Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1564 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- OA
Omar Al-Radideh, MD
University of Florida College of Medicine
Gainesville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmad Khan, 1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Sufyan Shahid, MBBS3, Muhammad Ahsan Asif, MBBS4, Rubab Zahra, MBBS5, Areesha Mansoor, 6, Qasim Mehmood, MBBS7, Yara Alswaiti, 8, Tahreem Mari, MBBS9, Omar Al-Radideh, MD10
1Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Khawaja Muhammad Safdar Medical College, Sialkot, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Jinnah Hospital Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Allama iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 7King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 9Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) involves liver fat accumulation in individuals with metabolic risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, and drink little to no alcohol. Approximately 20% develop metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), a more severe form that may progress to cirrhosis or end-stage liver disease. While liver biopsy is the diagnostic gold standard, its invasiveness limits use. Non-invasive biomarkers have emerged as promising alternatives in assessing fibrosis and steatosis severity. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the role of these biomarkers in improving NAFLD/NASH diagnosis.
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Embase was conducted to retrieve observational studies, which included prospective or retrospective cohorts or cross-sectional studies using novel biomarkers as a diagnostic test for MASLD/MASH. Outcomes included sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios. Analysis was performed in R using a random-effects model. Risk of bias assessment was assessed with ROBINS-I.
Results: 11 studies comprising 5,987 individuals were included. The mean age was 46.2 years, and 55% were male. The studies compared different novel biomarker types like NISA (IV), UAP, LSM, CK-18, OX NASH Score, Fuc-Hpt, M30 antigen, FIB-4, APRI, Age-Platelet Index, AST/ALT, Fibrosis Index (FI), Fibrosis Cirrhosis Index (FCI), and MACK-3 to diagnose MASLD or MASH.
Our results showed that the overall specificity of those novel biomarkers was 0.81 (95% CI: 0.693–0.890), and the pooled sensitivity was 0.800 (95% CI: 0.714 to 0.865). The results showed the pooled positive likelihood ratio was 4.172 (95% CI: 2.510 to 6.936), and the overall negative likelihood ratio was 0.244 (95% CI: 0.159–0.374). A summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was also constructed. The curve rises fairly consistently and levels off near the top left corner of the graph, indicating high sensitivity. It also exhibits a reasonable specificity.
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that non-invasive biomarkers exhibit strong diagnostic accuracy for MASLD/MASH, supported by high sensitivity, specificity, and robust likelihood ratios. The SROC curve further confirms their discriminatory ability. These findings support integrating non-invasive biomarkers into diagnostic algorithms to improve patient stratification and reduce reliance on invasive procedures.
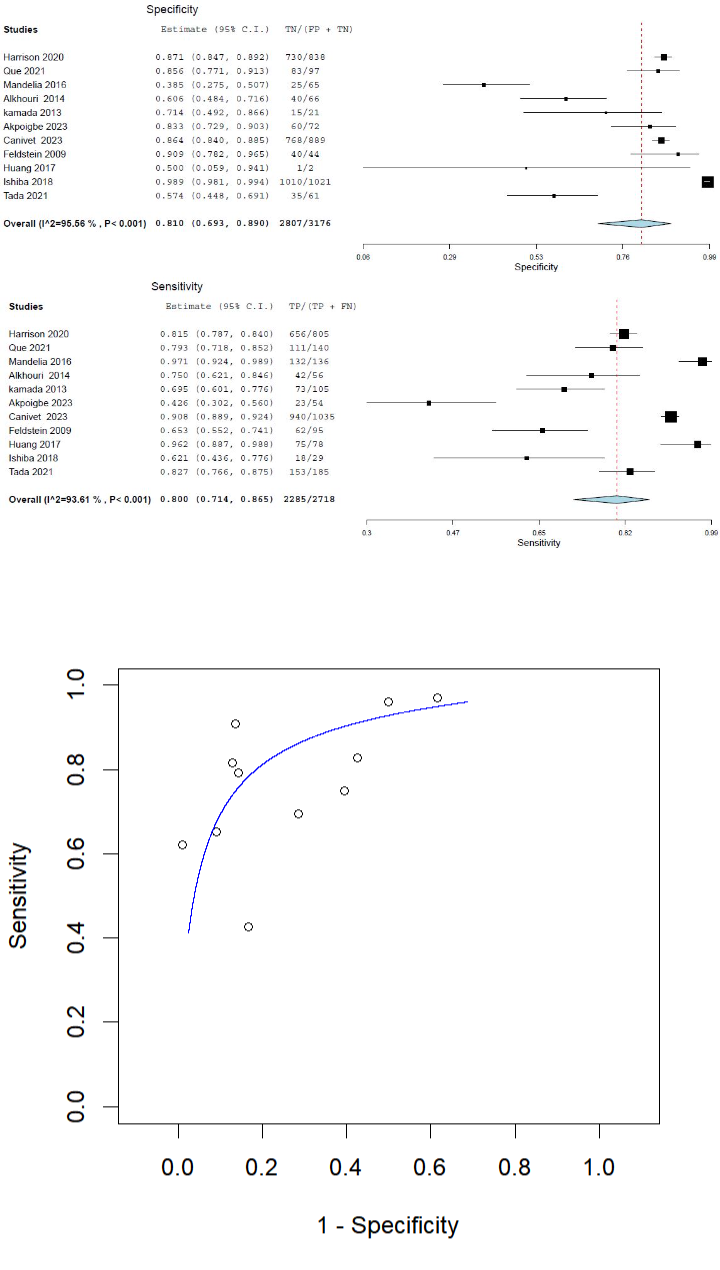
Figure: Forest plots of study-level and pooled estimates for (A) specificity and (B) sensitivity of non-invasive biomarkers for MASLD/MASH diagnosis.
Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for the diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive biomarkers in MASLD/MASH.
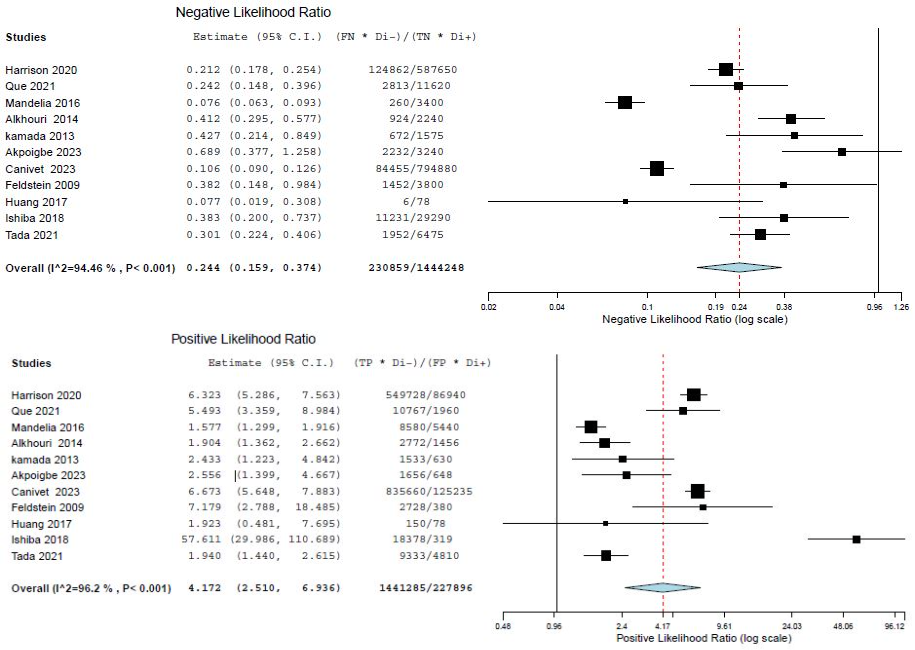
Figure: Forest plots of (A) negative likelihood ratio (NLR) and (B) positive likelihood ratio (PLR) for included studies.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sufyan Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahsan Asif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rubab Zahra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Areesha Mansoor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qasim Mehmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yara Alswaiti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tahreem Mari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Khan, 1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Sufyan Shahid, MBBS3, Muhammad Ahsan Asif, MBBS4, Rubab Zahra, MBBS5, Areesha Mansoor, 6, Qasim Mehmood, MBBS7, Yara Alswaiti, 8, Tahreem Mari, MBBS9, Omar Al-Radideh, MD10. P1564 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Khawaja Muhammad Safdar Medical College, Sialkot, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Jinnah Hospital Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Allama iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 7King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 9Dow Medical College, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 10University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) involves liver fat accumulation in individuals with metabolic risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, and drink little to no alcohol. Approximately 20% develop metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), a more severe form that may progress to cirrhosis or end-stage liver disease. While liver biopsy is the diagnostic gold standard, its invasiveness limits use. Non-invasive biomarkers have emerged as promising alternatives in assessing fibrosis and steatosis severity. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the role of these biomarkers in improving NAFLD/NASH diagnosis.
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Embase was conducted to retrieve observational studies, which included prospective or retrospective cohorts or cross-sectional studies using novel biomarkers as a diagnostic test for MASLD/MASH. Outcomes included sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios. Analysis was performed in R using a random-effects model. Risk of bias assessment was assessed with ROBINS-I.
Results: 11 studies comprising 5,987 individuals were included. The mean age was 46.2 years, and 55% were male. The studies compared different novel biomarker types like NISA (IV), UAP, LSM, CK-18, OX NASH Score, Fuc-Hpt, M30 antigen, FIB-4, APRI, Age-Platelet Index, AST/ALT, Fibrosis Index (FI), Fibrosis Cirrhosis Index (FCI), and MACK-3 to diagnose MASLD or MASH.
Our results showed that the overall specificity of those novel biomarkers was 0.81 (95% CI: 0.693–0.890), and the pooled sensitivity was 0.800 (95% CI: 0.714 to 0.865). The results showed the pooled positive likelihood ratio was 4.172 (95% CI: 2.510 to 6.936), and the overall negative likelihood ratio was 0.244 (95% CI: 0.159–0.374). A summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was also constructed. The curve rises fairly consistently and levels off near the top left corner of the graph, indicating high sensitivity. It also exhibits a reasonable specificity.
Discussion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that non-invasive biomarkers exhibit strong diagnostic accuracy for MASLD/MASH, supported by high sensitivity, specificity, and robust likelihood ratios. The SROC curve further confirms their discriminatory ability. These findings support integrating non-invasive biomarkers into diagnostic algorithms to improve patient stratification and reduce reliance on invasive procedures.

Figure: Forest plots of study-level and pooled estimates for (A) specificity and (B) sensitivity of non-invasive biomarkers for MASLD/MASH diagnosis.
Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for the diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive biomarkers in MASLD/MASH.

Figure: Forest plots of (A) negative likelihood ratio (NLR) and (B) positive likelihood ratio (PLR) for included studies.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sufyan Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ahsan Asif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rubab Zahra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Areesha Mansoor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qasim Mehmood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yara Alswaiti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tahreem Mari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Khan, 1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Sufyan Shahid, MBBS3, Muhammad Ahsan Asif, MBBS4, Rubab Zahra, MBBS5, Areesha Mansoor, 6, Qasim Mehmood, MBBS7, Yara Alswaiti, 8, Tahreem Mari, MBBS9, Omar Al-Radideh, MD10. P1564 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
