Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1765 - A Fatal Synergy: Acute Liver Failure From COVID-19 and Herbal Supplement With Undeclared Ingredients
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Jordan Barnett-Kradjian, DO
Stony Brook Medicine
Stony Brook, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Jordan Barnett-Kradjian, DO1, Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Alan Abboud, MD1, Michael J. Clores, DO2
1Stony Brook Medicine, Stony Brook, NY; 2Renaissance School of Medicine at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and viral infections are important considerations in the broad differential diagnosis of hepatobiliary injury, particularly after the exclusion of more common etiologies. We present a fatal case of biopsy-proven acute liver failure from concurrent Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) infection and DILI due to Artri King, an over-the-counter herbal supplement containing undisclosed hepatotoxic ingredients.
Case Description/
Methods: A 56-year-old male with systemic lupus erythematosus presented with abdominal distension and jaundice. The patient reported increased consumption of Artri King for joint pain and denied additional home medications. Labs demonstrated elevated total bilirubin (7.2 mg/dL), severe transaminitis (ALT 2909 IU/L), low fibrinogen, low platelets, elevated INR of 2, EBV reactivation, and positive SARS CoV-2 PCR. Negative workup included: CT of the abdomen, urine and serum toxicology, viral and autoimmune serology, and hereditary causes. Within 24 hours of admission, the patient started an N-acetyl cystine protocol. Despite improvement in transaminases, total bilirubin continued to rise to 30.3 mg/dL prompting liver biopsy. Liver core biopsy showed lymphocytic and foamy histiocytic infiltrates throughout the lobules, portal tract damage and focal loss of ducts, hepatitis, and bile ductular proliferation. Shortly after, the patient experienced encephalopathy, hypovolemic shock, and expired.
Discussion: In critically ill adults, severe hyperbilirubinemia above 30mg/dL is associated with multi-organ failure and a markedly increased risk of mortality. This patient presented without risk factors for chronic liver disease but was found to have acute liver failure in the setting of a recent viral infection and increased use of a hepatotoxic agent. Biopsy revealed a combination of liver insults, with lymphocytic infiltration and bile duct loss consistent with COVID-19 infection, and portal tract damage with interface hepatitis indicative of DILI. According to Food and Drug Administration reports, Artri King contains undisclosed diclofenac, dexamethasone and phenolphthalein, and is under scrutiny for potential liver toxicity. We demonstrate a potential synergistic effect between COVID-19 and DILI from Artri King supplement, leading to more severe liver injury than would be expected from either insult alone. This highlights the importance of thoroughly reviewing supplement use and maintaining a broad differential in evaluating any pattern of liver injury.
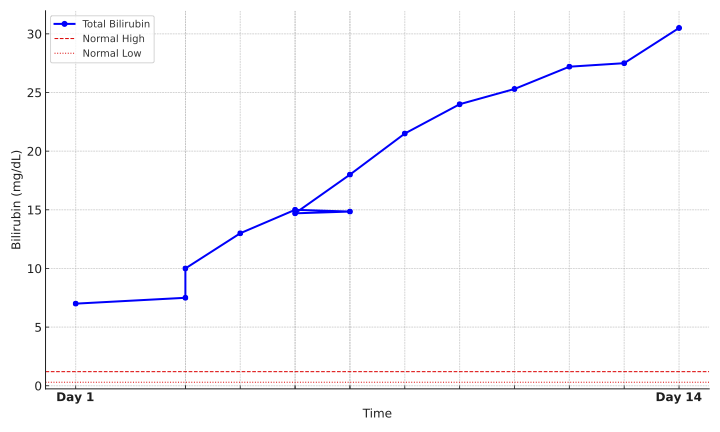
Figure: Total bilirubin overtime
Disclosures:
Jordan Barnett-Kradjian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Tripathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alan Abboud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Clores indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Barnett-Kradjian, DO1, Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Alan Abboud, MD1, Michael J. Clores, DO2. P1765 - A Fatal Synergy: Acute Liver Failure From COVID-19 and Herbal Supplement With Undeclared Ingredients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Stony Brook Medicine, Stony Brook, NY; 2Renaissance School of Medicine at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and viral infections are important considerations in the broad differential diagnosis of hepatobiliary injury, particularly after the exclusion of more common etiologies. We present a fatal case of biopsy-proven acute liver failure from concurrent Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) infection and DILI due to Artri King, an over-the-counter herbal supplement containing undisclosed hepatotoxic ingredients.
Case Description/
Methods: A 56-year-old male with systemic lupus erythematosus presented with abdominal distension and jaundice. The patient reported increased consumption of Artri King for joint pain and denied additional home medications. Labs demonstrated elevated total bilirubin (7.2 mg/dL), severe transaminitis (ALT 2909 IU/L), low fibrinogen, low platelets, elevated INR of 2, EBV reactivation, and positive SARS CoV-2 PCR. Negative workup included: CT of the abdomen, urine and serum toxicology, viral and autoimmune serology, and hereditary causes. Within 24 hours of admission, the patient started an N-acetyl cystine protocol. Despite improvement in transaminases, total bilirubin continued to rise to 30.3 mg/dL prompting liver biopsy. Liver core biopsy showed lymphocytic and foamy histiocytic infiltrates throughout the lobules, portal tract damage and focal loss of ducts, hepatitis, and bile ductular proliferation. Shortly after, the patient experienced encephalopathy, hypovolemic shock, and expired.
Discussion: In critically ill adults, severe hyperbilirubinemia above 30mg/dL is associated with multi-organ failure and a markedly increased risk of mortality. This patient presented without risk factors for chronic liver disease but was found to have acute liver failure in the setting of a recent viral infection and increased use of a hepatotoxic agent. Biopsy revealed a combination of liver insults, with lymphocytic infiltration and bile duct loss consistent with COVID-19 infection, and portal tract damage with interface hepatitis indicative of DILI. According to Food and Drug Administration reports, Artri King contains undisclosed diclofenac, dexamethasone and phenolphthalein, and is under scrutiny for potential liver toxicity. We demonstrate a potential synergistic effect between COVID-19 and DILI from Artri King supplement, leading to more severe liver injury than would be expected from either insult alone. This highlights the importance of thoroughly reviewing supplement use and maintaining a broad differential in evaluating any pattern of liver injury.

Figure: Total bilirubin overtime
Disclosures:
Jordan Barnett-Kradjian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Tripathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alan Abboud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Clores indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Barnett-Kradjian, DO1, Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Alan Abboud, MD1, Michael J. Clores, DO2. P1765 - A Fatal Synergy: Acute Liver Failure From COVID-19 and Herbal Supplement With Undeclared Ingredients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
