Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0626 - Detecting What Matters: A Meta-Analysis of a Minimally Invasive Screening Device for Long-Segment Barrett’s Esophagus in Surveillance Populations
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Eduardo A. Canto, BS
Creighton University Medical Center
Omaha, NE
Presenting Author(s)
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6
1Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 2Imperial College London, London, England, United Kingdom; 3University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 5CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 6Brown Medicine/Brown Physicians, Inc., Providence, RI
Introduction: Current guidelines recommend endoscopic surveillance every 3-to-5 years for patients diagnosed with Barrett’s Esophagus (BE) due to the risk of progression to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). However, long (≥3cm) segment BE (LSBE) carries a threefold higher risk of progression compared to short (< 3cm) segment BE. In this study, we assessed the screening performance of Cytosponge with Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3) for detecting BE and LSBE in individuals undergoing surveillance.
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, our study protocol was pre-registered in PROSPERO (CRD420250652091). Eligibility criteria included adults who were undergoing surveillance for BE or had a history of BE diagnosed by endoscopic assessment with biopsies. An extensive literature review of databases including Embase, PubMed and Cochrane Central was performed from January 2009, through March 29, 2025. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data using the COVIDENCE tool, then assessed risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 tool. Sensitivity and specificity were estimated in SAS v 9.4 using bivariate mixed models, which were used to estimate likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and predictive values, whereas forest plots were created in Stata v. 19.5.
Results: We included 9 studies involving 6,697 participants with history of BE, of which 5 studies (n = 6,298 participants) reported results stratified by BE length. The pooled screening performance of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting any BE was as follows: sensitivity 0.75 (95% CI: 0.56-0.87; Figure 1A), specificity 0.83 (95% CI: 0.66-0.92; Figure 1B) and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 14.63 (95% CI: 1.55-27.70). For LSBE, pooled estimates showed higher sensitivity at 0.83 (95% CI: 0.72-0.90; Figure 2A), lower specificity at 0.59 (95% CI: 0.28-0.84; Figure 2B), and lower DOR at 7.10 (95% CI: 2.09-12.10).
Discussion: This is the first meta-analysis to assess the screening performance of Cytosponge with TFF3 for detecting LSBE in patients with BE. Some heterogeneity existed across studies due to differences in timing of endoscopic BE diagnosis, and most studies were conducted in the UK. Nonetheless, the overall findings remain informative for evaluating performance in real-world BE populations. Cytosponge demonstrated reliable specificity for ruling out BE and strong sensitivity for detecting LSBE. Overall, Cytosponge combined with TFF3 is a valuable, minimally invasive tool for risk stratifying patients with BE in clinical practice.
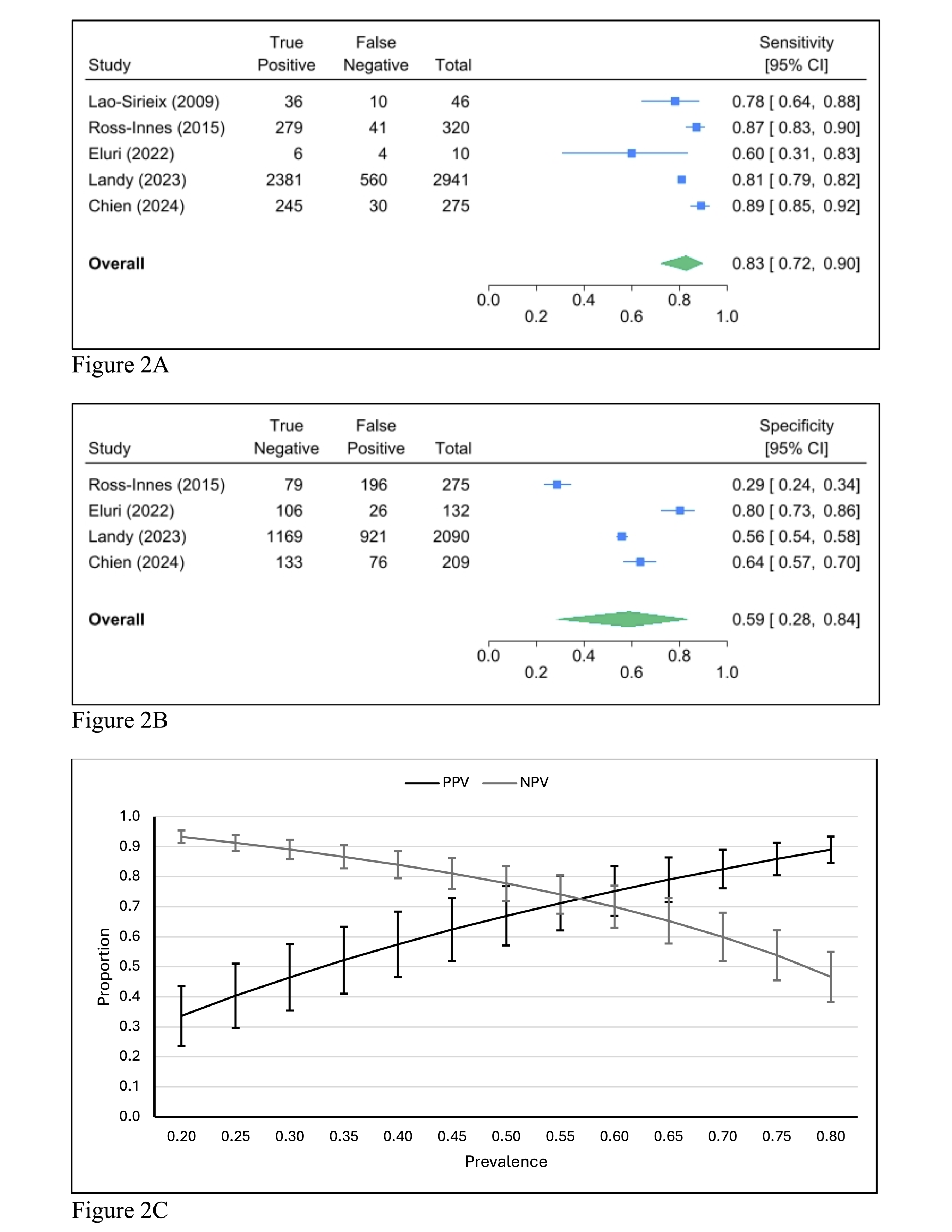
Figure: Figure 1A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with BE.
Figure 1B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with BE.
Figure 1C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting BE charted across a range of BE prevalence in patients with BE.
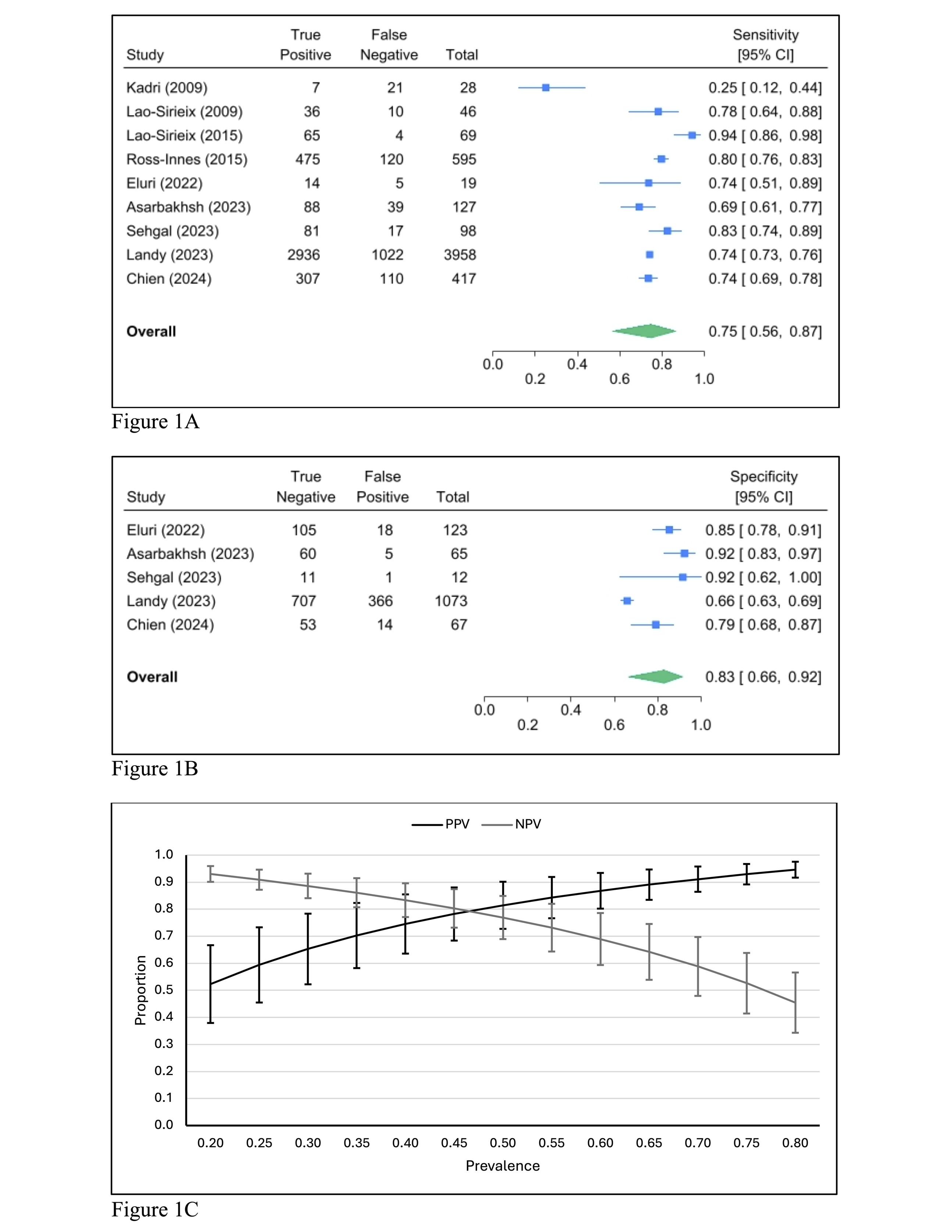
Figure: Figure 2A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting LSBE among patients with BE.
Figure 2B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting LSBE among patients with BE.
Figure 2C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting LSBE charted across a range of LSBE prevalence in patients with BE.
Disclosures:
Eduardo Canto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amar Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Lostetter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Round indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Walters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aun Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Moss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6. P0626 - Detecting What Matters: A Meta-Analysis of a Minimally Invasive Screening Device for Long-Segment Barrett’s Esophagus in Surveillance Populations, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 2Imperial College London, London, England, United Kingdom; 3University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 5CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 6Brown Medicine/Brown Physicians, Inc., Providence, RI
Introduction: Current guidelines recommend endoscopic surveillance every 3-to-5 years for patients diagnosed with Barrett’s Esophagus (BE) due to the risk of progression to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). However, long (≥3cm) segment BE (LSBE) carries a threefold higher risk of progression compared to short (< 3cm) segment BE. In this study, we assessed the screening performance of Cytosponge with Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3) for detecting BE and LSBE in individuals undergoing surveillance.
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, our study protocol was pre-registered in PROSPERO (CRD420250652091). Eligibility criteria included adults who were undergoing surveillance for BE or had a history of BE diagnosed by endoscopic assessment with biopsies. An extensive literature review of databases including Embase, PubMed and Cochrane Central was performed from January 2009, through March 29, 2025. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data using the COVIDENCE tool, then assessed risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 tool. Sensitivity and specificity were estimated in SAS v 9.4 using bivariate mixed models, which were used to estimate likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and predictive values, whereas forest plots were created in Stata v. 19.5.
Results: We included 9 studies involving 6,697 participants with history of BE, of which 5 studies (n = 6,298 participants) reported results stratified by BE length. The pooled screening performance of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting any BE was as follows: sensitivity 0.75 (95% CI: 0.56-0.87; Figure 1A), specificity 0.83 (95% CI: 0.66-0.92; Figure 1B) and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 14.63 (95% CI: 1.55-27.70). For LSBE, pooled estimates showed higher sensitivity at 0.83 (95% CI: 0.72-0.90; Figure 2A), lower specificity at 0.59 (95% CI: 0.28-0.84; Figure 2B), and lower DOR at 7.10 (95% CI: 2.09-12.10).
Discussion: This is the first meta-analysis to assess the screening performance of Cytosponge with TFF3 for detecting LSBE in patients with BE. Some heterogeneity existed across studies due to differences in timing of endoscopic BE diagnosis, and most studies were conducted in the UK. Nonetheless, the overall findings remain informative for evaluating performance in real-world BE populations. Cytosponge demonstrated reliable specificity for ruling out BE and strong sensitivity for detecting LSBE. Overall, Cytosponge combined with TFF3 is a valuable, minimally invasive tool for risk stratifying patients with BE in clinical practice.

Figure: Figure 1A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with BE.
Figure 1B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with BE.
Figure 1C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting BE charted across a range of BE prevalence in patients with BE.

Figure: Figure 2A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting LSBE among patients with BE.
Figure 2B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting LSBE among patients with BE.
Figure 2C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting LSBE charted across a range of LSBE prevalence in patients with BE.
Disclosures:
Eduardo Canto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amar Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Lostetter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Round indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Walters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aun Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Moss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6. P0626 - Detecting What Matters: A Meta-Analysis of a Minimally Invasive Screening Device for Long-Segment Barrett’s Esophagus in Surveillance Populations, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
