Sunday Poster Session
Category: Pediatrics
P1891 - Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Pediatric Patients of Functional Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Allah Dad, MD (he/him/his)
Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan
Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Muhammad Saad Khan, MBBS1, Maliha Khalid, MBBS2, Erum Siddiqui, MBBS1, Usman Mazhar, MBBS3, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD4, Allah Dad, MD5, Kinza Bakht, MBBS6, Muhammad Arham, 7, Fnu Veena, MD8, Adnan Bhat, MD9
1Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Pakistan, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 2Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 3Rawalpindi Medical University, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 8BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 9University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Functional constipation (FC) and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) are characterized by infrequent, painful, or difficult defecation, often accompanied by fecal incontinence and abdominal discomfort, whereas IBS-C is a gut–brain interaction disorder with recurrent abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of linaclotide for pediatric FC and IBS-C.
Methods: PubMed (Medline), EMBASE, and Google Scholar were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with children suffering from FC and IBS-C. This study used Review Manager and forest plots for visual display. Random effects models were used for this meta-analysis (RRs with 95% CIs) and (SMD with 95% CIs). Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0.
Results: Out of 1,653 identified records, three RCTs (309 patients) met the inclusion criteria. Linaclotide showed no statistically significant improvement over placebo in overall CSBMs (SMD = 0.01 [-0.19, 0.20], P = 0.94), abdominal pain (SMD = 0.12 [-0.07, 0.32], P = 0.21), or bloating (SMD = 0.14 [-0.05, 0.34], P = 0.14). However, it significantly improved stool consistency (SMD = 0.52 [0.31, 0.72], P < 0.00001) and reduced straining severity (SMD = -0.29 [-0.49, -0.09], P = 0.004), particularly with higher doses. Adverse events (TEAEs and TRAEs) did not significantly differ between linaclotide and placebo groups. Heterogeneity was low across most outcomes.
Discussion: Linaclotide improves stool consistency and reduces straining severity in pediatric FC and IBS-C, particularly at higher doses. However, it does not significantly enhance bowel movement frequency, complete spontaneous bowel movements, or alleviate abdominal pain. Safety assessments indicate no significant increase in adverse events compared to placebo. Overall, linaclotide may be beneficial for stool consistency but has limited impact on other symptoms.
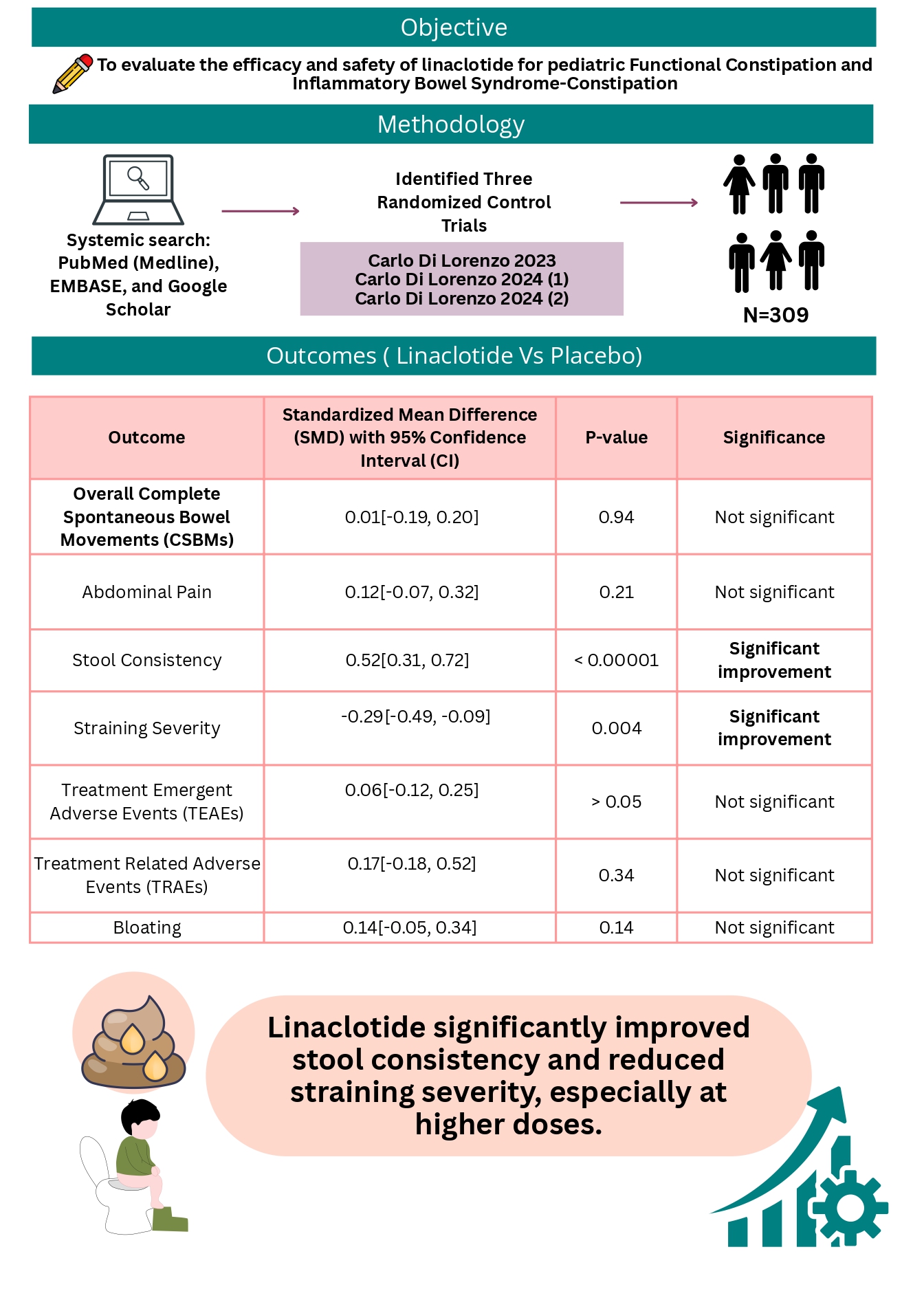
Figure: Central Illustration: Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Pediatric Functional Constipation and IBS-C: Meta-Analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maliha Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erum Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usman Mazhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Arham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Veena indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad Khan, MBBS1, Maliha Khalid, MBBS2, Erum Siddiqui, MBBS1, Usman Mazhar, MBBS3, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD4, Allah Dad, MD5, Kinza Bakht, MBBS6, Muhammad Arham, 7, Fnu Veena, MD8, Adnan Bhat, MD9. P1891 - Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Pediatric Patients of Functional Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Muhammad Saad Khan, MBBS1, Maliha Khalid, MBBS2, Erum Siddiqui, MBBS1, Usman Mazhar, MBBS3, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD4, Allah Dad, MD5, Kinza Bakht, MBBS6, Muhammad Arham, 7, Fnu Veena, MD8, Adnan Bhat, MD9
1Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Pakistan, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 2Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 3Rawalpindi Medical University, Pakistan, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Hospital, Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Sheikh Zayed Medical College, Pakistan, Rahim Yar Khan, Punjab, Pakistan; 8BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 9University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Functional constipation (FC) and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) are characterized by infrequent, painful, or difficult defecation, often accompanied by fecal incontinence and abdominal discomfort, whereas IBS-C is a gut–brain interaction disorder with recurrent abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of linaclotide for pediatric FC and IBS-C.
Methods: PubMed (Medline), EMBASE, and Google Scholar were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with children suffering from FC and IBS-C. This study used Review Manager and forest plots for visual display. Random effects models were used for this meta-analysis (RRs with 95% CIs) and (SMD with 95% CIs). Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0.
Results: Out of 1,653 identified records, three RCTs (309 patients) met the inclusion criteria. Linaclotide showed no statistically significant improvement over placebo in overall CSBMs (SMD = 0.01 [-0.19, 0.20], P = 0.94), abdominal pain (SMD = 0.12 [-0.07, 0.32], P = 0.21), or bloating (SMD = 0.14 [-0.05, 0.34], P = 0.14). However, it significantly improved stool consistency (SMD = 0.52 [0.31, 0.72], P < 0.00001) and reduced straining severity (SMD = -0.29 [-0.49, -0.09], P = 0.004), particularly with higher doses. Adverse events (TEAEs and TRAEs) did not significantly differ between linaclotide and placebo groups. Heterogeneity was low across most outcomes.
Discussion: Linaclotide improves stool consistency and reduces straining severity in pediatric FC and IBS-C, particularly at higher doses. However, it does not significantly enhance bowel movement frequency, complete spontaneous bowel movements, or alleviate abdominal pain. Safety assessments indicate no significant increase in adverse events compared to placebo. Overall, linaclotide may be beneficial for stool consistency but has limited impact on other symptoms.

Figure: Central Illustration: Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Pediatric Functional Constipation and IBS-C: Meta-Analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Saad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maliha Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erum Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usman Mazhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Arham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Veena indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Saad Khan, MBBS1, Maliha Khalid, MBBS2, Erum Siddiqui, MBBS1, Usman Mazhar, MBBS3, Muhammad Waqas Afzal, MBBS, MD4, Allah Dad, MD5, Kinza Bakht, MBBS6, Muhammad Arham, 7, Fnu Veena, MD8, Adnan Bhat, MD9. P1891 - Exploring the Efficacy and Safety of Linaclotide in Pediatric Patients of Functional Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

