Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4305 - Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Imaging Modalities to Detect Pancreatic Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- VB
Vinay Bellur
Ramaiah medical college
Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Presenting Author(s)
Shradha Chervittara Karaveetil, 1, Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 2, Omar Oudit, DO3, Ananya Prasad, 1, Aashray Alva, 1, Anmol Rao, 4, Samyuktha Vinu Nair, 5, Deepika A, 6, Sravani Bhavanam, 7, Anusha Giri, 1, Swaroop Raj Varma K R, 6, Aryan Gupta, 6, Druvadeep Srinivas, 8, A. Shree Charan, 9, Advaith N. Rao, MBBS10, Adithya Sathya narayana, MBBS10
1ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 2Ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 3Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4Ramaiah Medical College, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 5Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 6bangalore medical college and research institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 7Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 8rajarajeshwari medical college & hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 9Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 10M S Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Early identification and detection of pancreatic cancer significantly increases the median overall survival rate of patients. However, this is challenging since routinely utilized genetic tests are costly and time intensive. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology being used for interpretation of medical imaging. AI can aid in early and quick diagnosis of pancreatic cancer through analysis of medical images like CECT and Ultrasound which can contribute as a capable screening tool for the requirement of furthur testing. This study analyzes the accuracy of different models of AI in the diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms.
Methods: The study follows the PRISMA guidelines and medical databases were searched by creating a Boolean search string to retrieve and select articles which assessed the accuracy of Machine learning, Deep learning and Neural Network models in diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms. The Meta, Metadata and Mada packages were utilized to evaluate the measures of diagnostic accuracy tests ie; Sensitivity, Specificity and Diagnostic Odds Ratio(DOR).To evaluate sensitivity, the number of events was considered to be TP and the number of samples to be TP+FN. Similarly, pooled specificity was estimated by considering TN as events and TN and FP as the number of samples. The Random intercept logistic regression model for sensitivity and specificity and the Mantel-Haenszel method or Inverse variance method was used to determine DOR.The heterogeneity of the studies was assessed using the I^2 test.
Results: The study involved 20 different testing and validation models which assessed the diagnostic accuracy of machine learning and deep learning models.The pooled sensitivity was estimated by the random effects model to be 91%(88%-94%; 95% CI; p< 0.05) and the specificity to be 92% ( 87%-95%;95% CI;p< 0.05). The diagnostic odds ratio was estimated to be 4.05 (2.49-6.59; 95% CI ; p< 0.05).
Discussion: AI through machine learning and deep learning techniques, shows considerably high Sensitivity (91%) and Specificity (92%) in the detection of pancreatic carcinoma. Outcomes derived by AI had high correlation with histopathological data, establishing the role of AI in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. In order to implement AI technology for diagnosis of Pancreatic cancer, additional multicenter studies must be performed and DDW 2025 involvement of multiple disciplines to implement this technology is essential.
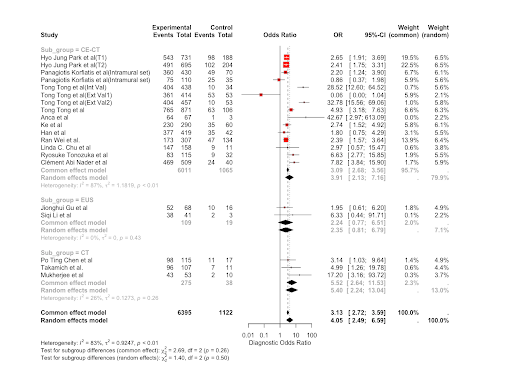
Figure: Sensitivity and Specificity of AI in detection of Pancreatic Neoplasm
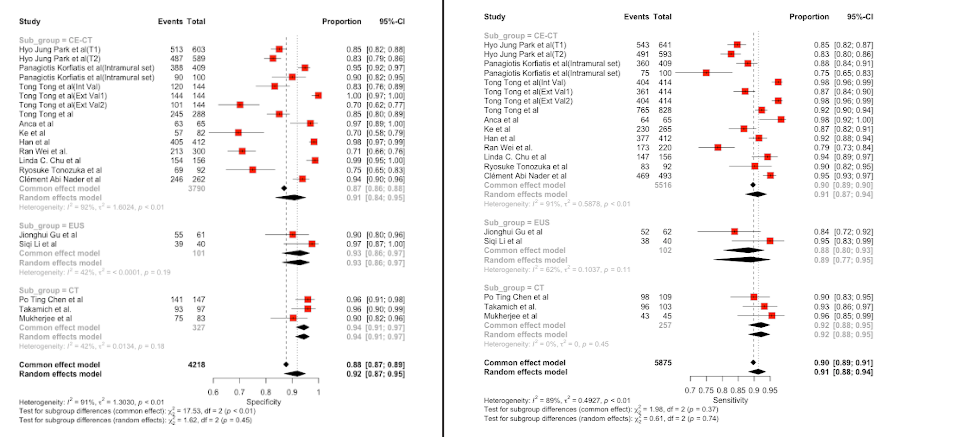
Figure: Diagnostic Odds Ratio of AI in the detection of Pancreatic Neoplasms
Disclosures:
Shradha Chervittara Karaveetil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Oudit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashray Alva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samyuktha Vinu Nair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepika A indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sravani Bhavanam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Giri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swaroop Raj Varma K R indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aryan Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Druvadeep Srinivas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
A. Shree Charan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Advaith Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adithya Sathya narayana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shradha Chervittara Karaveetil, 1, Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 2, Omar Oudit, DO3, Ananya Prasad, 1, Aashray Alva, 1, Anmol Rao, 4, Samyuktha Vinu Nair, 5, Deepika A, 6, Sravani Bhavanam, 7, Anusha Giri, 1, Swaroop Raj Varma K R, 6, Aryan Gupta, 6, Druvadeep Srinivas, 8, A. Shree Charan, 9, Advaith N. Rao, MBBS10, Adithya Sathya narayana, MBBS10. P4305 - Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Imaging Modalities to Detect Pancreatic Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 2Ramaiah medical college, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 3Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4Ramaiah Medical College, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 5Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India; 6bangalore medical college and research institute, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 7Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 8rajarajeshwari medical college & hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 9Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India; 10M S Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Introduction: Early identification and detection of pancreatic cancer significantly increases the median overall survival rate of patients. However, this is challenging since routinely utilized genetic tests are costly and time intensive. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology being used for interpretation of medical imaging. AI can aid in early and quick diagnosis of pancreatic cancer through analysis of medical images like CECT and Ultrasound which can contribute as a capable screening tool for the requirement of furthur testing. This study analyzes the accuracy of different models of AI in the diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms.
Methods: The study follows the PRISMA guidelines and medical databases were searched by creating a Boolean search string to retrieve and select articles which assessed the accuracy of Machine learning, Deep learning and Neural Network models in diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms. The Meta, Metadata and Mada packages were utilized to evaluate the measures of diagnostic accuracy tests ie; Sensitivity, Specificity and Diagnostic Odds Ratio(DOR).To evaluate sensitivity, the number of events was considered to be TP and the number of samples to be TP+FN. Similarly, pooled specificity was estimated by considering TN as events and TN and FP as the number of samples. The Random intercept logistic regression model for sensitivity and specificity and the Mantel-Haenszel method or Inverse variance method was used to determine DOR.The heterogeneity of the studies was assessed using the I^2 test.
Results: The study involved 20 different testing and validation models which assessed the diagnostic accuracy of machine learning and deep learning models.The pooled sensitivity was estimated by the random effects model to be 91%(88%-94%; 95% CI; p< 0.05) and the specificity to be 92% ( 87%-95%;95% CI;p< 0.05). The diagnostic odds ratio was estimated to be 4.05 (2.49-6.59; 95% CI ; p< 0.05).
Discussion: AI through machine learning and deep learning techniques, shows considerably high Sensitivity (91%) and Specificity (92%) in the detection of pancreatic carcinoma. Outcomes derived by AI had high correlation with histopathological data, establishing the role of AI in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. In order to implement AI technology for diagnosis of Pancreatic cancer, additional multicenter studies must be performed and DDW 2025 involvement of multiple disciplines to implement this technology is essential.

Figure: Sensitivity and Specificity of AI in detection of Pancreatic Neoplasm

Figure: Diagnostic Odds Ratio of AI in the detection of Pancreatic Neoplasms
Disclosures:
Shradha Chervittara Karaveetil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vinay Chandramouli Bellur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Oudit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ananya Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashray Alva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samyuktha Vinu Nair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepika A indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sravani Bhavanam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Giri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swaroop Raj Varma K R indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aryan Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Druvadeep Srinivas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
A. Shree Charan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Advaith Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adithya Sathya narayana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shradha Chervittara Karaveetil, 1, Vinay Chandramouli Bellur, 2, Omar Oudit, DO3, Ananya Prasad, 1, Aashray Alva, 1, Anmol Rao, 4, Samyuktha Vinu Nair, 5, Deepika A, 6, Sravani Bhavanam, 7, Anusha Giri, 1, Swaroop Raj Varma K R, 6, Aryan Gupta, 6, Druvadeep Srinivas, 8, A. Shree Charan, 9, Advaith N. Rao, MBBS10, Adithya Sathya narayana, MBBS10. P4305 - Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Imaging Modalities to Detect Pancreatic Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
