Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1674 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Outcomes in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Nationwide Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- CS
Carol Singh, MBBS
Dayanand Medical College and Hospital
New Jersey, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohammad Naseem, MBBS1, Ritika Dhruve, MBBS2, Joanne Lin, DO3, Carol Singh, MBBS4, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS5, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS6, Anmol Singh, MBBS7, Aalam Sohal, MD8, Marina Roytman, MD9
1Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, Dallas, TX; 3University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 6Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 7Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 8Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 9Hepatology Fellowship, UCSF Fresno, Fresno, CA
Introduction: Sarcopenia has been increasingly identified as a critical factor impacting outcomes in patients undergoing liver transplantation (LT). Emerging evidence underscores that sarcopenia in transplant recipients is also associated with an elevated risk of post-transplant complications, prolonged hospital stays and higher mortality rates. The current study aims to assess the impact and burden of sarcopenia on outcomes in LT recipients.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database (2016-2022) was used to identify all adult LT recipients. Patients were categorized into two groups based on the presence or absence of sarcopenia. Data was collected on patient demographics, etiology of liver disease and decompensations of liver disease. The outcomes studied include in-hospital mortality, shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), intensive care unit (ICU) stay and LT-related complications. The impact of sarcopenia was assessed using the multivariate logistic/linear regression analysis.
Results: Among 170,650 LT recipients, 24,525 (14.4%) developed sarcopenia. Most of the patients with sarcopenia were men (57.4%). A higher prevalence of hepatic encephalopathy (11.6% vs 5.5%), ascites (13.4% vs 5.8%), and hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) (2.3% vs. 0.7%) was noted in patients with sarcopenia. Patients with sarcopenia also had a higher incidence of in-patient mortality (4.9% vs. 1.9%), shock (9.1% vs. 3.6%), AKI (47.2% vs. 36.7%), ICU stay (10.1% vs 4.0%) and LT-related complications (3.7% vs 2.1%) as compared to those who did not have sarcopenia (Figure 1.). After adjusting for confounding factors, sarcopenia was associated with a higher odds of in-patient mortality (aOR-2.16, 95% CI-1.83-2.56, p< 0.001), shock (aOR-2.18, 95% CI-1.92-2.48, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.4, 95% CI-1.32-1.49, p< 0.001), ICU stay (aOR-2.23, 95% CI-1.98-2.52, p< 0.001), LT-related complications (aOR-1.47, 95% CI-1.23-1.75, p< 0.001), longer length of stay (adj. coefficient-4.71 days, 95% CI-4.31-5.10, p< 0.001) and total hospitalization charges (adj. coefficient-$56,359.88, 95% CI-$49,737.17-$62,982.58, p< 0.001) (Table 1.)
Discussion: Our study noted that sarcopenia is linked with worse clinical outcomes and higher resource utilization in LT recipients. Early detection and management of sarcopenia are therefore essential for identifying patients at risk and implementing targeted interventions to enhance recovery and minimize complications.
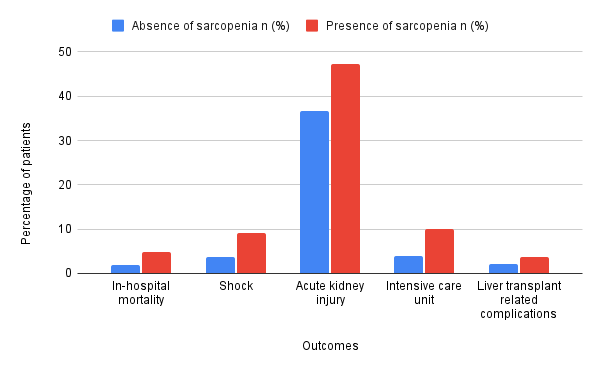
Figure: Figure 1. Bar chart comparing outcomes of liver transplant recipients stratified by the presence of sarcopenia.
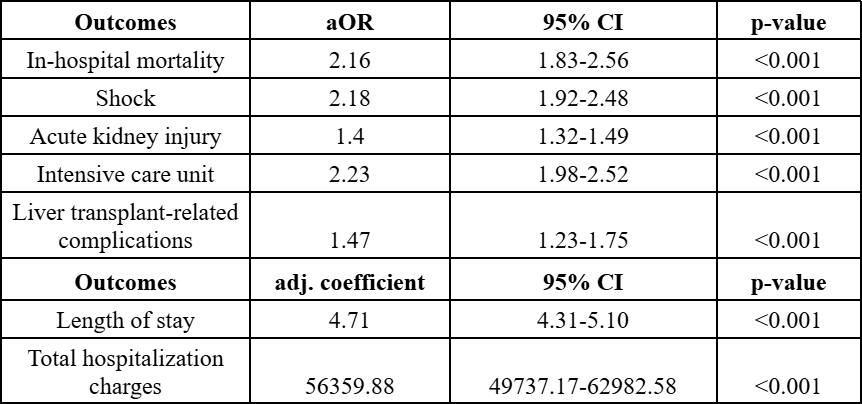
Figure: Table 1. Results of multivariate logistic regression highlighting the relationship between sarcopenia and worse clinical outcomes in liver transplant recipients.
Disclosures:
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritika Dhruve indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joanne Lin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sampada Bhasker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marina Roytman: Gilead – Speakers Bureau. Ipsen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Madrigal – Speakers Bureau. Salix – Speakers Bureau.
Mohammad Naseem, MBBS1, Ritika Dhruve, MBBS2, Joanne Lin, DO3, Carol Singh, MBBS4, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS5, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS6, Anmol Singh, MBBS7, Aalam Sohal, MD8, Marina Roytman, MD9. P1674 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Outcomes in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, Dallas, TX; 3University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 6Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 7Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 8Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 9Hepatology Fellowship, UCSF Fresno, Fresno, CA
Introduction: Sarcopenia has been increasingly identified as a critical factor impacting outcomes in patients undergoing liver transplantation (LT). Emerging evidence underscores that sarcopenia in transplant recipients is also associated with an elevated risk of post-transplant complications, prolonged hospital stays and higher mortality rates. The current study aims to assess the impact and burden of sarcopenia on outcomes in LT recipients.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database (2016-2022) was used to identify all adult LT recipients. Patients were categorized into two groups based on the presence or absence of sarcopenia. Data was collected on patient demographics, etiology of liver disease and decompensations of liver disease. The outcomes studied include in-hospital mortality, shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), intensive care unit (ICU) stay and LT-related complications. The impact of sarcopenia was assessed using the multivariate logistic/linear regression analysis.
Results: Among 170,650 LT recipients, 24,525 (14.4%) developed sarcopenia. Most of the patients with sarcopenia were men (57.4%). A higher prevalence of hepatic encephalopathy (11.6% vs 5.5%), ascites (13.4% vs 5.8%), and hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) (2.3% vs. 0.7%) was noted in patients with sarcopenia. Patients with sarcopenia also had a higher incidence of in-patient mortality (4.9% vs. 1.9%), shock (9.1% vs. 3.6%), AKI (47.2% vs. 36.7%), ICU stay (10.1% vs 4.0%) and LT-related complications (3.7% vs 2.1%) as compared to those who did not have sarcopenia (Figure 1.). After adjusting for confounding factors, sarcopenia was associated with a higher odds of in-patient mortality (aOR-2.16, 95% CI-1.83-2.56, p< 0.001), shock (aOR-2.18, 95% CI-1.92-2.48, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.4, 95% CI-1.32-1.49, p< 0.001), ICU stay (aOR-2.23, 95% CI-1.98-2.52, p< 0.001), LT-related complications (aOR-1.47, 95% CI-1.23-1.75, p< 0.001), longer length of stay (adj. coefficient-4.71 days, 95% CI-4.31-5.10, p< 0.001) and total hospitalization charges (adj. coefficient-$56,359.88, 95% CI-$49,737.17-$62,982.58, p< 0.001) (Table 1.)
Discussion: Our study noted that sarcopenia is linked with worse clinical outcomes and higher resource utilization in LT recipients. Early detection and management of sarcopenia are therefore essential for identifying patients at risk and implementing targeted interventions to enhance recovery and minimize complications.

Figure: Figure 1. Bar chart comparing outcomes of liver transplant recipients stratified by the presence of sarcopenia.

Figure: Table 1. Results of multivariate logistic regression highlighting the relationship between sarcopenia and worse clinical outcomes in liver transplant recipients.
Disclosures:
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritika Dhruve indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joanne Lin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sampada Bhasker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marina Roytman: Gilead – Speakers Bureau. Ipsen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Madrigal – Speakers Bureau. Salix – Speakers Bureau.
Mohammad Naseem, MBBS1, Ritika Dhruve, MBBS2, Joanne Lin, DO3, Carol Singh, MBBS4, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS5, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS6, Anmol Singh, MBBS7, Aalam Sohal, MD8, Marina Roytman, MD9. P1674 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Outcomes in Liver Transplant Recipients: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

