Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1121 - Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus Associated With Worse Outcome in Ulcerative Colitis Patients? Nationwide Inpatient Sample
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Amro Altarawneh, MD
Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine
Huntington, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Amro Altarawneh, MD1, Saba Altarawneh, MD2, Leen Kayali, MBBS1, Etan Spira, MD2, Joseph DePasquale, MD2
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 2Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City, NJ
Introduction: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common, contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system and has been linked to adverse outcomes in individuals with chronic diseases. This study investigates whether RSV infection is associated with worse outcomes in patients with Ulcerative Colitis (UC), including mortality, colectomy rates, and healthcare utilization.
Methods: Data from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) were analyzed to identify patients with RSV, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), and colectomy procedures using ICD-10 codes. Patients were categorized by RSV status. Comparative analyses were conducted using t-tests and chi-square tests. Logistic regression assessed binary outcomes, including mortality and colectomy rates, while linear regression analyzed continuous outcomes such as length of stay (LOS) and total hospital charges. Survey weights accounted for the NIS's complex sampling design.
Results: Among 512,965 UC patients, 600 (0.1%) were RSV-positive, with a mean age of 64 years; 58.3% were female. RSV was significantly associated with increased mortality (Odds Ratio [OR]: 2.2, 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 1.1–4.7, P = 0.03) and longer hospital stays (β: +2.8 days, 95% CI: 0.91–4.6, P = 0.003). Interestingly, RSV was associated with a decreased likelihood of colectomy (OR: 0.036, 95% CI: 0.15–0.87, P = 0.024). Total hospital charges were not significantly affected by RSV.
Discussion: RSV infection was associated with increased mortality and prolonged hospital stays in UC patients, underscoring the need for preventive measures, such as vaccination, in this vulnerable population. The unexpected association between RSV and reduced colectomy rates warrants further investigation to understand potential clinical or biological mechanisms. These findings highlight the importance of developing RSV vaccination strategies tailored to UC patients, including determining the optimal age and risk factors for immunization.
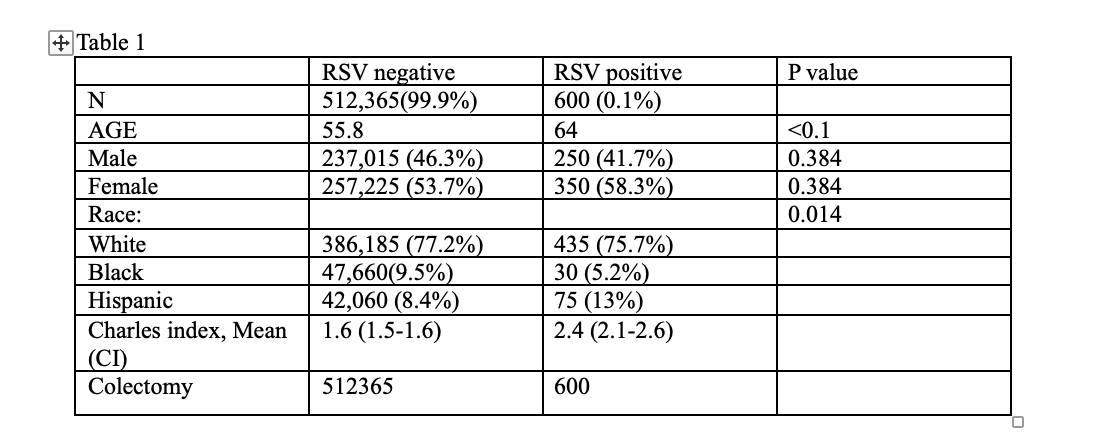
Figure: Table 1
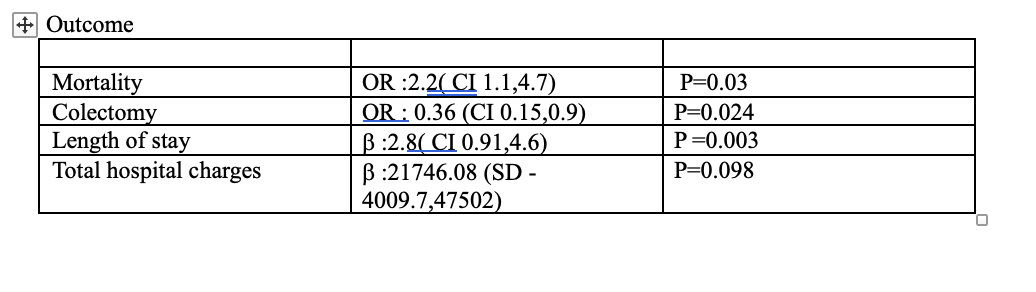
Figure: Table 2
Disclosures:
Amro Altarawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saba Altarawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leen Kayali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Etan Spira indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph DePasquale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amro Altarawneh, MD1, Saba Altarawneh, MD2, Leen Kayali, MBBS1, Etan Spira, MD2, Joseph DePasquale, MD2. P1121 - Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus Associated With Worse Outcome in Ulcerative Colitis Patients? Nationwide Inpatient Sample, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine, Huntington, WV; 2Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City, NJ
Introduction: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common, contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system and has been linked to adverse outcomes in individuals with chronic diseases. This study investigates whether RSV infection is associated with worse outcomes in patients with Ulcerative Colitis (UC), including mortality, colectomy rates, and healthcare utilization.
Methods: Data from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) were analyzed to identify patients with RSV, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), and colectomy procedures using ICD-10 codes. Patients were categorized by RSV status. Comparative analyses were conducted using t-tests and chi-square tests. Logistic regression assessed binary outcomes, including mortality and colectomy rates, while linear regression analyzed continuous outcomes such as length of stay (LOS) and total hospital charges. Survey weights accounted for the NIS's complex sampling design.
Results: Among 512,965 UC patients, 600 (0.1%) were RSV-positive, with a mean age of 64 years; 58.3% were female. RSV was significantly associated with increased mortality (Odds Ratio [OR]: 2.2, 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 1.1–4.7, P = 0.03) and longer hospital stays (β: +2.8 days, 95% CI: 0.91–4.6, P = 0.003). Interestingly, RSV was associated with a decreased likelihood of colectomy (OR: 0.036, 95% CI: 0.15–0.87, P = 0.024). Total hospital charges were not significantly affected by RSV.
Discussion: RSV infection was associated with increased mortality and prolonged hospital stays in UC patients, underscoring the need for preventive measures, such as vaccination, in this vulnerable population. The unexpected association between RSV and reduced colectomy rates warrants further investigation to understand potential clinical or biological mechanisms. These findings highlight the importance of developing RSV vaccination strategies tailored to UC patients, including determining the optimal age and risk factors for immunization.

Figure: Table 1

Figure: Table 2
Disclosures:
Amro Altarawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saba Altarawneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leen Kayali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Etan Spira indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph DePasquale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amro Altarawneh, MD1, Saba Altarawneh, MD2, Leen Kayali, MBBS1, Etan Spira, MD2, Joseph DePasquale, MD2. P1121 - Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus Associated With Worse Outcome in Ulcerative Colitis Patients? Nationwide Inpatient Sample, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
