Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0666 - Management Trends in Hospitalized Patients With Achalasia in the United States
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ritik Goyal, MBBS
Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Anand Shah, MBBS1, Rohan Karkra, MBBS1, Aagamjit Singh, MBBS2, Sameer Rao, MBBS1, Komal Arora, MBBS3, Amanda A. Rupert, MD1
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, MI; 3St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder characterized by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and dysfunctional peristalsis. The main treatment options are peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), Laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy (LHM), and pneumatic dilation (PD). Over the past decade, POEM has gained global acceptance, with its use increasing for achalasia. This study examines achalasia management trends from 2011 to 2022.
Methods: We performed a descriptive trend analysis using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2011 to 2022. Achalasia cases were identified using ICD-9 code 530.0 and ICD-10 code K22.0. Procedure codes identified LHM, POEM, PD, and esophagectomy. Percentages of patients undergoing each procedure were calculated for 2011–2022, while POEM was assessed from 2016 to 2022, as codes were unavailable before 2016. Annual percentage change (APC) and average APC (AAPC) were generated using Joinpoint Regression Software (v.5.0.2, NCI) via weighted Bayesian Information Criteria “BIC.”
Results: We identified 12,740 achalasia cases, representing 63,420 patients when weighted. The mean age was 60.4 years, with 46.7% males. The use of LHM decreased from 45.3% in 2011-12 to 29.3% in 2021-22 (AAPC: -4.66, 95% CI: -6 to -3.22, p< 0.001). Esophagectomy declined from 1.5% in 2011-12 to 0.5% in 2021-22 (AAPC: -13.61, 95% CI: -20.13 to -6.75, p< 0.001). POEM use increased from 5.8% in 2016 to 10.3% in 2022 (AAPC: 7.76, 95% CI: 0.02 to 16.41, p=0.049). PD remained stable from 2011-2014 (p=0.116), declined from 2014-2017 (APC: -48.45, 95% CI: -37.43 to -13.42, p=0.005), and increased from 2017-2022 (APC: 13.18, 95% CI: 3.02 to 44.39, p=0.014).
Discussion: This study highlights significant shifts in achalasia management over the past decade, with a trend toward less invasive options. POEM’s rise from 2016 to 2022 reflects its growing acceptance as an effective, minimally invasive therapy, while LHM’s decline indicates a preference for newer methods. The decrease in esophagectomy points to a move toward organ preservation, and fluctuating PD trends indicate its continued but limited role. Despite advancements, there is a need for wider dissemination and standardized adoption of evidence-based strategies to optimize outcomes. These trends reflect evolving clinical practices driven by advancements in therapy.
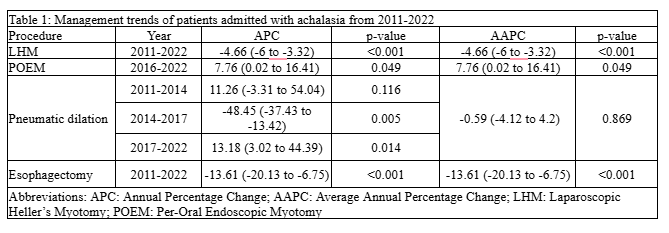
Figure: Management trends of patients admitted with achalasia from 2011-2022

Figure: Figure displaying joinpoint regression analyses of annual trends in the use of different Management Strategies for patients with achalasia from 2011 to 2022.
Disclosures:
Ritik M. Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anand Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Karkra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aagamjit Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Komal Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanda Rupert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Anand Shah, MBBS1, Rohan Karkra, MBBS1, Aagamjit Singh, MBBS2, Sameer Rao, MBBS1, Komal Arora, MBBS3, Amanda A. Rupert, MD1. P0666 - Management Trends in Hospitalized Patients With Achalasia in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2William Beaumont Hospital, Troy, MI; 3St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder characterized by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and dysfunctional peristalsis. The main treatment options are peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), Laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy (LHM), and pneumatic dilation (PD). Over the past decade, POEM has gained global acceptance, with its use increasing for achalasia. This study examines achalasia management trends from 2011 to 2022.
Methods: We performed a descriptive trend analysis using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2011 to 2022. Achalasia cases were identified using ICD-9 code 530.0 and ICD-10 code K22.0. Procedure codes identified LHM, POEM, PD, and esophagectomy. Percentages of patients undergoing each procedure were calculated for 2011–2022, while POEM was assessed from 2016 to 2022, as codes were unavailable before 2016. Annual percentage change (APC) and average APC (AAPC) were generated using Joinpoint Regression Software (v.5.0.2, NCI) via weighted Bayesian Information Criteria “BIC.”
Results: We identified 12,740 achalasia cases, representing 63,420 patients when weighted. The mean age was 60.4 years, with 46.7% males. The use of LHM decreased from 45.3% in 2011-12 to 29.3% in 2021-22 (AAPC: -4.66, 95% CI: -6 to -3.22, p< 0.001). Esophagectomy declined from 1.5% in 2011-12 to 0.5% in 2021-22 (AAPC: -13.61, 95% CI: -20.13 to -6.75, p< 0.001). POEM use increased from 5.8% in 2016 to 10.3% in 2022 (AAPC: 7.76, 95% CI: 0.02 to 16.41, p=0.049). PD remained stable from 2011-2014 (p=0.116), declined from 2014-2017 (APC: -48.45, 95% CI: -37.43 to -13.42, p=0.005), and increased from 2017-2022 (APC: 13.18, 95% CI: 3.02 to 44.39, p=0.014).
Discussion: This study highlights significant shifts in achalasia management over the past decade, with a trend toward less invasive options. POEM’s rise from 2016 to 2022 reflects its growing acceptance as an effective, minimally invasive therapy, while LHM’s decline indicates a preference for newer methods. The decrease in esophagectomy points to a move toward organ preservation, and fluctuating PD trends indicate its continued but limited role. Despite advancements, there is a need for wider dissemination and standardized adoption of evidence-based strategies to optimize outcomes. These trends reflect evolving clinical practices driven by advancements in therapy.

Figure: Management trends of patients admitted with achalasia from 2011-2022

Figure: Figure displaying joinpoint regression analyses of annual trends in the use of different Management Strategies for patients with achalasia from 2011 to 2022.
Disclosures:
Ritik M. Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anand Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Karkra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aagamjit Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Rao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Komal Arora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanda Rupert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Anand Shah, MBBS1, Rohan Karkra, MBBS1, Aagamjit Singh, MBBS2, Sameer Rao, MBBS1, Komal Arora, MBBS3, Amanda A. Rupert, MD1. P0666 - Management Trends in Hospitalized Patients With Achalasia in the United States, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
