Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1420 - LAMS Drainage of Pelvic Abscesses in the Pediatric Population
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Daniel Basta, MD
Westchester Medical Center
Elmwood Park, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Daniel Basta, MD1, Katia Vernord, MD2, Fady Beshara, BS3, Shireen Pais, MD2
1Westchester Medical Center, Elmwood Park, NJ; 2Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, NY; 3American University of the Caribbean, Nutley, NJ
Introduction: Pelvic abscesses in the pediatric population often arise as complications of appendicitis, posing significant management challenges. Traditionally, treatment has involved surgical intervention or percutaneous drainage, which can carry risks of morbidity. The advent of lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) offers a novel, minimally invasive alternative for drainage of pelvic abscesses. This study presents four cases of pediatric patients with appendicitis complicated by pelvic abscesses, managed using endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage with LAMS.
Case Description/
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of four pediatric patients (ages 8 to 14) diagnosed with ruptured appendicitis complicated by pelvic abscesses. All patients were admitted to the surgical service and presented with abdominal pain and fever. Imaging confirmed pelvic abscesses ranging from 5 to 8 cm in size. Interventional Radiology considered the locations not amenable to drainage. Each patient underwent EUS to confirm the characteristics of the abscess and proximity to the gastrointestinal tract. The LAMS was placed under doppler guidance, facilitating direct abscess drainage. Double pigtail stents were placed to ensure patency of the abscess to the GI tract. Follow-up evaluations demonstrated clinical improvement and imaging revealed decreased size of the abscesses, and patients returned for repeat sigmoidoscopy after 3-4 weeks for LAMS removal.
Discussion: The results from our cases demonstrated successful management of pelvic abscesses using LAMS, achieving symptomatic improvement and complete resolution. The minimally invasive nature of this approach reduced the need for more invasive surgical procedures. No complications occurred, and there were no cases of stent migration Our findings suggest that EUS-guided drainage with LAMS is a safe and effective option for managing pelvic abscesses in pediatric patients, particularly when traditional methods may pose greater risks. The use of LAMS stents for the management of pelvic abscesses in pediatric patients represents a promising alternative to conventional treatment approaches. This method enhances safety and minimizes recovery times. Given the positive outcomes observed in this small cohort, further prospective studies are necessary to validate these findings and evaluate long-term efficacy in larger pediatric populations. Overall, our experience supports the incorporation of endoscopic techniques into the management strategies for pediatric pelvic abscesses.
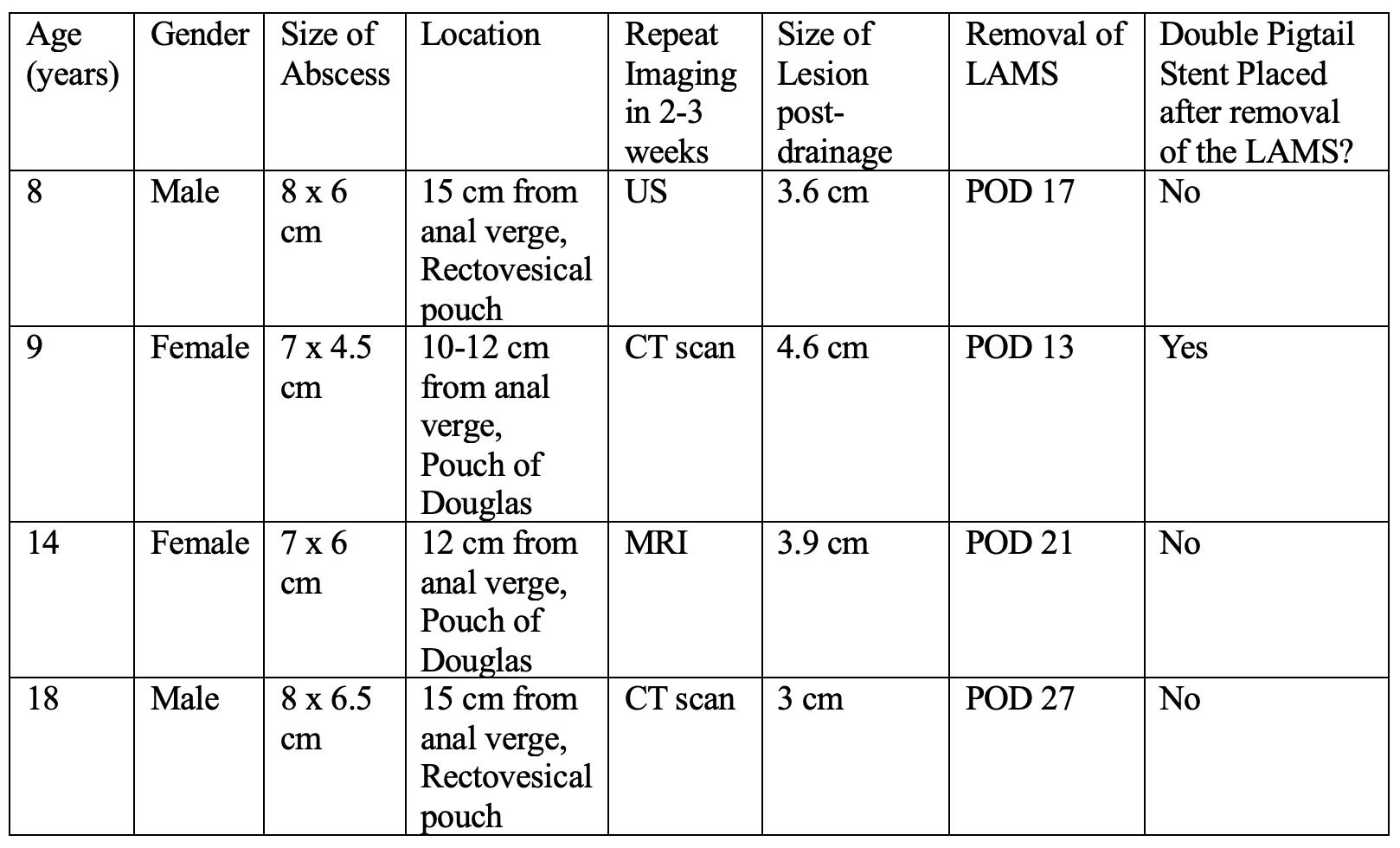
Figure: Four case descriptions involving drainage of pelvic abscesses using lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS).
Disclosures:
Daniel Basta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katia Vernord indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fady Beshara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shireen Pais indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Basta, MD1, Katia Vernord, MD2, Fady Beshara, BS3, Shireen Pais, MD2. P1420 - LAMS Drainage of Pelvic Abscesses in the Pediatric Population, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Daniel Basta, MD1, Katia Vernord, MD2, Fady Beshara, BS3, Shireen Pais, MD2
1Westchester Medical Center, Elmwood Park, NJ; 2Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, NY; 3American University of the Caribbean, Nutley, NJ
Introduction: Pelvic abscesses in the pediatric population often arise as complications of appendicitis, posing significant management challenges. Traditionally, treatment has involved surgical intervention or percutaneous drainage, which can carry risks of morbidity. The advent of lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) offers a novel, minimally invasive alternative for drainage of pelvic abscesses. This study presents four cases of pediatric patients with appendicitis complicated by pelvic abscesses, managed using endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage with LAMS.
Case Description/
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of four pediatric patients (ages 8 to 14) diagnosed with ruptured appendicitis complicated by pelvic abscesses. All patients were admitted to the surgical service and presented with abdominal pain and fever. Imaging confirmed pelvic abscesses ranging from 5 to 8 cm in size. Interventional Radiology considered the locations not amenable to drainage. Each patient underwent EUS to confirm the characteristics of the abscess and proximity to the gastrointestinal tract. The LAMS was placed under doppler guidance, facilitating direct abscess drainage. Double pigtail stents were placed to ensure patency of the abscess to the GI tract. Follow-up evaluations demonstrated clinical improvement and imaging revealed decreased size of the abscesses, and patients returned for repeat sigmoidoscopy after 3-4 weeks for LAMS removal.
Discussion: The results from our cases demonstrated successful management of pelvic abscesses using LAMS, achieving symptomatic improvement and complete resolution. The minimally invasive nature of this approach reduced the need for more invasive surgical procedures. No complications occurred, and there were no cases of stent migration Our findings suggest that EUS-guided drainage with LAMS is a safe and effective option for managing pelvic abscesses in pediatric patients, particularly when traditional methods may pose greater risks. The use of LAMS stents for the management of pelvic abscesses in pediatric patients represents a promising alternative to conventional treatment approaches. This method enhances safety and minimizes recovery times. Given the positive outcomes observed in this small cohort, further prospective studies are necessary to validate these findings and evaluate long-term efficacy in larger pediatric populations. Overall, our experience supports the incorporation of endoscopic techniques into the management strategies for pediatric pelvic abscesses.

Figure: Four case descriptions involving drainage of pelvic abscesses using lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS).
Disclosures:
Daniel Basta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katia Vernord indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fady Beshara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shireen Pais indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Basta, MD1, Katia Vernord, MD2, Fady Beshara, BS3, Shireen Pais, MD2. P1420 - LAMS Drainage of Pelvic Abscesses in the Pediatric Population, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

