM and NAC to bowel preparation prior to colonoscopy, using both the BBPS and CEBuS scores.
Methods: Patients at a single-center academic hospital completing routine colonoscopies between April 30, 2025, and May 31, 2025, were evaluated. Two groups of patients were analyzed: patients taking the standard bowel regimen of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate and then those who took the standard regimen in addition to the 600 mg of oral NAC and 250 mg of oral SIM. Primary outcomes were assessed using the CEBuS and the BBPS. Colonoscopy outcomes were analyzed using mean differences assessed by two-sample t-testing and Wilcoxon signed-rank non-parametric testing.
Results: We analyzed 53 eligible patients. Bubble scores assessed by CEBuS were improved in the combined standard bowel regimen and adjunct oral NAC and oral SIM group compared to the solo standard bowel regimen group (x̄ = 0.93 vs 3.5, p < 0.01). Bowel preparation scores assessed by BBPS were also improved in the combination standard bowel regimen and adjunct oral NAC and oral SIM group but not at a statistically significant level (7.64 vs 7.43, p = 0.37).
Discussion: Pretreatment with NAC and SIM significantly reduced intraluminal bubbles and improved endoscopic colonic visualization but did not significantly improve bowel preparation. Pre-procedure supplementation with oral SIM during colonoscopy preparation should be considered for routine colonoscopies.

Figure: Table 1: Boston Bowel Preparation Scale and Colon Endoscopic Bubble Scale Mean Score in the Standard Bowel Regimen in comparison to the Standard Bowel Regimen and Oral NAC and Oral Simethicone
Disclosures:
Monica Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Toby Bradford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karina Fatakhova indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramona Rajapakse indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Arora, DO, Toby Bradford, MD, Karina Fatakhova, MD, Ramona Rajapakse, MD, FACG. P4581 - Crystal Clear: NAC and Simethicone for Improved Colonoscopy Visualization: A Pilot Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

