Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P0509 - Post-Polypectomy Guideline Adherence in the Post-Pandemic Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Yizhong Wu, MD
Baylor Scott & White
Georgetown, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Yizhong Wu, MD1, Alexander Grieme, DO2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS1, Sanjay Prasad, MD2, Eric Smith, MD, MPH1, Bryce Bushe, MD2, Andrew Han, MD3
1Baylor Scott & White, Georgetown, TX; 2Baylor Scott & White, Round Rock, TX; 3University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX
Introduction: The US multi society task force (USMSTF) updated its guidelines for surveillance intervals in 2020, introducing longer recommended intervals for low risk adenomas (LRA). The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to evaluate adherence to the updated 2020 USMSTF guidelines in clinical practice.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Google Scholar from inception until May 2025 for studies reporting guideline adherence for surveillance colonoscopies. We specifically looked for adherence to the USMSTF 2020 guidelines update. We assessed the data for overall guideline adherence, longer and shorter surveillance intervals amongst non-adherent cases, and adherence stratified by findings of LRA, high risk adenomas (HRA), hyperplastic polyps (HP), and sessile serrated polyps (SSP). We used both a fixed and a random effects model, and the data was presented using odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Meta-analysis of proportions was performed using R software with the metafor package.
Results: A total of 3 studies totaling 2147 cases were included in this study. Overall adherence to the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was 66.9% (95% CI 43.2 - 84.4). Surveillance interval was shorter than the guideline recommendations in 25% (95% CI 10.1 - 49.2) of cases. There were less than 10 cases where the surveillance interval was longer than recommended. For LRA, surveillance interval guideline adherence was 30.7% (95% CI 1.9 - 90.8). For HRA, guideline adherence was 82.7% (95% CI 67.6 - 91.6). For HP, guideline adherence was 70.4% (95% CI 19.1 - 96.0). For SSP, guideline adherence was 79.6% (95% CI 39.6 - 95.9).
Discussion: Surveillance interval guideline adherence has previously been reported at 48.8% for guidelines prior to the 2020 USMSTF update. This analysis found higher guideline adherence since the 2020 update to the updated guidelines at 66.9%. Guideline adherence differed by the type of lesions found during colonoscopy, with the lowest being for LRA. Most non-adherent cases involved shorter than recommended surveillance intervals. We infer that providers were less comfortable with longer surveillance intervals for LRA, resulting in shorter than recommended intervals in this group.
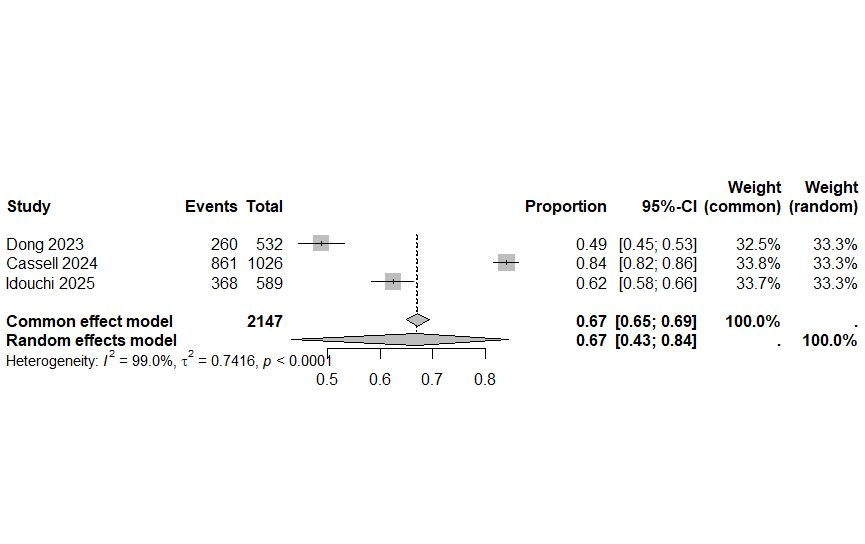
Figure: Figure 1. Overall Guideline Adherence.
Disclosures:
Yizhong Wu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Grieme indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manuel Garza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanjay Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Smith indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bryce Bushe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Han indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yizhong Wu, MD1, Alexander Grieme, DO2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS1, Sanjay Prasad, MD2, Eric Smith, MD, MPH1, Bryce Bushe, MD2, Andrew Han, MD3. P0509 - Post-Polypectomy Guideline Adherence in the Post-Pandemic Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Baylor Scott & White, Georgetown, TX; 2Baylor Scott & White, Round Rock, TX; 3University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX
Introduction: The US multi society task force (USMSTF) updated its guidelines for surveillance intervals in 2020, introducing longer recommended intervals for low risk adenomas (LRA). The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to evaluate adherence to the updated 2020 USMSTF guidelines in clinical practice.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Google Scholar from inception until May 2025 for studies reporting guideline adherence for surveillance colonoscopies. We specifically looked for adherence to the USMSTF 2020 guidelines update. We assessed the data for overall guideline adherence, longer and shorter surveillance intervals amongst non-adherent cases, and adherence stratified by findings of LRA, high risk adenomas (HRA), hyperplastic polyps (HP), and sessile serrated polyps (SSP). We used both a fixed and a random effects model, and the data was presented using odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Meta-analysis of proportions was performed using R software with the metafor package.
Results: A total of 3 studies totaling 2147 cases were included in this study. Overall adherence to the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was 66.9% (95% CI 43.2 - 84.4). Surveillance interval was shorter than the guideline recommendations in 25% (95% CI 10.1 - 49.2) of cases. There were less than 10 cases where the surveillance interval was longer than recommended. For LRA, surveillance interval guideline adherence was 30.7% (95% CI 1.9 - 90.8). For HRA, guideline adherence was 82.7% (95% CI 67.6 - 91.6). For HP, guideline adherence was 70.4% (95% CI 19.1 - 96.0). For SSP, guideline adherence was 79.6% (95% CI 39.6 - 95.9).
Discussion: Surveillance interval guideline adherence has previously been reported at 48.8% for guidelines prior to the 2020 USMSTF update. This analysis found higher guideline adherence since the 2020 update to the updated guidelines at 66.9%. Guideline adherence differed by the type of lesions found during colonoscopy, with the lowest being for LRA. Most non-adherent cases involved shorter than recommended surveillance intervals. We infer that providers were less comfortable with longer surveillance intervals for LRA, resulting in shorter than recommended intervals in this group.

Figure: Figure 1. Overall Guideline Adherence.
Disclosures:
Yizhong Wu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Grieme indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manuel Garza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanjay Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Smith indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bryce Bushe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Han indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yizhong Wu, MD1, Alexander Grieme, DO2, Manuel Garza, MD, MS1, Sanjay Prasad, MD2, Eric Smith, MD, MPH1, Bryce Bushe, MD2, Andrew Han, MD3. P0509 - Post-Polypectomy Guideline Adherence in the Post-Pandemic Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
