Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0625 - Minimally Invasive Cell Sampling Device for Screening of Barrett’s Esophagus in Patients With GERD: A Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Eduardo A. Canto, BS
Creighton University Medical Center
Omaha, NE
Presenting Author(s)
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6
1Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 2Imperial College London, London, England, United Kingdom; 3University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 5CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 6Brown Medicine/Brown Physicians, Inc., Providence, RI
Introduction: International guidelines now recommend non-endoscopic, swallowable sponge devices with biomarkers as valid alternatives to endoscopy for detecting Barrett’s Esophagus (BE) in at-risk patients. Understanding their screening performance is essential to ensure cases are not missed due to suboptimal test accuracy. In this study, we analyzed the screening performance of the Cytosponge with Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3) in patients with symptomatic acid reflux and no prior history of BE. We also assessed test performance in patients with and without additional BE risk factors.
Methods: Eligibility criteria included adults with reflux symptoms with no prior diagnosis of BE. Included studies reported results for both Cytosponge with TFF3 and the gold standard of endoscopic assessment with biopsy for BE diagnosis. Scopus, Embase, PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane Central, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched from January 2009, through March 29, 2025. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data using the COVIDENCE tool; risk of bias was assessed via QUADAS-2. Sensitivity and specificity were estimated in SAS v 9.4 using bivariate mixed models, which were used to estimate likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and predictive values; meta-regression models were estimated for individual risk factors. Forest plots were created in Stata v. 19.5.
Results: We identified 7 studies involving 1,735 participants from the general population in our meta-analysis. The pooled performance for Cytosponge with TFF3 for detecting BE included sensitivity 0.87 (95% CI: 0.81-0.93; Figure 1A), specificity 0.84 (95% CI: 0.82-0.86; Figure 1B), and diagnostic odds ratio of 35.84 (95% CI: 15.57-56.10). There were no statistically significant differences in sensitivity when comparing groups based on age, sex, race, smoking status, BMI, or acid suppressant use; all these risk factors, except for BMI, were associated with increased specificity (Figure 2).
Discussion: Overall, our findings show that Cytosponge is an effective minimally invasive screening tool for patients at risk of BE. All studies were conducted in the UK, which may limit the generalizability of results. Still, sensitivity remained consistent across risk factors, demonstrating reliable detection of BE in patients with GERD. Increased specificity in individuals over the age of 50 and higher than 95% negative predictive value in populations with 20% prevalence for BE (Figure 1C) may help reduce unnecessary endoscopies in these higher-risk groups.
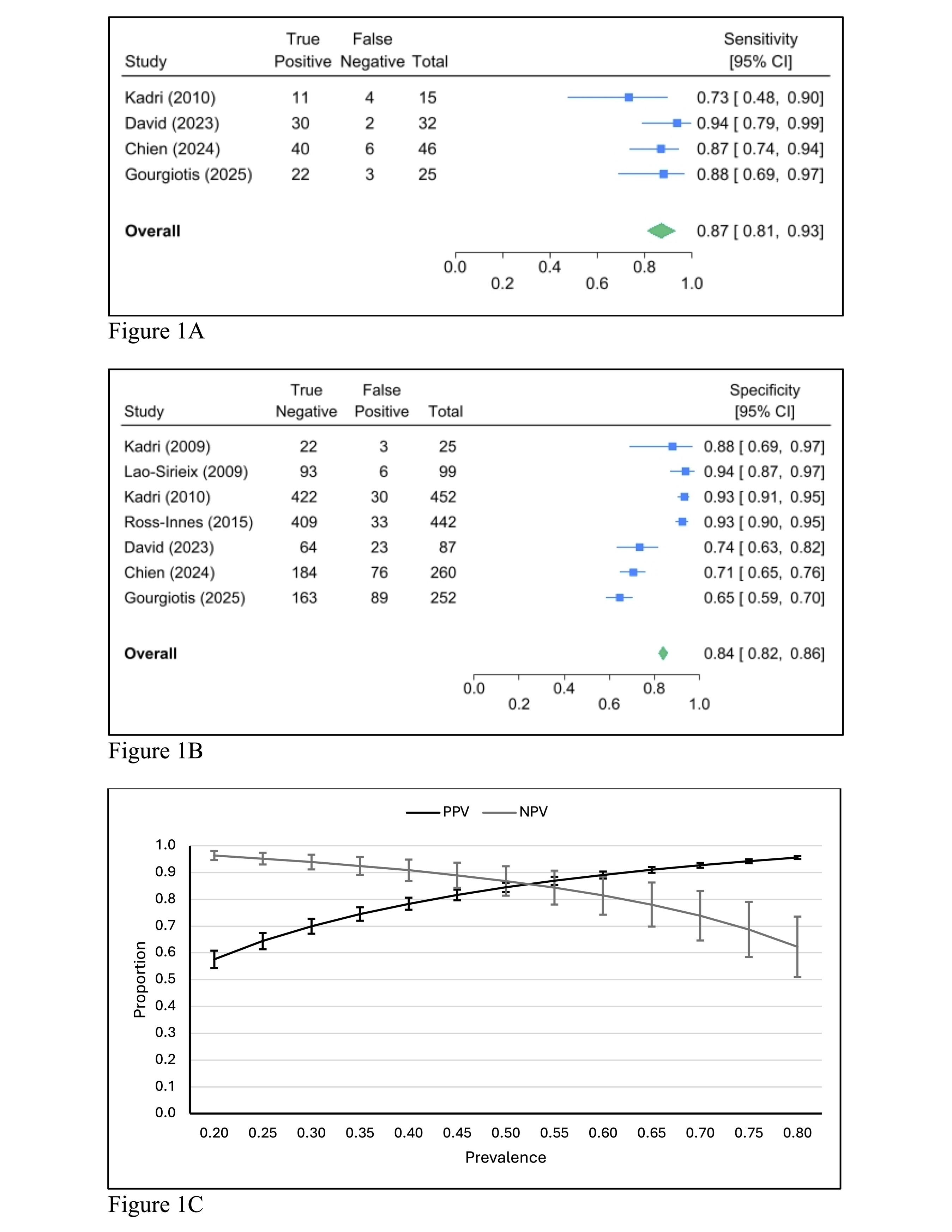
Figure: Figure 1A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with GERD.
Figure 1B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with GERD.
Figure 1C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting BE charted across a range of BE prevalence in patients with GERD.
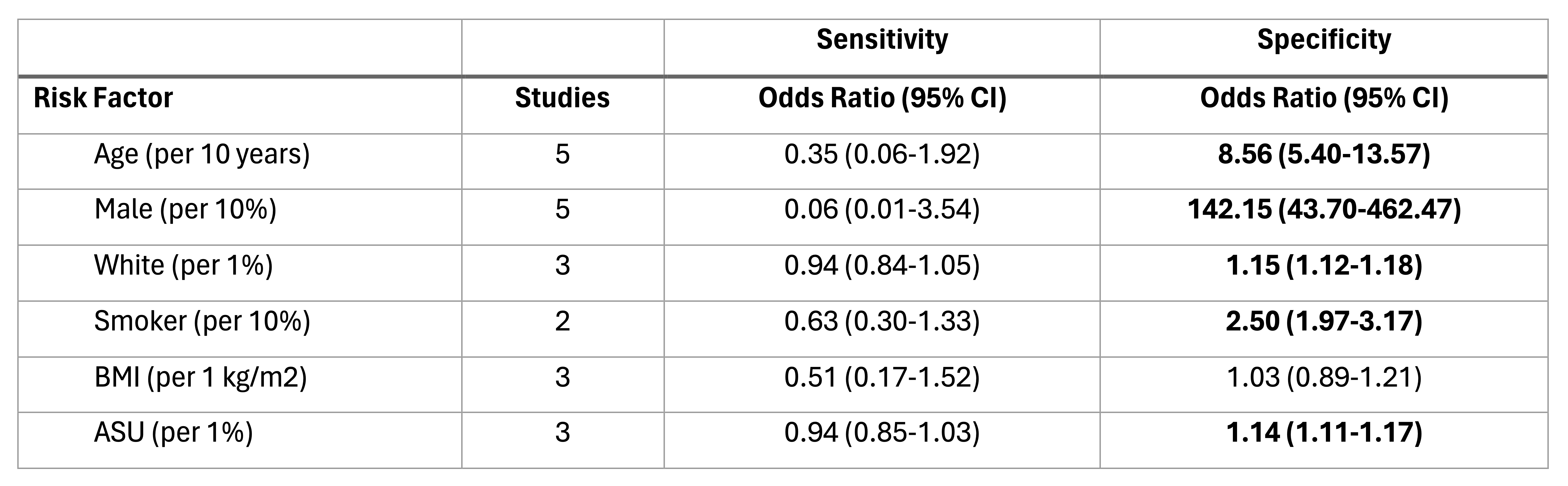
Figure: Sensitivity and specificity odds ratio by individual risk factor. Bolded values are statistically significant. All odds ratios predict truth. For sensitivity, truth is a true positive; for specificity, truth is a true negative. All odds ratios are interpreted per unit-increase in the risk factor (units are provided in parentheses). All risk factors are continuous variables.
Disclosures:
Eduardo Canto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amar Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Lostetter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Round indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Walters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aun Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Moss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6. P0625 - Minimally Invasive Cell Sampling Device for Screening of Barrett’s Esophagus in Patients With GERD: A Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 2Imperial College London, London, England, United Kingdom; 3University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 4King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, England, United Kingdom; 5CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 6Brown Medicine/Brown Physicians, Inc., Providence, RI
Introduction: International guidelines now recommend non-endoscopic, swallowable sponge devices with biomarkers as valid alternatives to endoscopy for detecting Barrett’s Esophagus (BE) in at-risk patients. Understanding their screening performance is essential to ensure cases are not missed due to suboptimal test accuracy. In this study, we analyzed the screening performance of the Cytosponge with Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3) in patients with symptomatic acid reflux and no prior history of BE. We also assessed test performance in patients with and without additional BE risk factors.
Methods: Eligibility criteria included adults with reflux symptoms with no prior diagnosis of BE. Included studies reported results for both Cytosponge with TFF3 and the gold standard of endoscopic assessment with biopsy for BE diagnosis. Scopus, Embase, PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane Central, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched from January 2009, through March 29, 2025. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data using the COVIDENCE tool; risk of bias was assessed via QUADAS-2. Sensitivity and specificity were estimated in SAS v 9.4 using bivariate mixed models, which were used to estimate likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and predictive values; meta-regression models were estimated for individual risk factors. Forest plots were created in Stata v. 19.5.
Results: We identified 7 studies involving 1,735 participants from the general population in our meta-analysis. The pooled performance for Cytosponge with TFF3 for detecting BE included sensitivity 0.87 (95% CI: 0.81-0.93; Figure 1A), specificity 0.84 (95% CI: 0.82-0.86; Figure 1B), and diagnostic odds ratio of 35.84 (95% CI: 15.57-56.10). There were no statistically significant differences in sensitivity when comparing groups based on age, sex, race, smoking status, BMI, or acid suppressant use; all these risk factors, except for BMI, were associated with increased specificity (Figure 2).
Discussion: Overall, our findings show that Cytosponge is an effective minimally invasive screening tool for patients at risk of BE. All studies were conducted in the UK, which may limit the generalizability of results. Still, sensitivity remained consistent across risk factors, demonstrating reliable detection of BE in patients with GERD. Increased specificity in individuals over the age of 50 and higher than 95% negative predictive value in populations with 20% prevalence for BE (Figure 1C) may help reduce unnecessary endoscopies in these higher-risk groups.

Figure: Figure 1A: Forest plot of pooled sensitivity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with GERD.
Figure 1B: Forest plot of pooled specificity for Cytosponge TFF3 in detecting BE among patients with GERD.
Figure 1C: Positive and negative predictive values of Cytosponge TFF3 for detecting BE charted across a range of BE prevalence in patients with GERD.

Figure: Sensitivity and specificity odds ratio by individual risk factor. Bolded values are statistically significant. All odds ratios predict truth. For sensitivity, truth is a true positive; for specificity, truth is a true negative. All odds ratios are interpreted per unit-increase in the risk factor (units are provided in parentheses). All risk factors are continuous variables.
Disclosures:
Eduardo Canto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amar Rai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Lostetter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Round indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Walters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aun Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Moss indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eduardo A. Canto, BS1, Amar Rai, MBBS2, Stephen J. Lostetter, BS3, Thomas Round, MBBS4, Ryan W. Walters, PhD5, Aun R. Shah, MBBS, MRCP5, Steven F. Moss, MD6. P0625 - Minimally Invasive Cell Sampling Device for Screening of Barrett’s Esophagus in Patients With GERD: A Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
