Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1024 - Diagnosis and Management of Immune Effector Cell (CAR-T)-Associated Enterocolitis in Multiple Myeloma Patients
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- NC
Navreet Chowla, MD, FACG (she/her/hers)
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Kenneth Lim, MBBS, Yi Lin, MD, Navreet Chowla, MD, FACG
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Cilta-cel is a highly effective chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy that targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) app for refractory Multiple Myeloma patients. We examined the clinical course and outcomes of CAR-T related enterocolitis.
Methods: Electronic medical records of multiple myeloma patients receiving CAR-T therapy and developing enterocolitis between 02/2022 and 12/2024 were reviewed.
Results: There were 235 patients who underwent CAR-T therapy for Multiple Myeloma and nine (3.8%) developed ≥ Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Effects (CTCAE) Grade 3 diarrhea. The median time for onset was 3.5 months (range 1.2-5.6). The median age was 65 years (range,31-86) and 53% were male. Patients had received a median of 4 prior lines of therapy prior to CAR-T therapy. The diarrhea was severe and required hospitalization in all patients and 6/9 patients had significant weight loss. Lab abnormalities included elevated CRP and Ferritin. Infectious work up showed Norovirus infection in 3 patients, Sapovirus in 1 and C difficile in 2 patients, however diarrhea persisted even after antimicrobial treatment. Abdominal imaging showed enterocolitis in one patient and pneumatosis in two patients. The most prominent endoscopic result was duodenal nodularity and villous blunting followed by non-specific erythema in the colon. Biopsy results showed a universal depletion of plasma cells, as well as increased lymphocyte infiltrate. Other findings include the presence of apoptosis and crypt dropout. Immunohistochemistry showed a predominantly CD4 population with one showing a CD4-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Anti-microbial therapy was used in 3 patients, and parenteral nutrition in 5 patients. Management included IVIG (100%), Steroids (100%), bile acid sequestrants and Octreotide. Five of the nine patients received Biologics (Infliximab:3, Vedolizumab:2), however salvage therapy with Cyclophosphamide, Cyclosporine and Upadacitinib was used in one patient each. Three patients have died related to Myeloma or Parkinson related complications.
Discussion: Enterocolitis is an uncommon and late consequence of CAR-T therapy and carries high morbidity and mortality. The small bowel is the most commonly and severely affected area. Duodenal biopsies can resemble autoimmune enteropathy and GVHD. Patients often require nutritional support, steroids, biologics or other immunosuppressants. These cases should be comanaged by Oncologists and Gastroenterologists.
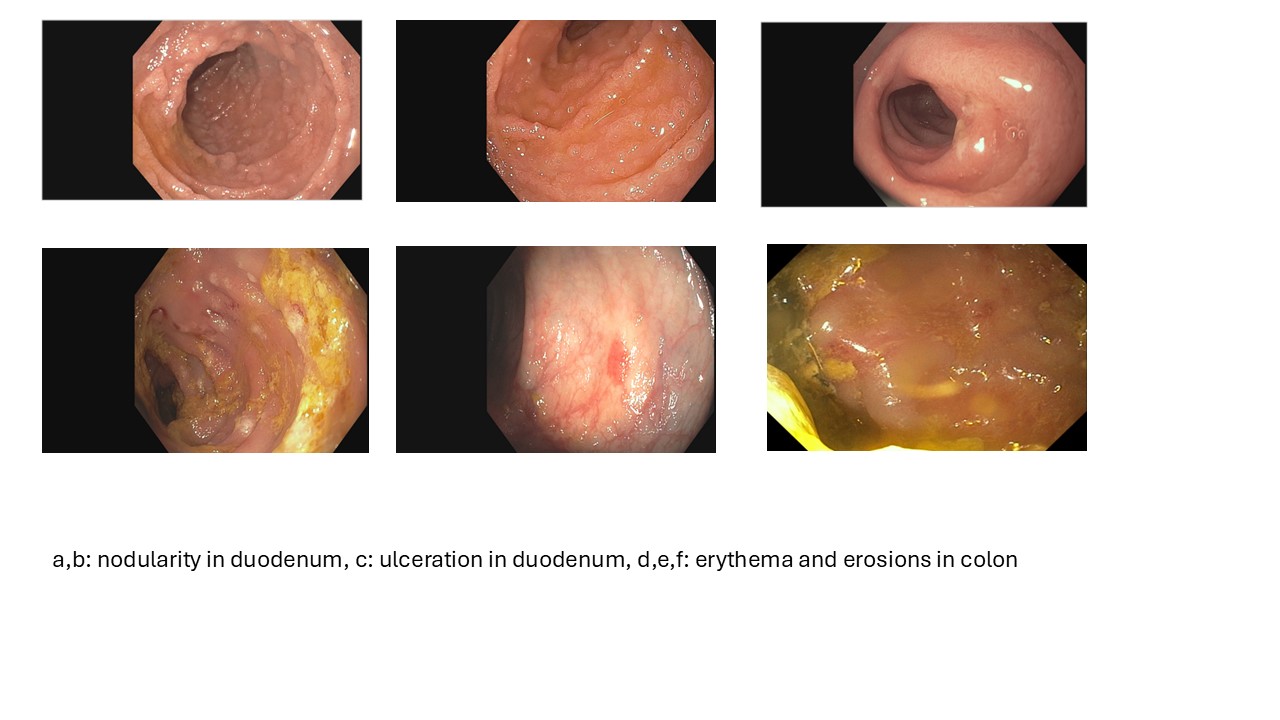
Figure: Clinical features of IEC enterocolitis at index hospitalization.
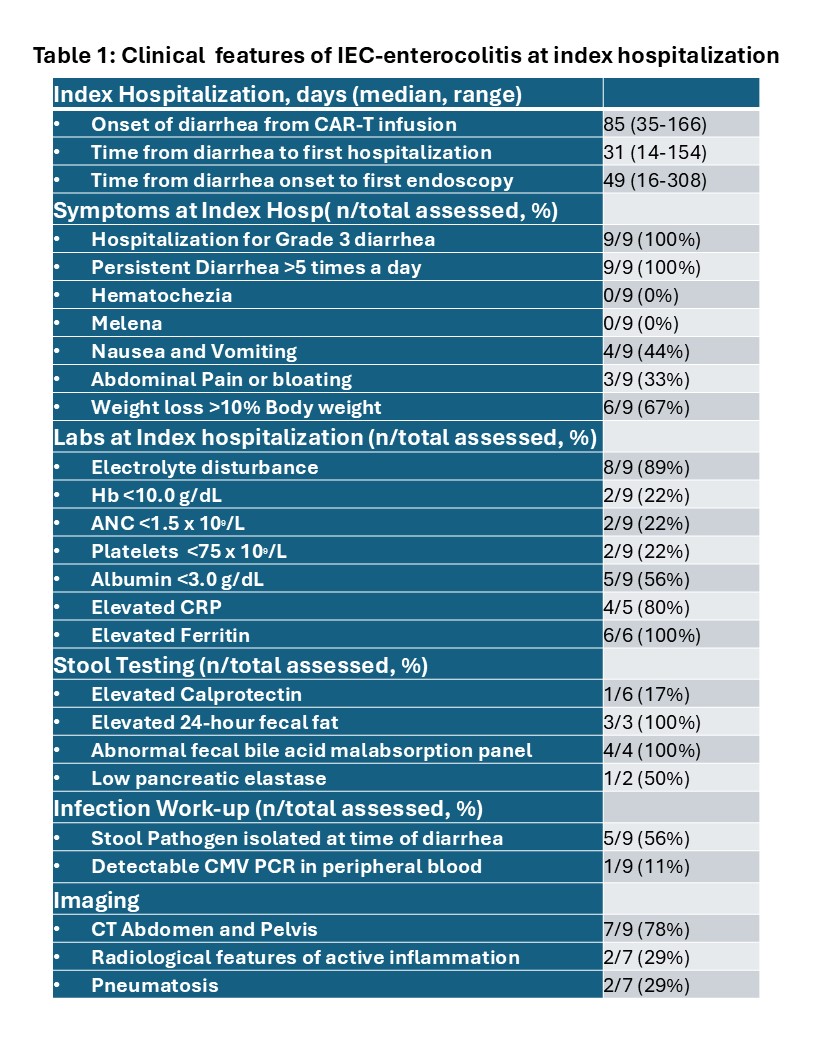
Figure: Endoscopic features of IEC enterocolitis.
Disclosures:
Kenneth Lim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yi Lin: BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Legend – Advisory Committee/Board Member. NexTTherapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Regeneron – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Navreet Chowla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Lim, MBBS, Yi Lin, MD, Navreet Chowla, MD, FACG. P1024 - Diagnosis and Management of Immune Effector Cell (CAR-T)-Associated Enterocolitis in Multiple Myeloma Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Cilta-cel is a highly effective chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy that targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) app for refractory Multiple Myeloma patients. We examined the clinical course and outcomes of CAR-T related enterocolitis.
Methods: Electronic medical records of multiple myeloma patients receiving CAR-T therapy and developing enterocolitis between 02/2022 and 12/2024 were reviewed.
Results: There were 235 patients who underwent CAR-T therapy for Multiple Myeloma and nine (3.8%) developed ≥ Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Effects (CTCAE) Grade 3 diarrhea. The median time for onset was 3.5 months (range 1.2-5.6). The median age was 65 years (range,31-86) and 53% were male. Patients had received a median of 4 prior lines of therapy prior to CAR-T therapy. The diarrhea was severe and required hospitalization in all patients and 6/9 patients had significant weight loss. Lab abnormalities included elevated CRP and Ferritin. Infectious work up showed Norovirus infection in 3 patients, Sapovirus in 1 and C difficile in 2 patients, however diarrhea persisted even after antimicrobial treatment. Abdominal imaging showed enterocolitis in one patient and pneumatosis in two patients. The most prominent endoscopic result was duodenal nodularity and villous blunting followed by non-specific erythema in the colon. Biopsy results showed a universal depletion of plasma cells, as well as increased lymphocyte infiltrate. Other findings include the presence of apoptosis and crypt dropout. Immunohistochemistry showed a predominantly CD4 population with one showing a CD4-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Anti-microbial therapy was used in 3 patients, and parenteral nutrition in 5 patients. Management included IVIG (100%), Steroids (100%), bile acid sequestrants and Octreotide. Five of the nine patients received Biologics (Infliximab:3, Vedolizumab:2), however salvage therapy with Cyclophosphamide, Cyclosporine and Upadacitinib was used in one patient each. Three patients have died related to Myeloma or Parkinson related complications.
Discussion: Enterocolitis is an uncommon and late consequence of CAR-T therapy and carries high morbidity and mortality. The small bowel is the most commonly and severely affected area. Duodenal biopsies can resemble autoimmune enteropathy and GVHD. Patients often require nutritional support, steroids, biologics or other immunosuppressants. These cases should be comanaged by Oncologists and Gastroenterologists.

Figure: Clinical features of IEC enterocolitis at index hospitalization.

Figure: Endoscopic features of IEC enterocolitis.
Disclosures:
Kenneth Lim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yi Lin: BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Legend – Advisory Committee/Board Member. NexTTherapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Regeneron – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Navreet Chowla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Lim, MBBS, Yi Lin, MD, Navreet Chowla, MD, FACG. P1024 - Diagnosis and Management of Immune Effector Cell (CAR-T)-Associated Enterocolitis in Multiple Myeloma Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

