Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0817 - Respiratory Virus, Gut Reaction: The Emerging Link Between RSV and IBS
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Dilman Natt, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, New York
Presenting Author(s)
Dilman Natt, MD, Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD, Venkata Panchagnula, MD, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD, Amilcar Guaschino, MD, Wing Hang Lau, DO, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD, Amina Zafar, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is commonly associated with respiratory illness, but recent studies suggest potential links to other chronic conditions. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder, may correlate with viral infections, hinting at a multifaceted pathogenesis. This study leverages the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) with data from 2,858,576 adults between 2019 and 2024 to investigate the relationship between RSV and IBS. Employing logistic regression, random forest, and gradient boosting, we aim to clarify the potential influence of RSV on IBS prevalence and assess the impact of demographic factors
Methods: This study analyzed data from the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP), involving 2,858,576 adults from 2019 to 2024 to explore the relationship between Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). We utilized logistic regression, random forest, and gradient boosting to evaluate predictive capabilities. Logistic regression assessed predictors like SEX and RACE, while machine learning models explored their predictive accuracy through AUC values from ROC curves. A binomial test determined the significance of IBS occurrence among RSV patients.
Results: From 2019 to 2024, data on 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions was gathered from the HCUP, focusing on patients diagnosed with IBS and RSV. Out of 100,124 patients with IBS, 43,510 tested positive for RSV. The incidence rate of IBS among RSV patients stood at 50.84% with a p-value of 0.00016. Logistic regression analysis indicated a statistically significant association between RSV- positive female sex (p = 0.043) and RSV - positive white race (p = 0.0415) with IBS. Both random forest and gradient boosting models demonstrated predictive capabilities with AUC scores of 0.69.
Discussion: The findings reveal a significant incidence of IBS among patients with RSV, suggesting a potential linkage between respiratory viral infections and gastrointestinal disorders. The statistically significant associations of IBS with the female sex and white race highlight demographic susceptibilities that warrant further investigation. Advanced predictive models, which demonstrated moderate accuracy (AUC = 0.69), underscore the complexity of predicting IBS in RSV-infected patients. This study invites further research to confirm these associations and explore the mechanisms behind the influence of RSV on IBS, potentially leading to targeted therapies and improved patient outcomes.
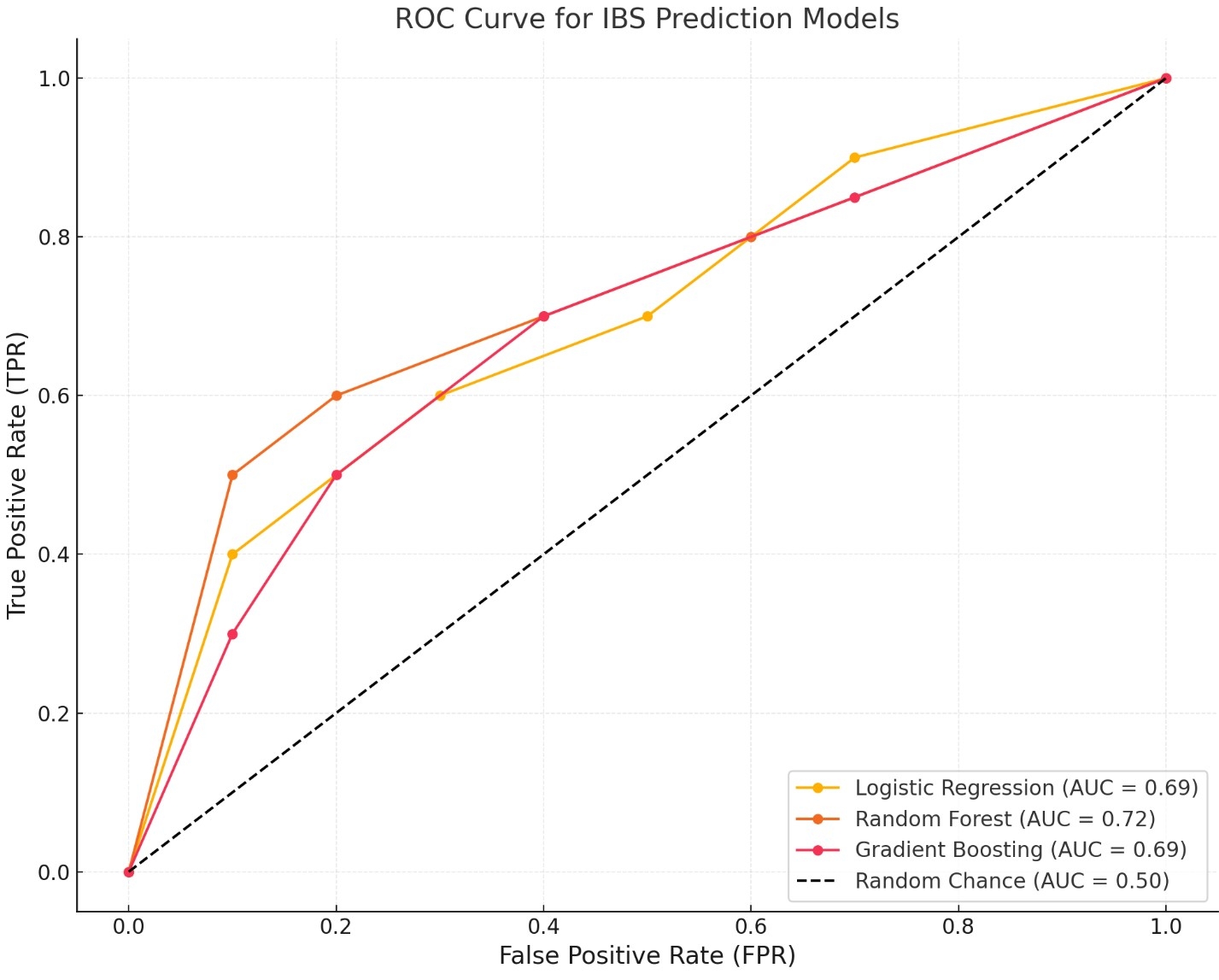
Figure: RSV–IBS Connection: A Nationwide Database Analysis
Disclosures:
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajmohan Rammohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhuja Giridharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Panchagnula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Harsha Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amilcar Guaschino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wing Hang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amina Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt, MD, Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD, Venkata Panchagnula, MD, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD, Amilcar Guaschino, MD, Wing Hang Lau, DO, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD, Amina Zafar, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD. P0817 - Respiratory Virus, Gut Reaction: The Emerging Link Between RSV and IBS, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is commonly associated with respiratory illness, but recent studies suggest potential links to other chronic conditions. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder, may correlate with viral infections, hinting at a multifaceted pathogenesis. This study leverages the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) with data from 2,858,576 adults between 2019 and 2024 to investigate the relationship between RSV and IBS. Employing logistic regression, random forest, and gradient boosting, we aim to clarify the potential influence of RSV on IBS prevalence and assess the impact of demographic factors
Methods: This study analyzed data from the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP), involving 2,858,576 adults from 2019 to 2024 to explore the relationship between Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). We utilized logistic regression, random forest, and gradient boosting to evaluate predictive capabilities. Logistic regression assessed predictors like SEX and RACE, while machine learning models explored their predictive accuracy through AUC values from ROC curves. A binomial test determined the significance of IBS occurrence among RSV patients.
Results: From 2019 to 2024, data on 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions was gathered from the HCUP, focusing on patients diagnosed with IBS and RSV. Out of 100,124 patients with IBS, 43,510 tested positive for RSV. The incidence rate of IBS among RSV patients stood at 50.84% with a p-value of 0.00016. Logistic regression analysis indicated a statistically significant association between RSV- positive female sex (p = 0.043) and RSV - positive white race (p = 0.0415) with IBS. Both random forest and gradient boosting models demonstrated predictive capabilities with AUC scores of 0.69.
Discussion: The findings reveal a significant incidence of IBS among patients with RSV, suggesting a potential linkage between respiratory viral infections and gastrointestinal disorders. The statistically significant associations of IBS with the female sex and white race highlight demographic susceptibilities that warrant further investigation. Advanced predictive models, which demonstrated moderate accuracy (AUC = 0.69), underscore the complexity of predicting IBS in RSV-infected patients. This study invites further research to confirm these associations and explore the mechanisms behind the influence of RSV on IBS, potentially leading to targeted therapies and improved patient outcomes.

Figure: RSV–IBS Connection: A Nationwide Database Analysis
Disclosures:
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajmohan Rammohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhuja Giridharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Panchagnula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Harsha Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amilcar Guaschino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wing Hang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amina Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt, MD, Rajmohan Rammohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Achal Patel, MD, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD, Venkata Panchagnula, MD, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD, Amilcar Guaschino, MD, Wing Hang Lau, DO, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD, Amina Zafar, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD. P0817 - Respiratory Virus, Gut Reaction: The Emerging Link Between RSV and IBS, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
