Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1870 - Periaortic Histoplasmoma Causing Hepatic Artery Stenosis in a Liver Transplant Recipient
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Arham Siddiqui, MD
University of Texas Health San Antonio
San Antonio, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Arham Siddiqui, MD1, Jason N. Chen, MD1, Brian Lee, DO1, Daniel Wheeler, DO1, Lisa D. Pedicone, PhD2, Fabian Rodas, MD1, Carmen landaverde, MD1, Jan Petrasek, MD1, Fred Poordad, MD1, Eric Lawitz, MD1, Andres Gomez-Aldana, MD1, Eugenia Tsai, MD2
1University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 2Texas Liver Institute, Austin, TX
Introduction: Histoplasmomas are mycotic granulomatous nodules caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum that present primarily as pulmonary nodules. We present a rare case of a histoplasmoma manifesting as a periaortic mass causing hepatic artery stenosis in a liver transplant recipient.
Case Description/
Methods: A 65-year-old female two years status post deceased donor liver transplantation for hepatitis C-related decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma with excellent graft function undergoes routine surveillance liver ultrasound. Labs were normal: AST 15 U/L (8-33), ALT 27 U/L (7-56), total bilirubin 0.3 mg/dL (0.2-1.1), ALP 123 IU/L (45-117), and INR 1 (0.8-1.2). Abdominal imaging demonstrated low resistive indices of the hepatic arteries with a parvus tardus pattern suggestive of anastomotic narrowing. CT angiography revealed a 2.6 cm periaortic soft tissue mass causing severe stenosis of the proximal vascular anastomosis from the distal abdominal aorta into the hepatic artery (Figure 1). The mass was biopsied and histology demonstrated small, uniform, oval yeasts with narrow-based budding and nuclei clustered within histiocytes consistent with a histoplasma infection (Figure 2). Patient was initially treated with itraconazole but due to the lack of improvement in size and concern for vascular anastomosis compromise, patient underwent hepatic artery stenting. She was transitioned to amphotericin B due to concern for reactivation in the setting of immunosuppression with ultimate resolution of histoplasmoma.
Discussion: H. capsulatum is a ubiquitous and dimorphic fungus which is transmitted via inhalation of spore-containing dusts or aerosols. Although rare, chronic infection can lead to histoplasmoma formation, a slow-growing nodule that can be difficult to distinguish from malignancy or tuberculoma. The gold standard for diagnosis is biopsy which will show H. capsulatum under GMS or PAS stains and granulomatous inflammation. While histoplasmomas classically present as solitary pulmonary nodules, our case highlights a unique complication of a histoplasmoma due to its proximity to the arterial anastomosis in a liver transplant recipient. A key risk factor for histoplasma infection is chronic immunosuppression. Antifungal treatment with itraconazole or amphotericin B is typically used for patients that are symptomatic or immunocompromised. Early recognition and targeted management of histoplasmoma in at-risk populations are critical to preventing severe complications and optimizing outcomes.
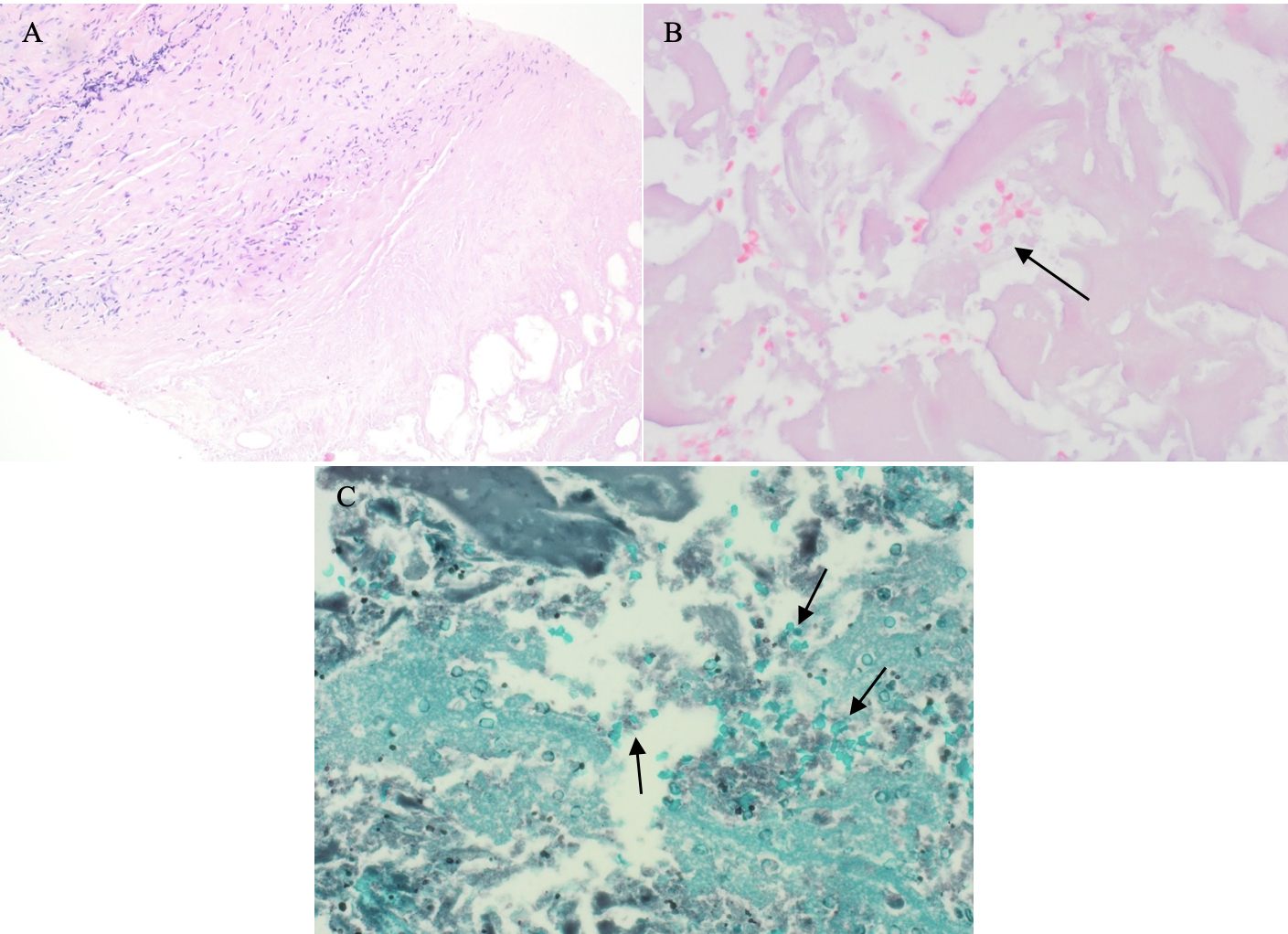
Figure: Figure 1: Axial view of CT angiography of abdomen revealing a 2.2 x 3.0 cm soft tissue mass encasing the bypass near the proximal anastomosis, resulting in severe stenosis
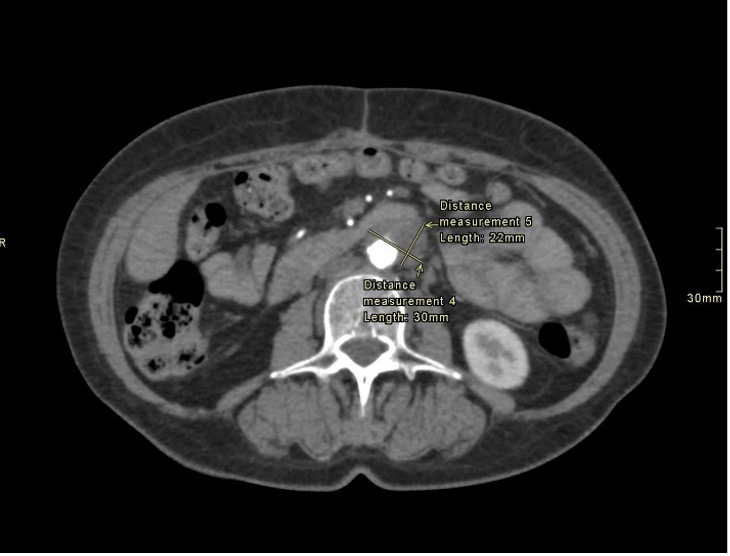
Figure: Figure 2: A) Low power (10x magnification) view, hematoxylin and eosin; B) High power (40x magnification) view demonstrating uniformly small yeast (black arrow) in a background of necrotic debris, hematoxylin and eosin; C) High power (40x magnification) view demonstrating small uniform clustered yeast (black arrow), Gomori-methenamine silver stain.
Disclosures:
Arham Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Wheeler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa D. Pedicone indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fabian Rodas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carmen landaverde indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jan Petrasek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fred Poordad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Lawitz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Gomez-Aldana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eugenia Tsai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arham Siddiqui, MD1, Jason N. Chen, MD1, Brian Lee, DO1, Daniel Wheeler, DO1, Lisa D. Pedicone, PhD2, Fabian Rodas, MD1, Carmen landaverde, MD1, Jan Petrasek, MD1, Fred Poordad, MD1, Eric Lawitz, MD1, Andres Gomez-Aldana, MD1, Eugenia Tsai, MD2. P1870 - Periaortic Histoplasmoma Causing Hepatic Artery Stenosis in a Liver Transplant Recipient, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 2Texas Liver Institute, Austin, TX
Introduction: Histoplasmomas are mycotic granulomatous nodules caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum that present primarily as pulmonary nodules. We present a rare case of a histoplasmoma manifesting as a periaortic mass causing hepatic artery stenosis in a liver transplant recipient.
Case Description/
Methods: A 65-year-old female two years status post deceased donor liver transplantation for hepatitis C-related decompensated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma with excellent graft function undergoes routine surveillance liver ultrasound. Labs were normal: AST 15 U/L (8-33), ALT 27 U/L (7-56), total bilirubin 0.3 mg/dL (0.2-1.1), ALP 123 IU/L (45-117), and INR 1 (0.8-1.2). Abdominal imaging demonstrated low resistive indices of the hepatic arteries with a parvus tardus pattern suggestive of anastomotic narrowing. CT angiography revealed a 2.6 cm periaortic soft tissue mass causing severe stenosis of the proximal vascular anastomosis from the distal abdominal aorta into the hepatic artery (Figure 1). The mass was biopsied and histology demonstrated small, uniform, oval yeasts with narrow-based budding and nuclei clustered within histiocytes consistent with a histoplasma infection (Figure 2). Patient was initially treated with itraconazole but due to the lack of improvement in size and concern for vascular anastomosis compromise, patient underwent hepatic artery stenting. She was transitioned to amphotericin B due to concern for reactivation in the setting of immunosuppression with ultimate resolution of histoplasmoma.
Discussion: H. capsulatum is a ubiquitous and dimorphic fungus which is transmitted via inhalation of spore-containing dusts or aerosols. Although rare, chronic infection can lead to histoplasmoma formation, a slow-growing nodule that can be difficult to distinguish from malignancy or tuberculoma. The gold standard for diagnosis is biopsy which will show H. capsulatum under GMS or PAS stains and granulomatous inflammation. While histoplasmomas classically present as solitary pulmonary nodules, our case highlights a unique complication of a histoplasmoma due to its proximity to the arterial anastomosis in a liver transplant recipient. A key risk factor for histoplasma infection is chronic immunosuppression. Antifungal treatment with itraconazole or amphotericin B is typically used for patients that are symptomatic or immunocompromised. Early recognition and targeted management of histoplasmoma in at-risk populations are critical to preventing severe complications and optimizing outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1: Axial view of CT angiography of abdomen revealing a 2.2 x 3.0 cm soft tissue mass encasing the bypass near the proximal anastomosis, resulting in severe stenosis

Figure: Figure 2: A) Low power (10x magnification) view, hematoxylin and eosin; B) High power (40x magnification) view demonstrating uniformly small yeast (black arrow) in a background of necrotic debris, hematoxylin and eosin; C) High power (40x magnification) view demonstrating small uniform clustered yeast (black arrow), Gomori-methenamine silver stain.
Disclosures:
Arham Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Wheeler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa D. Pedicone indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fabian Rodas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carmen landaverde indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jan Petrasek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fred Poordad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Lawitz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Gomez-Aldana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eugenia Tsai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arham Siddiqui, MD1, Jason N. Chen, MD1, Brian Lee, DO1, Daniel Wheeler, DO1, Lisa D. Pedicone, PhD2, Fabian Rodas, MD1, Carmen landaverde, MD1, Jan Petrasek, MD1, Fred Poordad, MD1, Eric Lawitz, MD1, Andres Gomez-Aldana, MD1, Eugenia Tsai, MD2. P1870 - Periaortic Histoplasmoma Causing Hepatic Artery Stenosis in a Liver Transplant Recipient, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
