Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4298 - Diagnostic Utility of Fecal Elastase Testing for Identifying Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency in IBS-D Patients
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Fariha Hasan, MD
Cooper University Hospital
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Maryanna Schweininger, DO1, Anika Pruthi, BS2, Jaclyn Levendusky, BS2, Sohum Patel, BS3, Isabella Trachtenberg, BS4, Chelsea Edirisuriya, MD1, Krystal Hunter, PhD, MBA1, Apeksha Shah, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD, FACG2, Anthony Infantolino, MD5, Krysta Contino, MD6
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 3Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Voorhees, NJ; 4Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Philadelphia, PA; 5MD Anderson Cooper Digestive Health, Mt Laurel, NJ; 6Cooper Health Gastroenterology, Mount Laurel, NJ
Introduction: Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) is a common functional disorder, yet emerging data suggests some cases may represent unrecognized exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). Fecal elastase (FE) testing is a non-invasive method to assess pancreatic function, though its role in IBS-D populations remains unclear. This study evaluates the utility of FE in identifying EPI among IBS-D patients, determines the prevalence of low FE in this group, and assesses whether appropriate diagnostic workup (e.g., fat-soluble vitamin testing, imaging) was performed in those with abnormal results.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of IBS-D patients who underwent FE testing between 2015 and 2024 at a tertiary care center. EPI was defined by low FE levels, supportive imaging or clinical response to enzyme therapy (PERT). Chi-squared test was used for categorical variables, and the independent student’s t-test was used for continuous variables.
Results: Of 289 patients with IBS-D who underwent FE testing, 131 (45.3%) had low FE levels (< 200 μg/g). Among these, 64 (48.9%) had severe FE reduction (< 100 μg/g), and 67 (51.1%) had moderate reduction (100–199 μg/g). Imaging was obtained in 68.7% of patients with low FE; 31.3% had no follow-up imaging. GERD (81.3% vs. 59.7%, p=0.007) and cholecystectomy (40.6% vs. 17.9%, p=0.004) were significantly more prevalent in those with severe vs. moderate FE reduction.
Among patients with low FE, 67 (51.1%) met criteria for EPI based on labs or imaging findings or clinical response to PERT. Fat-soluble vitamin testing was more common in the EPI group (53.7% vs. 28.1%, p=0.003), as were EUS findings of hyperechoic strands (6% vs. 0%, p=0.012). Patients with EPI were significantly more likely to report symptom improvement with PERT (93.4% vs. 0%, p< 0.001). On logistic regression, male sex (OR 2.46, 95% CI: 1.40–4.30, p=0.002) and family history of pancreatic cancer (OR 3.51, 95% CI: 1.02–12.13, p=0.047) were independently associated with low FE levels.
Discussion: Fecal elastase testing is sensitive in distinguishing EPI among IBS-D patients, and about half of these cases represent true EPI. While clinical features alone are not reliable predictors, confirmatory testing, such as EUS, correlates with structural changes.. Patients with EPI were also significantly more likely to benefit from PERT. Selective use of FE testing with appropriate follow-up can improve the diagnosis and management of misclassified IBS-D cases.
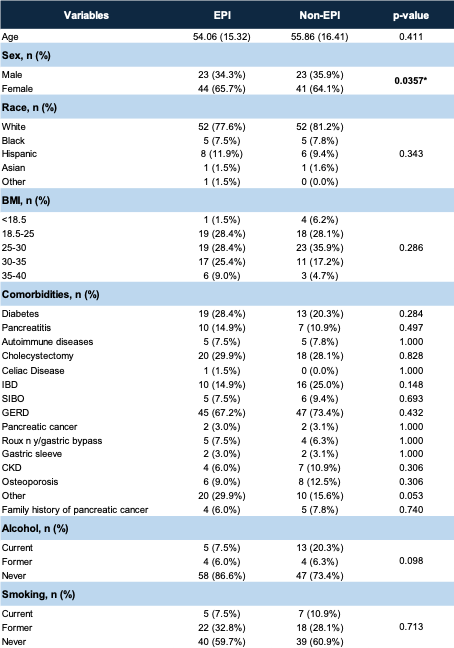
Figure: Table 1: Demographics between the EPI and non-EPI groups
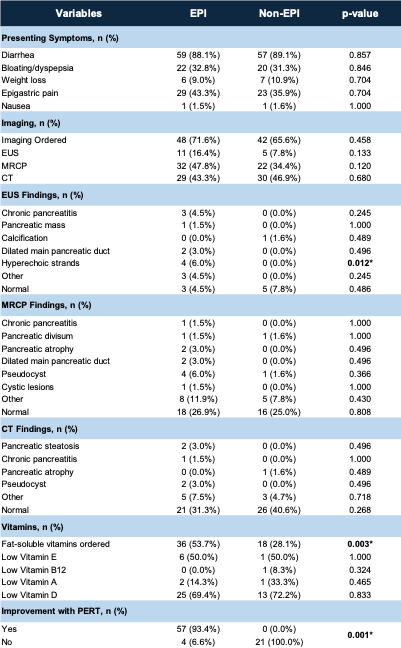
Figure: Table 2: Outcomes between the EPI and non-EPI groups
Disclosures:
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryanna Schweininger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anika Pruthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaclyn Levendusky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sohum Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Isabella Trachtenberg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chelsea Edirisuriya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krystal Hunter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apeksha Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christina Tofani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Infantolino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krysta Contino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Maryanna Schweininger, DO1, Anika Pruthi, BS2, Jaclyn Levendusky, BS2, Sohum Patel, BS3, Isabella Trachtenberg, BS4, Chelsea Edirisuriya, MD1, Krystal Hunter, PhD, MBA1, Apeksha Shah, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD, FACG2, Anthony Infantolino, MD5, Krysta Contino, MD6. P4298 - Diagnostic Utility of Fecal Elastase Testing for Identifying Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency in IBS-D Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ; 3Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Voorhees, NJ; 4Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Philadelphia, PA; 5MD Anderson Cooper Digestive Health, Mt Laurel, NJ; 6Cooper Health Gastroenterology, Mount Laurel, NJ
Introduction: Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) is a common functional disorder, yet emerging data suggests some cases may represent unrecognized exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). Fecal elastase (FE) testing is a non-invasive method to assess pancreatic function, though its role in IBS-D populations remains unclear. This study evaluates the utility of FE in identifying EPI among IBS-D patients, determines the prevalence of low FE in this group, and assesses whether appropriate diagnostic workup (e.g., fat-soluble vitamin testing, imaging) was performed in those with abnormal results.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of IBS-D patients who underwent FE testing between 2015 and 2024 at a tertiary care center. EPI was defined by low FE levels, supportive imaging or clinical response to enzyme therapy (PERT). Chi-squared test was used for categorical variables, and the independent student’s t-test was used for continuous variables.
Results: Of 289 patients with IBS-D who underwent FE testing, 131 (45.3%) had low FE levels (< 200 μg/g). Among these, 64 (48.9%) had severe FE reduction (< 100 μg/g), and 67 (51.1%) had moderate reduction (100–199 μg/g). Imaging was obtained in 68.7% of patients with low FE; 31.3% had no follow-up imaging. GERD (81.3% vs. 59.7%, p=0.007) and cholecystectomy (40.6% vs. 17.9%, p=0.004) were significantly more prevalent in those with severe vs. moderate FE reduction.
Among patients with low FE, 67 (51.1%) met criteria for EPI based on labs or imaging findings or clinical response to PERT. Fat-soluble vitamin testing was more common in the EPI group (53.7% vs. 28.1%, p=0.003), as were EUS findings of hyperechoic strands (6% vs. 0%, p=0.012). Patients with EPI were significantly more likely to report symptom improvement with PERT (93.4% vs. 0%, p< 0.001). On logistic regression, male sex (OR 2.46, 95% CI: 1.40–4.30, p=0.002) and family history of pancreatic cancer (OR 3.51, 95% CI: 1.02–12.13, p=0.047) were independently associated with low FE levels.
Discussion: Fecal elastase testing is sensitive in distinguishing EPI among IBS-D patients, and about half of these cases represent true EPI. While clinical features alone are not reliable predictors, confirmatory testing, such as EUS, correlates with structural changes.. Patients with EPI were also significantly more likely to benefit from PERT. Selective use of FE testing with appropriate follow-up can improve the diagnosis and management of misclassified IBS-D cases.

Figure: Table 1: Demographics between the EPI and non-EPI groups

Figure: Table 2: Outcomes between the EPI and non-EPI groups
Disclosures:
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryanna Schweininger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anika Pruthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaclyn Levendusky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sohum Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Isabella Trachtenberg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chelsea Edirisuriya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krystal Hunter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Apeksha Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christina Tofani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Infantolino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krysta Contino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan, MD1, Maryanna Schweininger, DO1, Anika Pruthi, BS2, Jaclyn Levendusky, BS2, Sohum Patel, BS3, Isabella Trachtenberg, BS4, Chelsea Edirisuriya, MD1, Krystal Hunter, PhD, MBA1, Apeksha Shah, MD1, Christina Tofani, MD, FACG2, Anthony Infantolino, MD5, Krysta Contino, MD6. P4298 - Diagnostic Utility of Fecal Elastase Testing for Identifying Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency in IBS-D Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
