Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1114 - Ustekinumab Is Superior to Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF Naïve and Anti-TNF Exposed Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Matched Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ismail Elkhattib, MBBCh
University of Nebraska
Hartford, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Khaled Elfert, MD1, Ismail Elkhattib, MBBCh2, Mohamed Eldesouki, MD3, Eslam Rabea, MBBCh4, Muhammad Elsharkawy, MD4, Mohamed A. Aldemerdash, 5, George Obeng, MD6, Kanwarpreet Tandon, MBBS1, Jennifer Hadam-Veverka, MD1
1West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 2University of Nebraska, Hartford, CT; 3Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 4Alexandria University, Alexandria, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt; 5Sohag University, Faculty of Medicine, Sohag, Suhaj, Egypt; 6West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Ustekinumab and vedolizumab are commonly used in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. However, direct comparative studies evaluating their long-term efficacy, particularly in anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed populations, remain limited.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network database was conducted to compare the real-world efficacy of Ustekinumab and vedolizumab in adult CD patients. Patients were stratified into anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed cohorts, and 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was employed. The primary outcome was the need for corticosteroid use at 12 and 24 months. Secondary outcomes included all-cause hospitalization rates, and emergency department (ED) visits.
Results: In the anti-TNF-naïve cohort, Ustekinumab was associated with significantly lower corticosteroid use at 12 months (29.3% vs. 38.0%, p< 0.01) with HR of 0.69 (95% CI: 0.63–0.75) and 24 months (39.4% vs. 45.6%, p< 0.01) with HR of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.71–0.83). Additionally, Ustekinumab-treated patients had fewer all-cause ED visits. No significant differences were observed in all-cause hospitalization rates.
In the anti-TNF-exposed cohort, Ustekinumab was similarly associated with reduced corticosteroid use at 12 months (39.3% vs. 46.7%, p< 0.01) (HR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.68–0.87) and 24 months (51.5% vs. 55.0%, p< 0.01) (HR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93). Ustekinumab-treated patients also demonstrated lower ED visit rates and reduced hospitalizations.
Discussion: Ustekinumab demonstrated superior corticosteroid-sparing effects and fewer healthcare utilization events compared to vedolizumab in both anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed CD patients. These findings suggest that ustekinumab may offer improved long-term disease control and reduced healthcare burden.
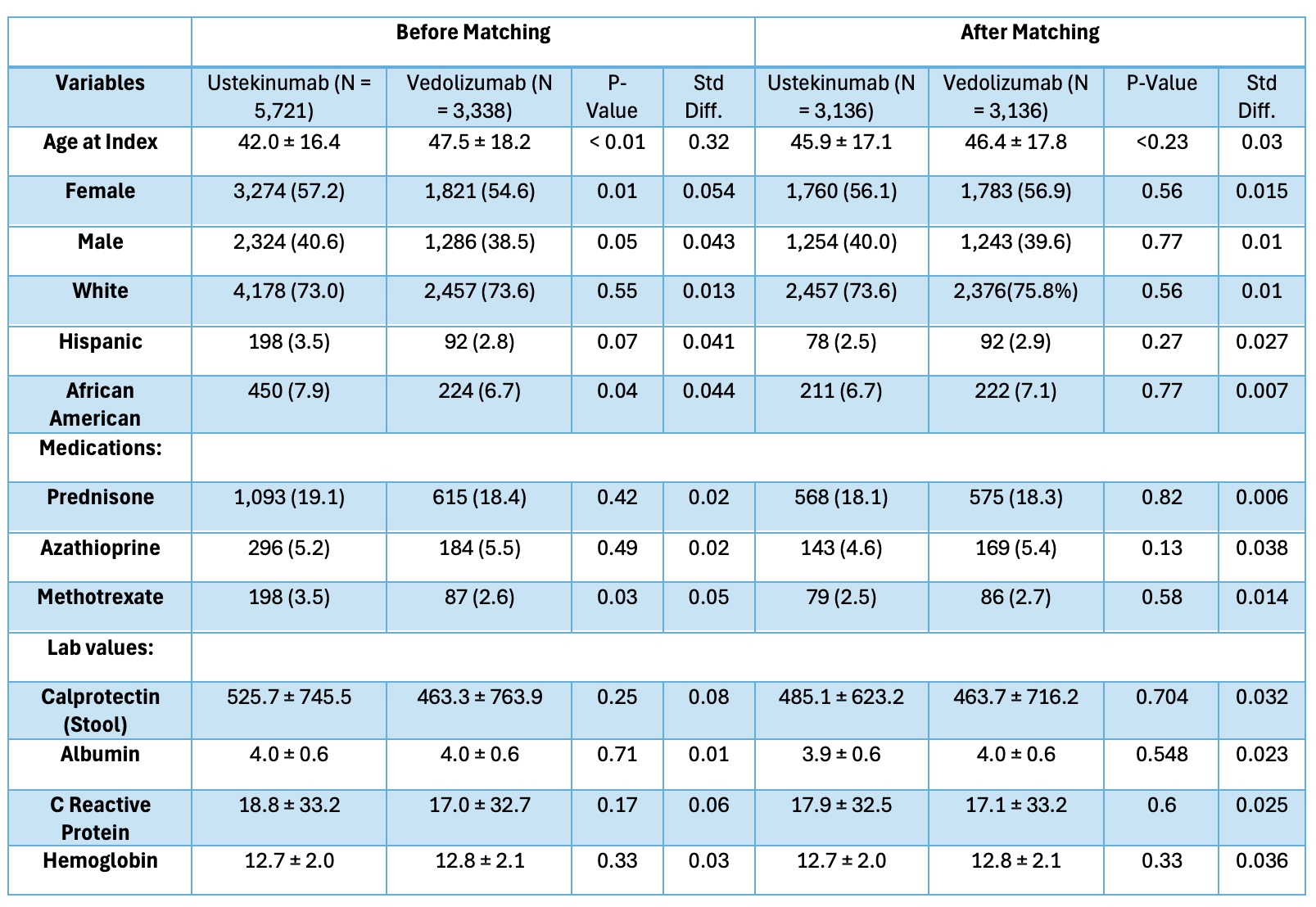
Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of TNF-naïve patients in ustekinumab cohort and vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching
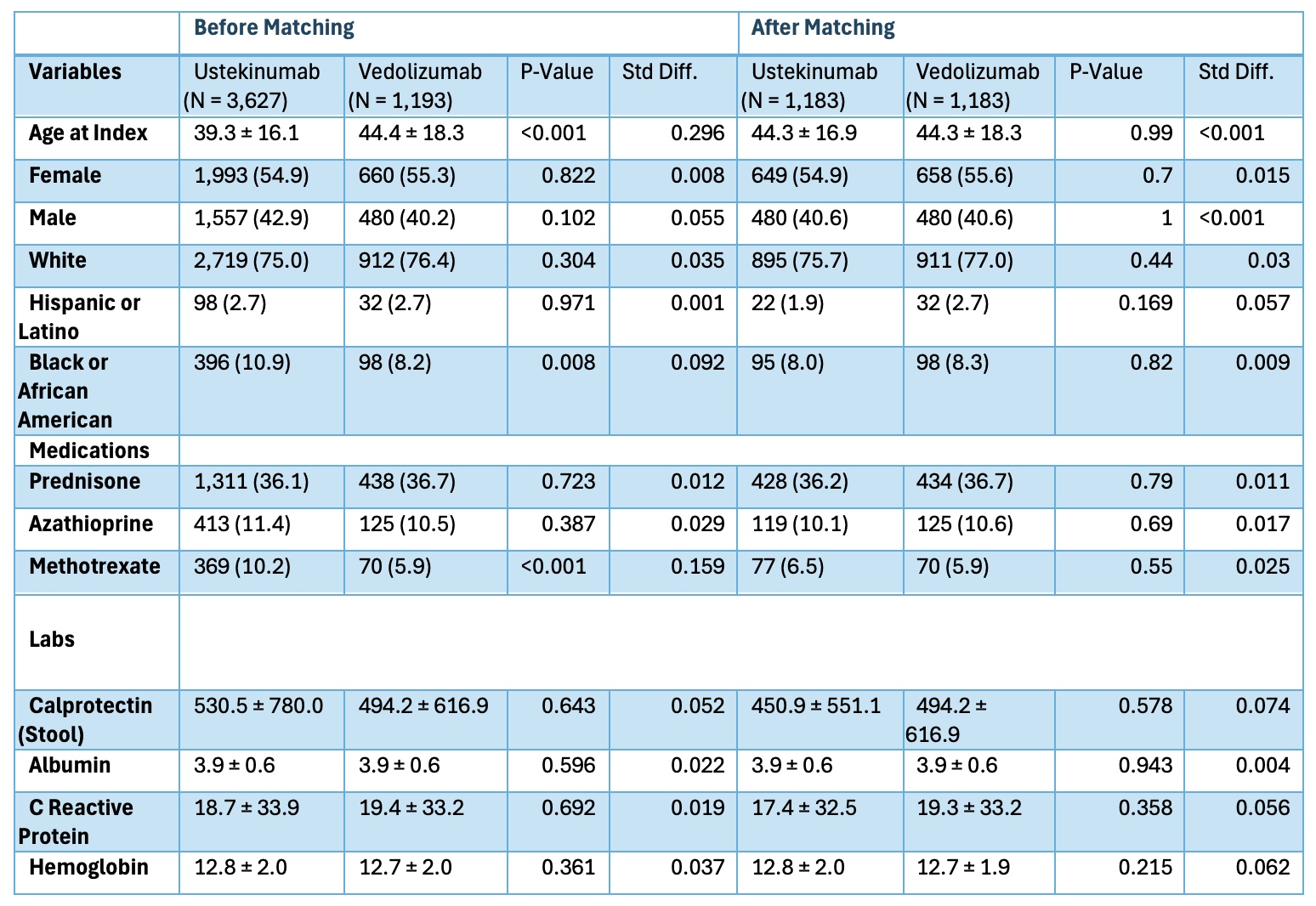
Figure: Table 2. Baseline characteristics of patients after TNF in the ustekinumab cohort and the vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching
Disclosures:
Khaled Elfert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Elkhattib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eslam Rabea indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Elsharkawy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed A. Aldemerdash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Obeng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kanwarpreet Tandon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer Hadam-Veverka: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Khaled Elfert, MD1, Ismail Elkhattib, MBBCh2, Mohamed Eldesouki, MD3, Eslam Rabea, MBBCh4, Muhammad Elsharkawy, MD4, Mohamed A. Aldemerdash, 5, George Obeng, MD6, Kanwarpreet Tandon, MBBS1, Jennifer Hadam-Veverka, MD1. P1114 - Ustekinumab Is Superior to Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF Naïve and Anti-TNF Exposed Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 2University of Nebraska, Hartford, CT; 3Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 4Alexandria University, Alexandria, Al Iskandariyah, Egypt; 5Sohag University, Faculty of Medicine, Sohag, Suhaj, Egypt; 6West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Ustekinumab and vedolizumab are commonly used in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. However, direct comparative studies evaluating their long-term efficacy, particularly in anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed populations, remain limited.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study utilizing the TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network database was conducted to compare the real-world efficacy of Ustekinumab and vedolizumab in adult CD patients. Patients were stratified into anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed cohorts, and 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was employed. The primary outcome was the need for corticosteroid use at 12 and 24 months. Secondary outcomes included all-cause hospitalization rates, and emergency department (ED) visits.
Results: In the anti-TNF-naïve cohort, Ustekinumab was associated with significantly lower corticosteroid use at 12 months (29.3% vs. 38.0%, p< 0.01) with HR of 0.69 (95% CI: 0.63–0.75) and 24 months (39.4% vs. 45.6%, p< 0.01) with HR of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.71–0.83). Additionally, Ustekinumab-treated patients had fewer all-cause ED visits. No significant differences were observed in all-cause hospitalization rates.
In the anti-TNF-exposed cohort, Ustekinumab was similarly associated with reduced corticosteroid use at 12 months (39.3% vs. 46.7%, p< 0.01) (HR: 0.76, 95% CI: 0.68–0.87) and 24 months (51.5% vs. 55.0%, p< 0.01) (HR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93). Ustekinumab-treated patients also demonstrated lower ED visit rates and reduced hospitalizations.
Discussion: Ustekinumab demonstrated superior corticosteroid-sparing effects and fewer healthcare utilization events compared to vedolizumab in both anti-TNF-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed CD patients. These findings suggest that ustekinumab may offer improved long-term disease control and reduced healthcare burden.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of TNF-naïve patients in ustekinumab cohort and vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching

Figure: Table 2. Baseline characteristics of patients after TNF in the ustekinumab cohort and the vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching
Disclosures:
Khaled Elfert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Elkhattib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eslam Rabea indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Elsharkawy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed A. Aldemerdash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Obeng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kanwarpreet Tandon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer Hadam-Veverka: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Khaled Elfert, MD1, Ismail Elkhattib, MBBCh2, Mohamed Eldesouki, MD3, Eslam Rabea, MBBCh4, Muhammad Elsharkawy, MD4, Mohamed A. Aldemerdash, 5, George Obeng, MD6, Kanwarpreet Tandon, MBBS1, Jennifer Hadam-Veverka, MD1. P1114 - Ustekinumab Is Superior to Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF Naïve and Anti-TNF Exposed Patients With Crohn’s Disease: A Matched Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

