Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1032 - Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Indications, Outcomes, and Safety
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohammed Al-Aquily, MD
Norwalk Hospital/Yale University
Norwalk, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Husam Abu Suilik, MD1, Sara Irshaidat, MD2, Mohammed Al-Aquily, MD3, Ekram Hasanin, MBBS4, Hashem Abu Serhan, MD2, Allaa Khirfan, MD5
1The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 2Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 3Norwalk Hospital/Yale University, Norwalk, CT; 4Tripoli University Faculty of Medicine, Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya; 5University of Jordan School of Medicine, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan
Introduction: The efficacy and safety of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for children and adolescents with refractory inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remain unclear. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate clinical outcomes, remission rates, and adverse events associated with HSCT.
Methods: Five different databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, SCOPUS, Cochrane, and Embase, were searched up to May 24, 2025. Outcomes of interest included clinical remission, endoscopic remission, steroid-free remission, survival, relapse, acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), chronic GVHD, graft failure, mortality, and other adverse events. Pooled proportions and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using random effects models in R (version 4.4.3).
Results: A total of six studies were included with 144 participants. Using random-effects models, (HSCT) resulted in a clinical remission rate of 93% (95% CI: 85% to 97%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.64) and endoscopic remission was achieved in 80% of patients (95% CI: 48% to 95%; I²=13%, p for heterogeneity=0.29). Steroid-free remission occurred in 92% (95% CI: 81% to 97%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.85), as outlined in Figure 1. Overall survival was 80% (95% CI: 68% to 88%; I²=43%, p for heterogeneity=0.12). Relapse occurred in 9% of patients (95% CI: 4% to 21%; I²=39%, p for heterogeneity=0.14). The rate of acute GVHD was 42% (95% CI: 22% to 65%; I²=77%, p for heterogeneity < 0.01) and chronic GVHD was 13% (95% CI: 8% to 21%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.63). Graft failure was observed in 14% (95% CI: 7% to 26%; I²=48%, p for heterogeneity=0.09). Overall mortality rate of 19%, 95% CI 11%-31%, I2=44%, p for heterogeneity=0.11) and other adverse events had a pooled incidence of 38% (95% CI: 25% to 54%; I2=53%, p for heterogeneity=0.08, as shown in Figure 2.
Discussion: Hematopoietic replacement therapy leads to high remission rates and low relapse and complication rates, but mortality remains a concern. Further studies are needed to clarify its overall benefit.
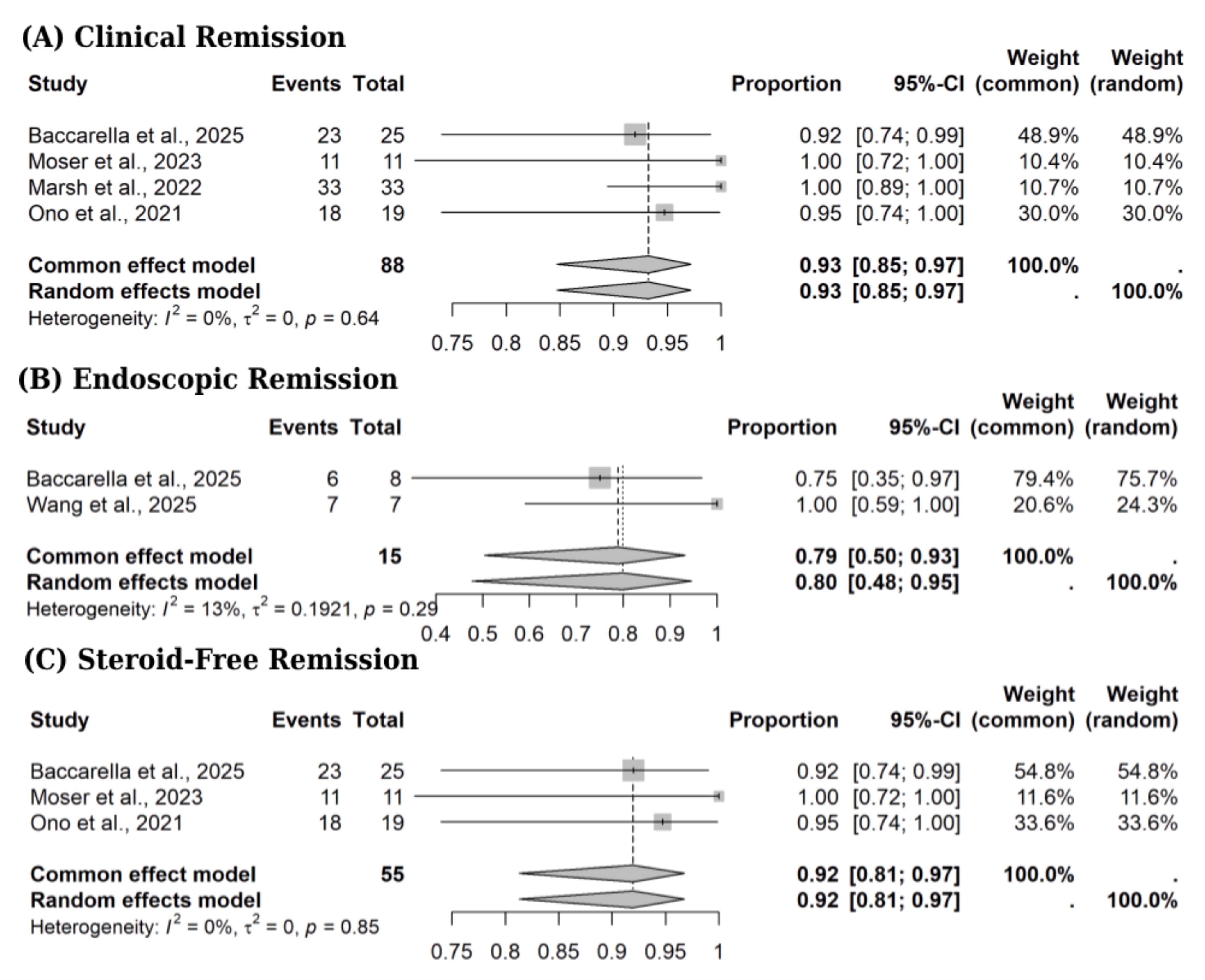
Figure: Figure 1: Forest plots of (A) Clinical remission, (B) Endoscopic remission, and (C) Steroid-free remission. Proportion and 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
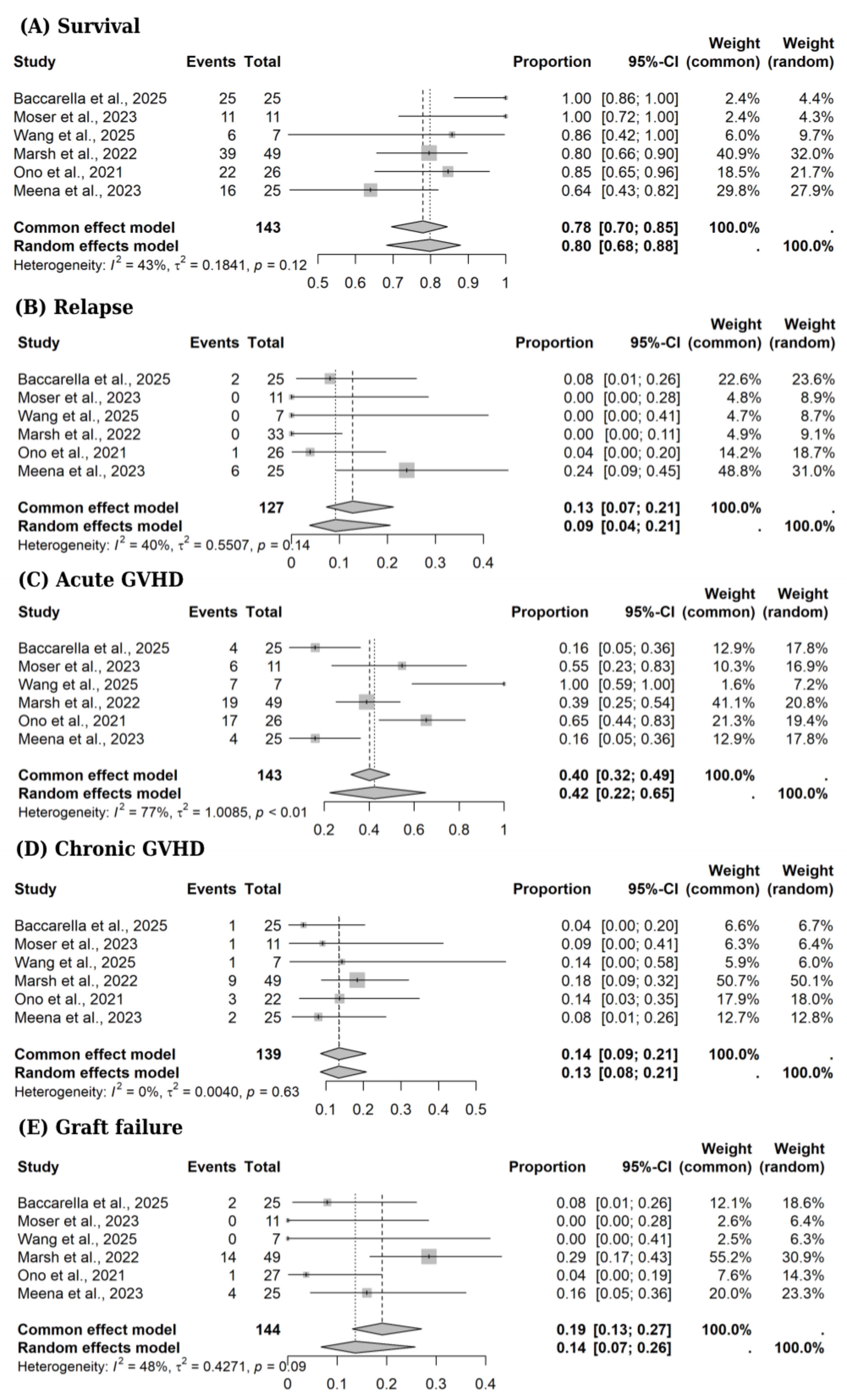
Figure: Figure 2: Forest plots of (A) Survival, (B) Relapse, (C) Acute GVHD, (D) Chronic GVHD, and (E) Graft failure. Proportion and 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Irshaidat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Al-Aquily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ekram Hasanin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hashem Abu Serhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allaa Khirfan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik, MD1, Sara Irshaidat, MD2, Mohammed Al-Aquily, MD3, Ekram Hasanin, MBBS4, Hashem Abu Serhan, MD2, Allaa Khirfan, MD5. P1032 - Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Indications, Outcomes, and Safety, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan; 2Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; 3Norwalk Hospital/Yale University, Norwalk, CT; 4Tripoli University Faculty of Medicine, Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya; 5University of Jordan School of Medicine, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan
Introduction: The efficacy and safety of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for children and adolescents with refractory inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remain unclear. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate clinical outcomes, remission rates, and adverse events associated with HSCT.
Methods: Five different databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, SCOPUS, Cochrane, and Embase, were searched up to May 24, 2025. Outcomes of interest included clinical remission, endoscopic remission, steroid-free remission, survival, relapse, acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), chronic GVHD, graft failure, mortality, and other adverse events. Pooled proportions and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using random effects models in R (version 4.4.3).
Results: A total of six studies were included with 144 participants. Using random-effects models, (HSCT) resulted in a clinical remission rate of 93% (95% CI: 85% to 97%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.64) and endoscopic remission was achieved in 80% of patients (95% CI: 48% to 95%; I²=13%, p for heterogeneity=0.29). Steroid-free remission occurred in 92% (95% CI: 81% to 97%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.85), as outlined in Figure 1. Overall survival was 80% (95% CI: 68% to 88%; I²=43%, p for heterogeneity=0.12). Relapse occurred in 9% of patients (95% CI: 4% to 21%; I²=39%, p for heterogeneity=0.14). The rate of acute GVHD was 42% (95% CI: 22% to 65%; I²=77%, p for heterogeneity < 0.01) and chronic GVHD was 13% (95% CI: 8% to 21%; I²=0%, p for heterogeneity=0.63). Graft failure was observed in 14% (95% CI: 7% to 26%; I²=48%, p for heterogeneity=0.09). Overall mortality rate of 19%, 95% CI 11%-31%, I2=44%, p for heterogeneity=0.11) and other adverse events had a pooled incidence of 38% (95% CI: 25% to 54%; I2=53%, p for heterogeneity=0.08, as shown in Figure 2.
Discussion: Hematopoietic replacement therapy leads to high remission rates and low relapse and complication rates, but mortality remains a concern. Further studies are needed to clarify its overall benefit.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plots of (A) Clinical remission, (B) Endoscopic remission, and (C) Steroid-free remission. Proportion and 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.

Figure: Figure 2: Forest plots of (A) Survival, (B) Relapse, (C) Acute GVHD, (D) Chronic GVHD, and (E) Graft failure. Proportion and 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Husam Abu Suilik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Irshaidat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Al-Aquily indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ekram Hasanin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hashem Abu Serhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allaa Khirfan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Husam Abu Suilik, MD1, Sara Irshaidat, MD2, Mohammed Al-Aquily, MD3, Ekram Hasanin, MBBS4, Hashem Abu Serhan, MD2, Allaa Khirfan, MD5. P1032 - Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Indications, Outcomes, and Safety, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
