Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0599 - Dupilumab Normalizes Histopathologic Features in Adults and Adolescents With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Margaret H. Collins, MD
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cincinnati, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Margaret H. Collins, MD1, Nirmala P. Gonsalves, MD2, Dhandapani Ashok, MBBS, MRCPCH3, Kevin O. Turner, DO4, Carlos Gonzalez, MS5, Sherif Zaghloul, MD, MSc6, Bram P. Raphael, MD5, James T. Angello, PharmD6, Amr Radwan, MBBCh, MA5
1Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 3Children’s Hospital, London Health Sciences Centre, Western University, London, ON, Canada; 4Pathology Department, University of Minnesota, Medical School, Minneapolis, MN; 5Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 6Sanofi, Morristown, NJ
Introduction: The diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) relies on symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and esophageal eosinophil density >15 eosinophils/high-power field. The EoE Histologic Scoring System (EoEHSS) provides a comprehensive assessment of 8 histopathologic features commonly seen in EoE patients. Here, we assessed the proportion of adolescents and adults with EoE who resolved each individual EoEHSS feature with dupilumab vs placebo in LIBERTY EoE TREET (NCT03633617).
Methods: In Part B, patients aged ≥12 years with EoE were randomized 1:1 to 24 weeks of dupilumab 300 mg weekly (qw) or placebo. Eligible patients entered Part C and received dupilumab 300 mg qw to Week (W) 52. EoEHSS component (esophageal inflammation [EI], eosinophil abscesses [EA], eosinophil surface layering [ESL], surface epithelial alteration [SEA], basal zone hyperplasia [BZH], dilated intercellular spaces [DIS], dyskeratotic epithelial cells [DEC], and lamina propria fibrosis [LPF]) scores were evaluated at baseline, W24, and W52. The proportion of patients who achieved a score of 0 (resolution) for each EoEHSS grade and stage component was assessed.
Results: The proportions of patients with EoEHSS grade/stage component scores of 0 at baseline were similar in the dupilumab vs placebo groups: EA (31% vs 32%/31% vs 32%), ESL (14% vs 23%/14% vs 23%), SEA (35% vs 42%/35% vs 42%), BZH (0% vs 4%/0% vs 4%), LPF (36% vs 37%/36% vs 37%), DEC (73% vs 84%/73% vs 84%); no patients had EI or DIS grade/stage scores of 0. Dupilumab treatment vs placebo led to a greater proportion of patients achieving resolution in both grade/stage EA (97% vs 49%/97% vs 49%), ESL (96% vs 30%/96% vs 30%), SEA (87% vs 50%/87% vs 50%), BZH (78% vs 11%/78% vs 11%), LPF (90% vs 35%/90% vs 35%) (all P< 0.0001), EI (15% vs 0%/88% vs 8%; P< 0.001), and DEC (93% vs 74%/93% vs 74%; P< 0.01) at W24 (Figure). Resolution was not observed in DIS (0% vs 2.8%; P=0.2415). At W52, effects were maintained or improved further with continued dupilumab; improvements in most EoEHSS components were observed in patients who switched from placebo to dupilumab at W24 (Figure).
Discussion: Dupilumab led to resolution of both grade and stage scores in most EoEHSS histopathologic features vs placebo after 24 weeks of treatment; resolution was maintained or achieved in patients receiving continuous dupilumab for 52 weeks. The greatest improvements occurred in eosinophil- (ESL) and epithelial-related (DEC and BZH) features, and LPF.
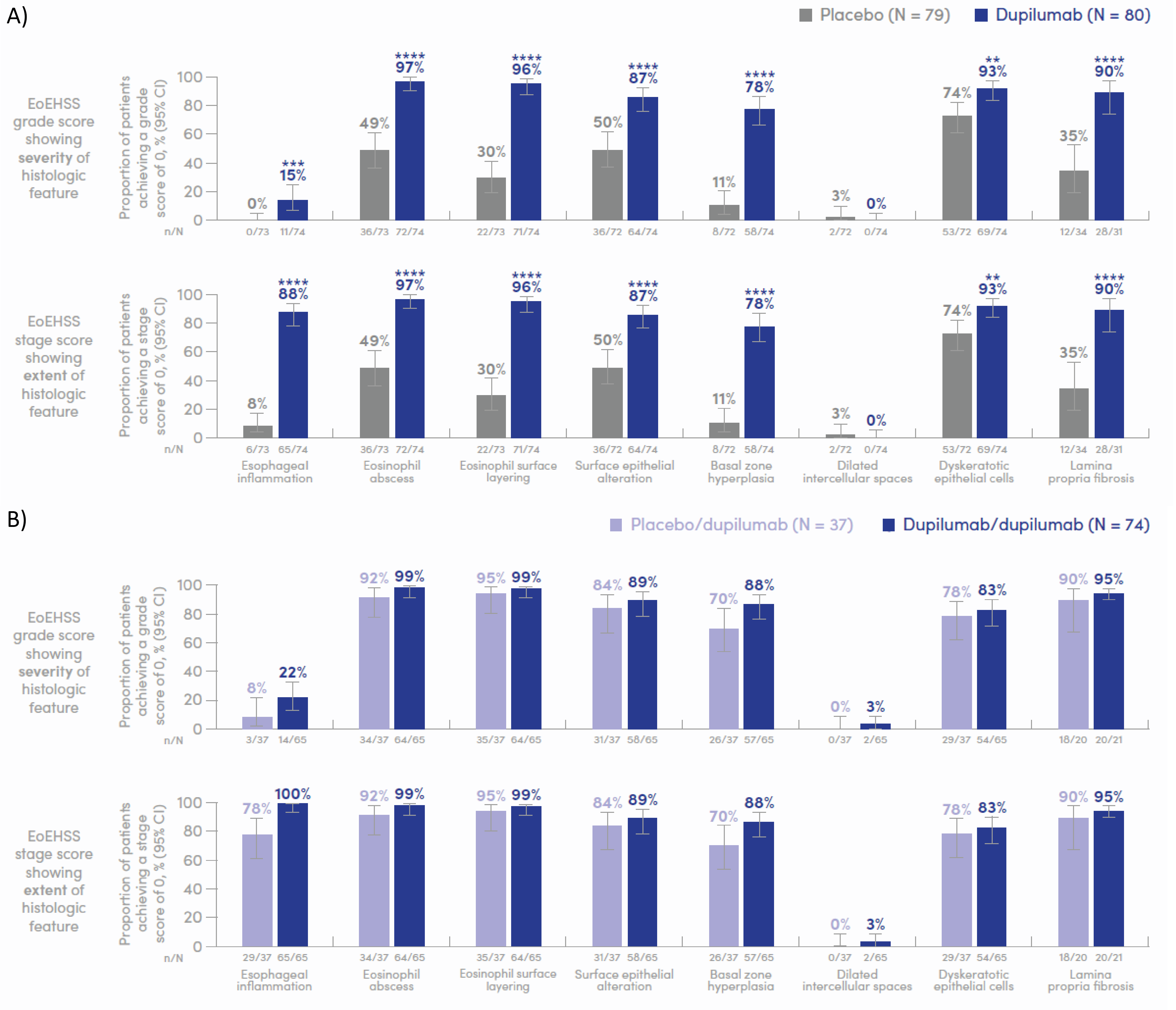
Figure: Figure. Proportion of patients with histologic features that were resolved at A) Week 24 and B) Week 52.
**Nominal P<0.01, ***P <0.001, ****P <0.0001 vs placebo. N = number of patients with non-missing values at each visit. P-values are from Fisher’s exact test if expected counts are <5; otherwise from Chi-square test.
CI, confidence interval; EoEHSS, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histologic Scoring System.
Disclosures:
Margaret Collins: Alimentiv – Consultant. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Calypso Biotech – Consultant. EsoCap Biotech – Consultant. GSK – Consultant. Receptos/Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Shire – Consultant.
Nirmala Gonsalves: Allakos – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Dhandapani Ashok: Alexion Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. LaunchitDTx – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Mirum Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sanofi – Speakers Bureau.
Kevin Turner: Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ellodi – Grant/Research Support. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Carlos Gonzalez: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sherif Zaghloul: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Bram Raphael: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
James Angello: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Amr Radwan: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Margaret H. Collins, MD1, Nirmala P. Gonsalves, MD2, Dhandapani Ashok, MBBS, MRCPCH3, Kevin O. Turner, DO4, Carlos Gonzalez, MS5, Sherif Zaghloul, MD, MSc6, Bram P. Raphael, MD5, James T. Angello, PharmD6, Amr Radwan, MBBCh, MA5. P0599 - Dupilumab Normalizes Histopathologic Features in Adults and Adolescents With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Margaret H. Collins, MD1, Nirmala P. Gonsalves, MD2, Dhandapani Ashok, MBBS, MRCPCH3, Kevin O. Turner, DO4, Carlos Gonzalez, MS5, Sherif Zaghloul, MD, MSc6, Bram P. Raphael, MD5, James T. Angello, PharmD6, Amr Radwan, MBBCh, MA5
1Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH; 2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 3Children’s Hospital, London Health Sciences Centre, Western University, London, ON, Canada; 4Pathology Department, University of Minnesota, Medical School, Minneapolis, MN; 5Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tarrytown, NY; 6Sanofi, Morristown, NJ
Introduction: The diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) relies on symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and esophageal eosinophil density >15 eosinophils/high-power field. The EoE Histologic Scoring System (EoEHSS) provides a comprehensive assessment of 8 histopathologic features commonly seen in EoE patients. Here, we assessed the proportion of adolescents and adults with EoE who resolved each individual EoEHSS feature with dupilumab vs placebo in LIBERTY EoE TREET (NCT03633617).
Methods: In Part B, patients aged ≥12 years with EoE were randomized 1:1 to 24 weeks of dupilumab 300 mg weekly (qw) or placebo. Eligible patients entered Part C and received dupilumab 300 mg qw to Week (W) 52. EoEHSS component (esophageal inflammation [EI], eosinophil abscesses [EA], eosinophil surface layering [ESL], surface epithelial alteration [SEA], basal zone hyperplasia [BZH], dilated intercellular spaces [DIS], dyskeratotic epithelial cells [DEC], and lamina propria fibrosis [LPF]) scores were evaluated at baseline, W24, and W52. The proportion of patients who achieved a score of 0 (resolution) for each EoEHSS grade and stage component was assessed.
Results: The proportions of patients with EoEHSS grade/stage component scores of 0 at baseline were similar in the dupilumab vs placebo groups: EA (31% vs 32%/31% vs 32%), ESL (14% vs 23%/14% vs 23%), SEA (35% vs 42%/35% vs 42%), BZH (0% vs 4%/0% vs 4%), LPF (36% vs 37%/36% vs 37%), DEC (73% vs 84%/73% vs 84%); no patients had EI or DIS grade/stage scores of 0. Dupilumab treatment vs placebo led to a greater proportion of patients achieving resolution in both grade/stage EA (97% vs 49%/97% vs 49%), ESL (96% vs 30%/96% vs 30%), SEA (87% vs 50%/87% vs 50%), BZH (78% vs 11%/78% vs 11%), LPF (90% vs 35%/90% vs 35%) (all P< 0.0001), EI (15% vs 0%/88% vs 8%; P< 0.001), and DEC (93% vs 74%/93% vs 74%; P< 0.01) at W24 (Figure). Resolution was not observed in DIS (0% vs 2.8%; P=0.2415). At W52, effects were maintained or improved further with continued dupilumab; improvements in most EoEHSS components were observed in patients who switched from placebo to dupilumab at W24 (Figure).
Discussion: Dupilumab led to resolution of both grade and stage scores in most EoEHSS histopathologic features vs placebo after 24 weeks of treatment; resolution was maintained or achieved in patients receiving continuous dupilumab for 52 weeks. The greatest improvements occurred in eosinophil- (ESL) and epithelial-related (DEC and BZH) features, and LPF.

Figure: Figure. Proportion of patients with histologic features that were resolved at A) Week 24 and B) Week 52.
**Nominal P<0.01, ***P <0.001, ****P <0.0001 vs placebo. N = number of patients with non-missing values at each visit. P-values are from Fisher’s exact test if expected counts are <5; otherwise from Chi-square test.
CI, confidence interval; EoEHSS, Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histologic Scoring System.
Disclosures:
Margaret Collins: Alimentiv – Consultant. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Calypso Biotech – Consultant. EsoCap Biotech – Consultant. GSK – Consultant. Receptos/Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Shire – Consultant.
Nirmala Gonsalves: Allakos – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Exact Sciences – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Dhandapani Ashok: Alexion Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. LaunchitDTx – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Mirum Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sanofi – Speakers Bureau.
Kevin Turner: Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ellodi – Grant/Research Support. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Carlos Gonzalez: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sherif Zaghloul: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Bram Raphael: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
James Angello: Sanofi – Employee, Stock Options.
Amr Radwan: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Margaret H. Collins, MD1, Nirmala P. Gonsalves, MD2, Dhandapani Ashok, MBBS, MRCPCH3, Kevin O. Turner, DO4, Carlos Gonzalez, MS5, Sherif Zaghloul, MD, MSc6, Bram P. Raphael, MD5, James T. Angello, PharmD6, Amr Radwan, MBBCh, MA5. P0599 - Dupilumab Normalizes Histopathologic Features in Adults and Adolescents With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase 3 LIBERTY EoE TREET Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

