Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1583 - Trends, Burden, and Impact of Pneumococcal Pneumonia on Outcomes in Patients With Cirrhosis: Insights From the National Inpatient Sample Database
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Nishma Dhand, MBBS (she/her/hers)
Dayanand Medical College and Hospital
Moga, Punjab, India
Presenting Author(s)
Nishma Dhand, MBBS1, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS2, Carol Singh, MBBS3, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS4, Isha Kohli, MBBS, MPH5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Nilofar Najafian, MD6
1Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Moga, Punjab, India; 2Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 3Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 4Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 5Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Patients with cirrhosis have impaired immune function and are susceptible to developing infections. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia, which causes severe respiratory and systemic illness and thus affects prognosis in patients with cirrhosis. This study analyzes national trends, burden, and impact of pneumococcal disease on clinical outcomes in cirrhosis.
Methods: Data from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database (2016-2022) was used to identify adult patients with cirrhosis. Patients were stratified into two groups—those with and without pneumococcal pneumonia. We collected data on patient demographics, liver disease etiology, liver-related decompensations, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes. The study outcomes included in-hospital mortality, shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), intensive care unit (ICU) stay, and non-home discharges. A multivariate logistic/linear regression analysis was used to assess the impact of pneumococcal pneumonia on these outcomes.
Results: Among the 4,716,863 patients diagnosed with cirrhosis, 90,680 (1.9%) developed pneumococcal pneumonia. The majority of patients were 45-64 years old (49.9%), males (62.1%), White (68.3%), and had Medicare insurance (50.1%). The rate of pneumococcal pneumonia increased from 1.7% in 2016 to 2.23% in 2022 (p < 0.001). Pneumococcal pneumonia was also associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes including in-hospital mortality (19.4% vs. 6.1%), AKI (46.9% vs. 31.1%), ICU admissions (40.9% vs. 7.6%), non-home discharges (71.1% vs. 47.5%), and shock (31.5% vs 7.9%) (Figure 1.). After adjusting for confounding factors, we noted higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-2.95, 95% CI-2.84-3.09, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.85, 95% CI- 1.79-1.91, p< 0.001), shock (aOR-4.75, 95% CI-4.58-4.93, p< 0.001), ICU admissions (aOR-7.55, 95% CI-7.28-7.83, p< 0.001) and non-home discharges (aOR-2.29, 95% CI-2.21-2.38, p< 0.001), longer length of stay (adj. coefficient- 6.61 days, 95% CI-6.38-6.83, p< 0.001) and higher hospitalization charges (adj. Coefficient- $112,230.5, 95% CI-$106,802.3-$117,658.7, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: The rates of pneumococcal pneumonia in patients with cirrhosis have increased from 2016 to 2022. Our findings highlight the importance of implementing preventative measures such as pneumococcal vaccination to these at-risk patients, as this infection is associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes, including increased mortality and healthcare burden.
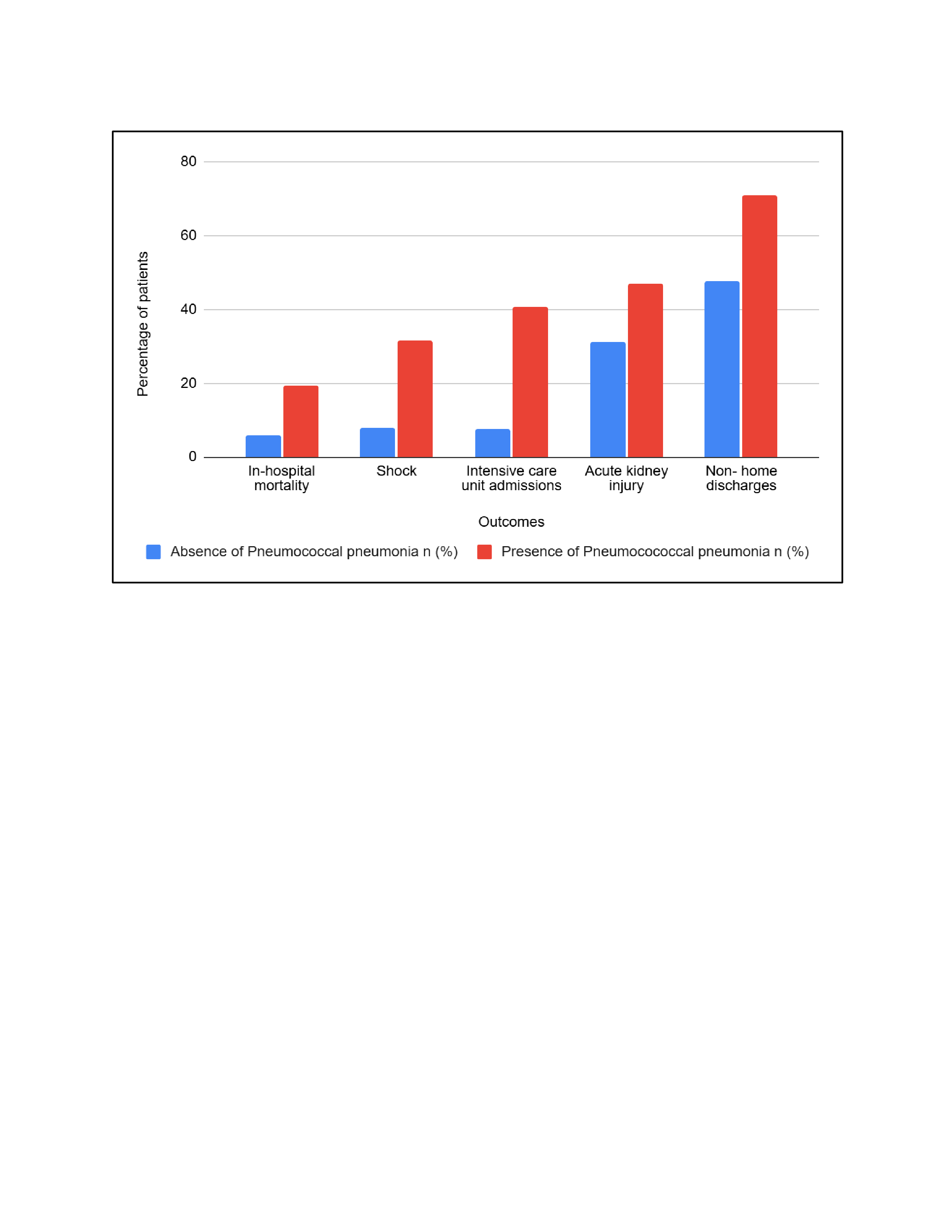
Figure: Figure 1. Bar chart comparing outcomes of liver cirrhosis stratified by the presence of pneumococcal pneumonia
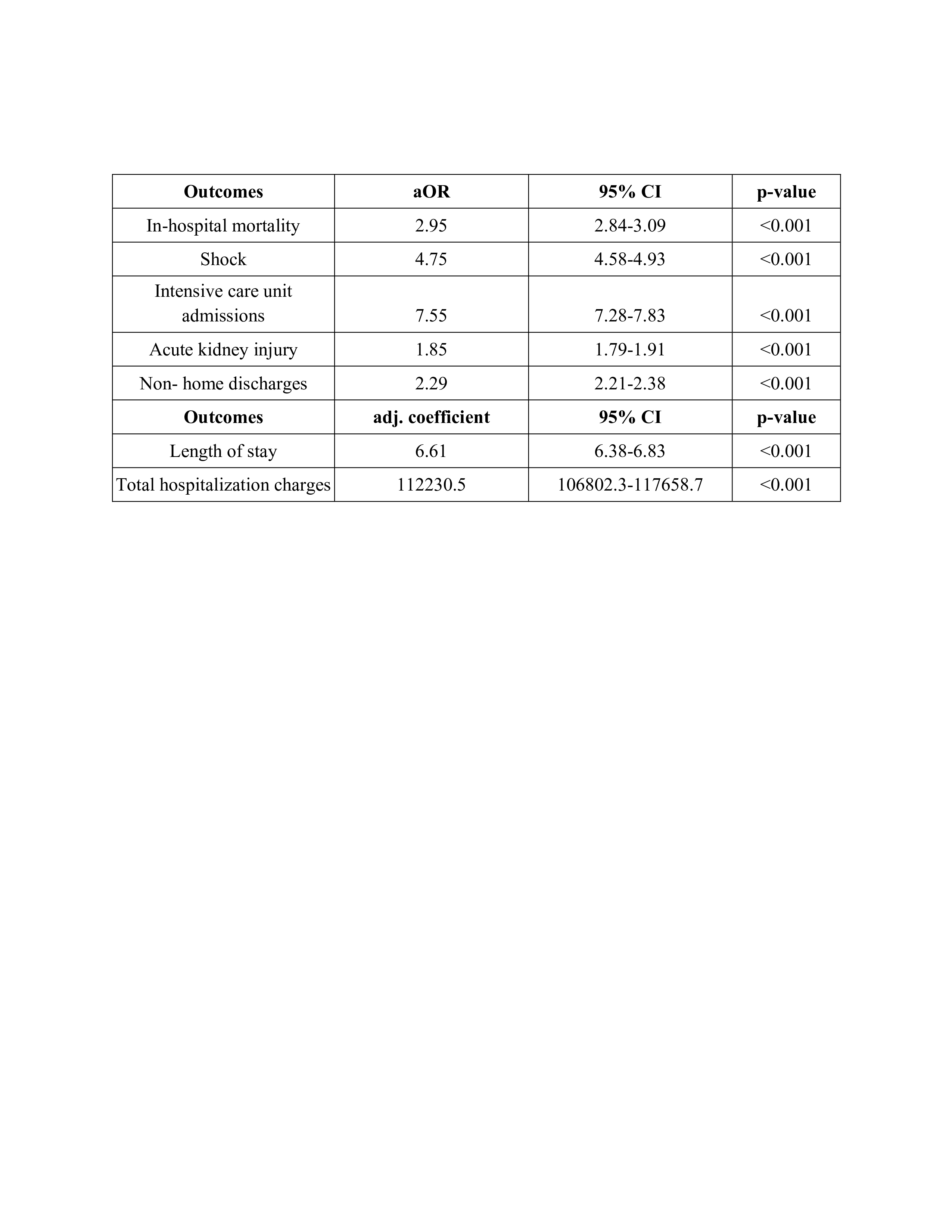
Figure: Table 1. Results of multivariate logistic regression, assessing the impact of pneumococcal pneumonia on outcomes and resource utilization.
Disclosures:
Nishma Dhand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Isha Kohli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilofar Najafian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nishma Dhand, MBBS1, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS2, Carol Singh, MBBS3, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS4, Isha Kohli, MBBS, MPH5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Nilofar Najafian, MD6. P1583 - Trends, Burden, and Impact of Pneumococcal Pneumonia on Outcomes in Patients With Cirrhosis: Insights From the National Inpatient Sample Database, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Moga, Punjab, India; 2Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 3Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 4Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 5Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Patients with cirrhosis have impaired immune function and are susceptible to developing infections. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia, which causes severe respiratory and systemic illness and thus affects prognosis in patients with cirrhosis. This study analyzes national trends, burden, and impact of pneumococcal disease on clinical outcomes in cirrhosis.
Methods: Data from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database (2016-2022) was used to identify adult patients with cirrhosis. Patients were stratified into two groups—those with and without pneumococcal pneumonia. We collected data on patient demographics, liver disease etiology, liver-related decompensations, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes. The study outcomes included in-hospital mortality, shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), intensive care unit (ICU) stay, and non-home discharges. A multivariate logistic/linear regression analysis was used to assess the impact of pneumococcal pneumonia on these outcomes.
Results: Among the 4,716,863 patients diagnosed with cirrhosis, 90,680 (1.9%) developed pneumococcal pneumonia. The majority of patients were 45-64 years old (49.9%), males (62.1%), White (68.3%), and had Medicare insurance (50.1%). The rate of pneumococcal pneumonia increased from 1.7% in 2016 to 2.23% in 2022 (p < 0.001). Pneumococcal pneumonia was also associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes including in-hospital mortality (19.4% vs. 6.1%), AKI (46.9% vs. 31.1%), ICU admissions (40.9% vs. 7.6%), non-home discharges (71.1% vs. 47.5%), and shock (31.5% vs 7.9%) (Figure 1.). After adjusting for confounding factors, we noted higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-2.95, 95% CI-2.84-3.09, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.85, 95% CI- 1.79-1.91, p< 0.001), shock (aOR-4.75, 95% CI-4.58-4.93, p< 0.001), ICU admissions (aOR-7.55, 95% CI-7.28-7.83, p< 0.001) and non-home discharges (aOR-2.29, 95% CI-2.21-2.38, p< 0.001), longer length of stay (adj. coefficient- 6.61 days, 95% CI-6.38-6.83, p< 0.001) and higher hospitalization charges (adj. Coefficient- $112,230.5, 95% CI-$106,802.3-$117,658.7, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: The rates of pneumococcal pneumonia in patients with cirrhosis have increased from 2016 to 2022. Our findings highlight the importance of implementing preventative measures such as pneumococcal vaccination to these at-risk patients, as this infection is associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes, including increased mortality and healthcare burden.

Figure: Figure 1. Bar chart comparing outcomes of liver cirrhosis stratified by the presence of pneumococcal pneumonia

Figure: Table 1. Results of multivariate logistic regression, assessing the impact of pneumococcal pneumonia on outcomes and resource utilization.
Disclosures:
Nishma Dhand indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Isha Kohli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nilofar Najafian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nishma Dhand, MBBS1, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS2, Carol Singh, MBBS3, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS4, Isha Kohli, MBBS, MPH5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Nilofar Najafian, MD6. P1583 - Trends, Burden, and Impact of Pneumococcal Pneumonia on Outcomes in Patients With Cirrhosis: Insights From the National Inpatient Sample Database, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
