Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1493 - Comparative Effectiveness of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole, Ciprofloxacin, and Norfloxacin for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Prophylaxis in Cirrhosis: A TriNetX Network Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Archit Garg, MD (he/him/his)
Saint Peter's University Hospital / Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
New Brunswick, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Archit Garg, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD2, Aashi Garg, MD3, Sahil Raval, MD1, Mannat Bhatia, MD1, Pujitha Vallivedu Chennakesavulu, MD, MBBS4, Aadhithyaraman Santharaman, MD1, Marcella Pimpinelli, MD1, Andrew Korman, MD1, Louisa Recinos-Arenas, MD1, Arkady Broder, MD, FACG1
1Saint Peter's University Hospital / Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, MA; 4Quinnipiac University Frank H Netter School of Medicine/ St Vincent medical center, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) prophylaxis is critical in cirrhosis, but optimal antibiotic selection remains debated. We compared real-world outcomes of three first-line agents for SBP prophylaxis, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX).
Methods: This retrospective TriNetX study analyzed de-identified EHRs of adults with cirrhosis (ICD-10) initiating SBP prophylaxis. We compared TMP-SMX (n=57,625) vs. ciprofloxacin (n=81,037) and norfloxacin (n=1,246) vs. ciprofloxacin in patients with ascites. Outcomes included risk differences, odds ratios, and Kaplan-Meier survival.
Results: After propensity matching, TMP-SMX was associated with significantly lower incidence of SBP (3.9% vs. 6.3%; OR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.58-0.65, p-value < 0.001) and mortality (17.6% vs. 25.5%; OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.61-0.64, p-value < 0.001) in comparison to ciprofloxacin. However, there was an increased risk of clostridium difficile infection (3.3% vs. 2.5%; OR 1.33, 95% CI 1.24-1.42, p-value< 0.001) and pneumonia (9.8% vs. 9.2%; OR 1.08, 95% CI 1.03-1.12, p-value< 0.001) with TMP-SMX. The results were statistically non-significant for AKI (TMP-SMX, 22.7% vs. ciprofloxacin, 23.3%; OR 0.97, 95% CI: 0.93-1.0, p-value 0.07) and sepsis (TMP-SMX, 13% vs. ciprofloxacin, 13.2%; OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.95-1.03, p-value 0.57).
Propensity matched comparative analysis of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin showed that norfloxacin was associated with significantly higher incidence of SBP (10.1% vs. 6.3%; OR 1.68, 95% CI: 1.36-2.08, p-value < 0.001) and pneumonia (11.1% vs. 9.2%; OR 1.23, 95% CI 1.02-1.50, p-value 0.035). Norfloxacin had significantly decreased mortality rates (18.8% vs. 25.5%; OR 0.68, 95% CI 0.59-0.78, p-value < 0.001) compared to ciprofloxacin. The results of for AKI (norfloxacin, 23.4% vs. ciprofloxacin, 23.3%; OR 1.01, 95% CI: 0.84-1.20, p-value 0.95), clostridium difficile infection (norfloxacin, 3.3% vs. ciprofloxacin, 2.5%; OR 1.21, 95% CI 0.86-1.69, p-value 0.27) and sepsis (norfloxacin, 12% vs. ciprofloxacin, 13.2%; OR 0.90, 95% CI 0.74-1.09, p-value 0.27) were not significant.
Discussion: In this real-world study, TMP-SMX reduced SBP and mortality compared to ciprofloxacin but carried higher risks of C. difficile infection and pneumonia. Ciprofloxacin outperformed norfloxacin in preventing SBP and pneumonia, though with higher mortality. Other adverse event rates were similar, highlighting the need to individualize SBP prophylaxis based on patient risk profiles.
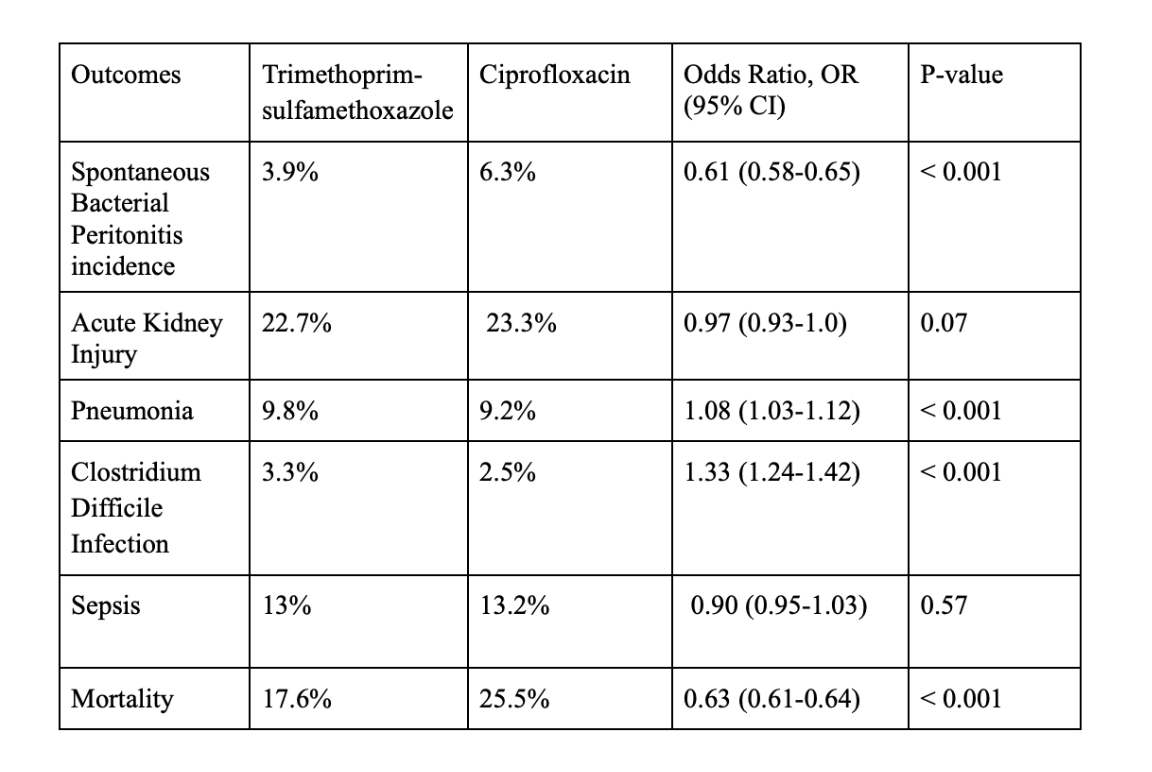
Figure: Table 1: Outcomes comparing trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin in primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
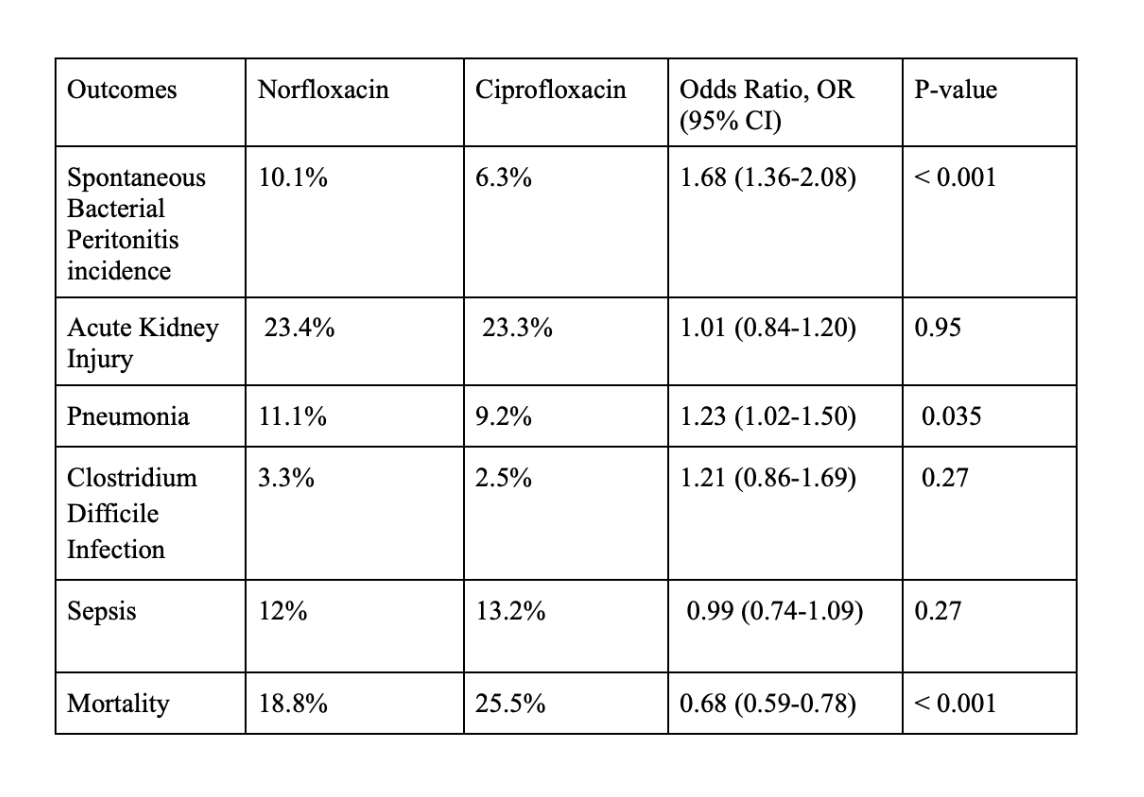
Figure: Table 2: Outcomes comparing norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin in primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Disclosures:
Archit Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umesh Bhagat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashi Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahil Raval indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mannat Bhatia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pujitha Vallivedu Chennakesavulu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aadhithyaraman Santharaman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marcella Pimpinelli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Korman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Louisa Recinos-Arenas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arkady Broder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Archit Garg, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD2, Aashi Garg, MD3, Sahil Raval, MD1, Mannat Bhatia, MD1, Pujitha Vallivedu Chennakesavulu, MD, MBBS4, Aadhithyaraman Santharaman, MD1, Marcella Pimpinelli, MD1, Andrew Korman, MD1, Louisa Recinos-Arenas, MD1, Arkady Broder, MD, FACG1. P1493 - Comparative Effectiveness of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole, Ciprofloxacin, and Norfloxacin for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Prophylaxis in Cirrhosis: A TriNetX Network Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Saint Peter's University Hospital / Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 3Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, MA; 4Quinnipiac University Frank H Netter School of Medicine/ St Vincent medical center, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) prophylaxis is critical in cirrhosis, but optimal antibiotic selection remains debated. We compared real-world outcomes of three first-line agents for SBP prophylaxis, norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX).
Methods: This retrospective TriNetX study analyzed de-identified EHRs of adults with cirrhosis (ICD-10) initiating SBP prophylaxis. We compared TMP-SMX (n=57,625) vs. ciprofloxacin (n=81,037) and norfloxacin (n=1,246) vs. ciprofloxacin in patients with ascites. Outcomes included risk differences, odds ratios, and Kaplan-Meier survival.
Results: After propensity matching, TMP-SMX was associated with significantly lower incidence of SBP (3.9% vs. 6.3%; OR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.58-0.65, p-value < 0.001) and mortality (17.6% vs. 25.5%; OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.61-0.64, p-value < 0.001) in comparison to ciprofloxacin. However, there was an increased risk of clostridium difficile infection (3.3% vs. 2.5%; OR 1.33, 95% CI 1.24-1.42, p-value< 0.001) and pneumonia (9.8% vs. 9.2%; OR 1.08, 95% CI 1.03-1.12, p-value< 0.001) with TMP-SMX. The results were statistically non-significant for AKI (TMP-SMX, 22.7% vs. ciprofloxacin, 23.3%; OR 0.97, 95% CI: 0.93-1.0, p-value 0.07) and sepsis (TMP-SMX, 13% vs. ciprofloxacin, 13.2%; OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.95-1.03, p-value 0.57).
Propensity matched comparative analysis of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin showed that norfloxacin was associated with significantly higher incidence of SBP (10.1% vs. 6.3%; OR 1.68, 95% CI: 1.36-2.08, p-value < 0.001) and pneumonia (11.1% vs. 9.2%; OR 1.23, 95% CI 1.02-1.50, p-value 0.035). Norfloxacin had significantly decreased mortality rates (18.8% vs. 25.5%; OR 0.68, 95% CI 0.59-0.78, p-value < 0.001) compared to ciprofloxacin. The results of for AKI (norfloxacin, 23.4% vs. ciprofloxacin, 23.3%; OR 1.01, 95% CI: 0.84-1.20, p-value 0.95), clostridium difficile infection (norfloxacin, 3.3% vs. ciprofloxacin, 2.5%; OR 1.21, 95% CI 0.86-1.69, p-value 0.27) and sepsis (norfloxacin, 12% vs. ciprofloxacin, 13.2%; OR 0.90, 95% CI 0.74-1.09, p-value 0.27) were not significant.
Discussion: In this real-world study, TMP-SMX reduced SBP and mortality compared to ciprofloxacin but carried higher risks of C. difficile infection and pneumonia. Ciprofloxacin outperformed norfloxacin in preventing SBP and pneumonia, though with higher mortality. Other adverse event rates were similar, highlighting the need to individualize SBP prophylaxis based on patient risk profiles.

Figure: Table 1: Outcomes comparing trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin in primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis

Figure: Table 2: Outcomes comparing norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin in primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Disclosures:
Archit Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umesh Bhagat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aashi Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahil Raval indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mannat Bhatia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pujitha Vallivedu Chennakesavulu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aadhithyaraman Santharaman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marcella Pimpinelli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Korman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Louisa Recinos-Arenas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arkady Broder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Archit Garg, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD2, Aashi Garg, MD3, Sahil Raval, MD1, Mannat Bhatia, MD1, Pujitha Vallivedu Chennakesavulu, MD, MBBS4, Aadhithyaraman Santharaman, MD1, Marcella Pimpinelli, MD1, Andrew Korman, MD1, Louisa Recinos-Arenas, MD1, Arkady Broder, MD, FACG1. P1493 - Comparative Effectiveness of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole, Ciprofloxacin, and Norfloxacin for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Prophylaxis in Cirrhosis: A TriNetX Network Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
