Sunday Poster Session
Category: Infections and Microbiome
P1306 - Antiretroviral Therapy Enhances the Cardioprotective Benefit of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in People With HIV
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH
Yale New Haven Health
Bridgeport, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Yussif Issaka, MBChB2, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD3, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil4, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD5, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS6, Amoafo Boampong, MD7, Bary Malik, MD8, Geraldine Nabeta, MD9, Akif Altinbas, MD10, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH11
1Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 3Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 4Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 6Yale University, New Haven, CT; 7Howard University, Washington, DC; 8Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 9University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 10UConn Health, Simsbury, CT; 11VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT
Introduction: GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) provide cardiovascular protection in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and obesity. However, their benefit in people with HIV (PWH)—a population at elevated cardiovascular risk—remains understudied. Moreover, whether antiretroviral therapy (ART) modifies this cardioprotective association is unclear. We evaluated the association between GLP-1 RA use and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in PWH and tested for interaction by ART exposure.
Methods: We analyzed data from the All of Us Research Program (2016–2022), a nationwide EHR-based cohort, to identify adults (≥18 years) living with HIV and without prior MACE. Eligible participants had T2DM and/or obesity and ≥3 months of GLP-1 RA use. We excluded individuals with pancreatitis, CKD stage 3–5, or personal/family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia. ART use was defined as ≥3 months of continuous exposure. The primary outcome was new-onset MACE, including myocardial infarction, stroke , or cardiovascular death. Propensity score matching (2:1 nearest-neighbor; caliper 0.1) was performed on age, gender, race/ethnicity, and income. Adjusted logistic regression estimated odds of MACE, controlling for CKD, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, MASLD, smoking, CD4 count, and BMI. Interaction by ART was tested, and models were stratified by ART status.
Results: Among 2,712 eligible PWH, 14.7% (n=398) used GLP-1 RAs. The matched cohort included 1,194 individuals (398 users; 796 non-users); mean age was 58.9 ±10.6 years, 40% were female, 48% Black, and 25% Hispanic.
During follow-up, 130 MACE events occurred. GLP-1 use was associated with 87% lower odds of MACE (aOR: 0.13; 95% CI: 0.03–0.39; p=0.001). A significant interaction was observed between GLP-1 use and ART (p=0.020).
In stratified models, GLP-1 RA use remained protective among ART users (aOR: 0.28; 95% CI: 0.15–0.48; p< 0.001) but was attenuated and nonsignificant among non-ART users (aOR: 0.42; 95% CI: 0.15–1.04; p=0.080). Among ART users, CKD (aOR: 1.70; 95% CI: 1.06–2.71; p=0.026) and hyperlipidemia (aOR: 5.04; 95% CI: 2.72–10.2; p< 0.001) were also associated with MACE.
Discussion: GLP-1 RA use was associated with significantly lower cardiovascular risk among PWH with T2DM and/or obesity, particularly in those receiving ART. These findings suggest that ART may enhance the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs and highlight the importance of integrated HIV-metabolic care to reduce cardiovascular risk.
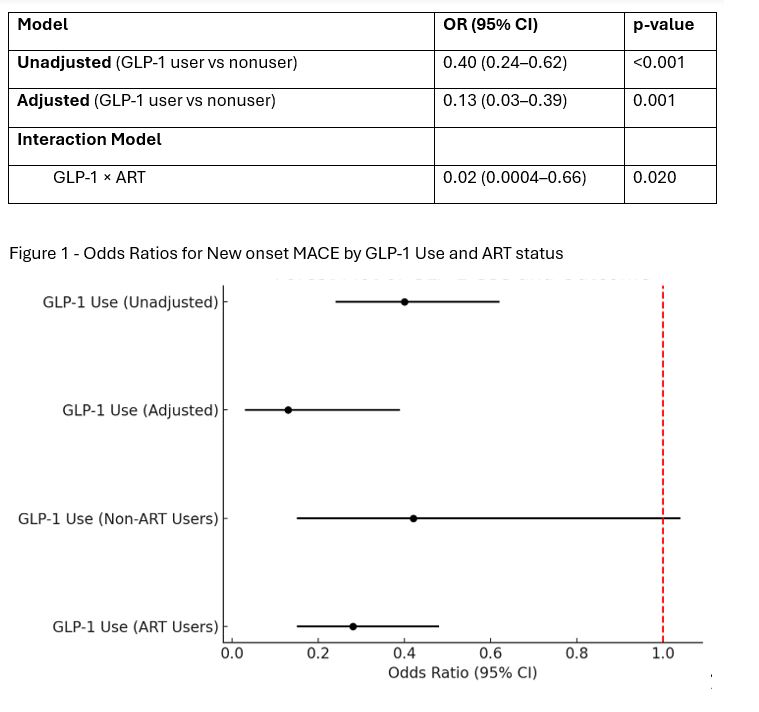
Figure: Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of People with HIV by GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use After Propensity Score Matching on Demographic Characteristics
GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
SMD: Standardized Mean Difference. A value >0.1 may indicate imbalance.
MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
CKD: Chronic kidney disease
BMI: Body mass index
ART: Antiretroviral therapy
CD4: Lowest recorded CD4+ T-cell count
Percentages are column percentages unless otherwise specified.
p-values derived from χ² test (categorical) or t-test (continuous)
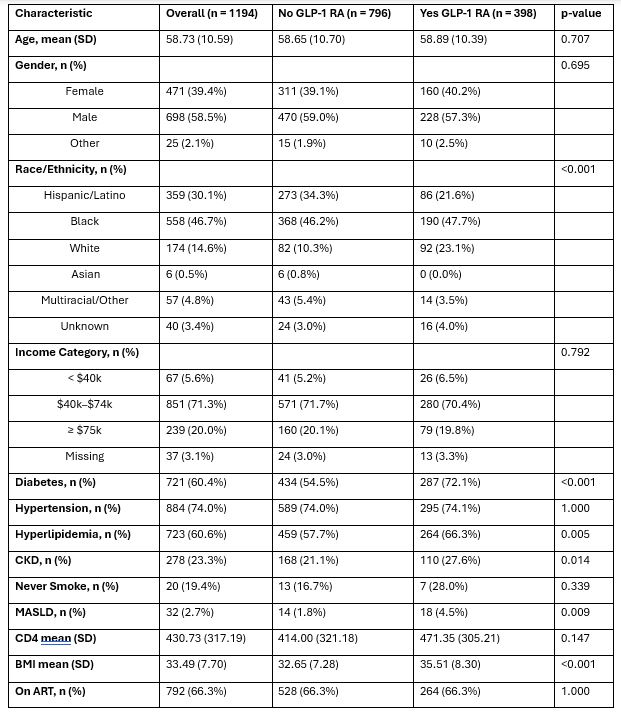
Figure: Table 2 – Odds Ratios for New onset MACE by GLP-1 Use
Figure 1 - Odds Ratios for New onset MACE by GLP-1 Use and ART status
All models are logistic regressions with odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals. Adjusted models include diabetes, CKD, hyperlipidemia, MASLD, CD4 count, and BMI.
MACE - myocardial infarction, stroke , or cardiovascular death.
Disclosures:
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amoafo Boampong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bary Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Geraldine Nabeta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akif Altinbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Yussif Issaka, MBChB2, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD3, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil4, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD5, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS6, Amoafo Boampong, MD7, Bary Malik, MD8, Geraldine Nabeta, MD9, Akif Altinbas, MD10, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH11. P1306 - Antiretroviral Therapy Enhances the Cardioprotective Benefit of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in People With HIV, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 3Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 4Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 5Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 6Yale University, New Haven, CT; 7Howard University, Washington, DC; 8Howard University Hospital, Washington, DC; 9University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 10UConn Health, Simsbury, CT; 11VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT
Introduction: GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) provide cardiovascular protection in individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and obesity. However, their benefit in people with HIV (PWH)—a population at elevated cardiovascular risk—remains understudied. Moreover, whether antiretroviral therapy (ART) modifies this cardioprotective association is unclear. We evaluated the association between GLP-1 RA use and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in PWH and tested for interaction by ART exposure.
Methods: We analyzed data from the All of Us Research Program (2016–2022), a nationwide EHR-based cohort, to identify adults (≥18 years) living with HIV and without prior MACE. Eligible participants had T2DM and/or obesity and ≥3 months of GLP-1 RA use. We excluded individuals with pancreatitis, CKD stage 3–5, or personal/family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia. ART use was defined as ≥3 months of continuous exposure. The primary outcome was new-onset MACE, including myocardial infarction, stroke , or cardiovascular death. Propensity score matching (2:1 nearest-neighbor; caliper 0.1) was performed on age, gender, race/ethnicity, and income. Adjusted logistic regression estimated odds of MACE, controlling for CKD, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, MASLD, smoking, CD4 count, and BMI. Interaction by ART was tested, and models were stratified by ART status.
Results: Among 2,712 eligible PWH, 14.7% (n=398) used GLP-1 RAs. The matched cohort included 1,194 individuals (398 users; 796 non-users); mean age was 58.9 ±10.6 years, 40% were female, 48% Black, and 25% Hispanic.
During follow-up, 130 MACE events occurred. GLP-1 use was associated with 87% lower odds of MACE (aOR: 0.13; 95% CI: 0.03–0.39; p=0.001). A significant interaction was observed between GLP-1 use and ART (p=0.020).
In stratified models, GLP-1 RA use remained protective among ART users (aOR: 0.28; 95% CI: 0.15–0.48; p< 0.001) but was attenuated and nonsignificant among non-ART users (aOR: 0.42; 95% CI: 0.15–1.04; p=0.080). Among ART users, CKD (aOR: 1.70; 95% CI: 1.06–2.71; p=0.026) and hyperlipidemia (aOR: 5.04; 95% CI: 2.72–10.2; p< 0.001) were also associated with MACE.
Discussion: GLP-1 RA use was associated with significantly lower cardiovascular risk among PWH with T2DM and/or obesity, particularly in those receiving ART. These findings suggest that ART may enhance the cardioprotective effects of GLP-1 RAs and highlight the importance of integrated HIV-metabolic care to reduce cardiovascular risk.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of People with HIV by GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use After Propensity Score Matching on Demographic Characteristics
GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
SMD: Standardized Mean Difference. A value >0.1 may indicate imbalance.
MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
CKD: Chronic kidney disease
BMI: Body mass index
ART: Antiretroviral therapy
CD4: Lowest recorded CD4+ T-cell count
Percentages are column percentages unless otherwise specified.
p-values derived from χ² test (categorical) or t-test (continuous)

Figure: Table 2 – Odds Ratios for New onset MACE by GLP-1 Use
Figure 1 - Odds Ratios for New onset MACE by GLP-1 Use and ART status
All models are logistic regressions with odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals. Adjusted models include diabetes, CKD, hyperlipidemia, MASLD, CD4 count, and BMI.
MACE - myocardial infarction, stroke , or cardiovascular death.
Disclosures:
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amoafo Boampong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bary Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Geraldine Nabeta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akif Altinbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Yussif Issaka, MBChB2, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD3, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil4, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD5, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS6, Amoafo Boampong, MD7, Bary Malik, MD8, Geraldine Nabeta, MD9, Akif Altinbas, MD10, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH11. P1306 - Antiretroviral Therapy Enhances the Cardioprotective Benefit of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in People With HIV, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

