Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P0508 - Neoplasia Detection in Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing White Light Endoscopy With Dye-Based and Virtual Chromoendoscopy (Narrow Band Imaging, Intelligent-Scan, Linked Color Imaging)
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahmad Zulaid, MD (he/him/his)
Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan
Elizabeth, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mahnoor Baloch, MBBS1, Ahmad Zulaid, MD2, Muhammad A. Kamal, MBBS3, Omama Ayatullah, MBBS4, Allah Dad, MD5, Asra Amjad, MBBS6, Kinza Bakht, MBBS7, Ayesha Nazeef, 1
1Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Quaid e Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Dow Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 6King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Pakistan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Lynch syndrome (LS) is chracterized by the presence of flat, sessile, and often microsatellite instability (MSI-H) lesions with elevated lifetime risk up to 80% for Colorectal Cancer in affected individuals. These lesions are frequently missed on conventional white light endoscopy (WLE). Chromoendoscopy (ChE), both dye-based and virtual modalities, has been proposed to improve neoplasia detection in LS patients. Therefore, In this meta-analysis, we aim to systematically analyze the comparison of the efficacy of conventional WLE with ChE.
Methods: A systematic search was performed on PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library till May 2025 since the inception, yielding 258 results. After exclusion of studies through deduplication, Title/Abstract and full text screening we finalized 8 studies that met our inclusion criteria. The statistical analysis was performed on RevMan 5 (version 5.4), pooling
Rate Ratios of detection rates (RRs) with 95% Confidence Interval for ChE (dye-based or virtual) and WLE in LS surveillance. The outcomes reported were Lesion Detection Rate (LDR), Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR), and detection of advanced adenomas, flat lesions, serrated lesions, hyperplastic polyps, and proximal lesions.
Results: The analysis encompassed the total of 1469 lesions with 748 lesions that were detected in the ChE group versus 721 in the WLE group.The RR for overall LDR was 1.01 (95% CI: 0.92–1.10), while the ADR was (RR: 0.93, 95% CI: 0.74–1.17). Detection of flat lesions (RR: 1.09, 95% CI: 0.84–1.47) and proximal lesions (RR: 1.15, 95% CI: 0.98–1.34) favored ChE, however the results were non-significant. No significant differences were observed in advanced adenoma (RR: 0.72, 95% CI: 0.40–1.29), serrated lesion (RR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.49–1.71), or sessile serrated lesion (RR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.45–1.56) detection.
Discussion: This ChE, including both dye-based and virtual modalities, yields non-significant, however, slightly better detection rates compared to WLE in LS surveillance and can offer modest benefits in detecting flat and proximal lesions. These findings support the potential for integration of ChE into surveillance protocols to optimize neoplasia detection and outcomes in this high-risk population. Nonetheless, more studies are required to address this comparison in detail.
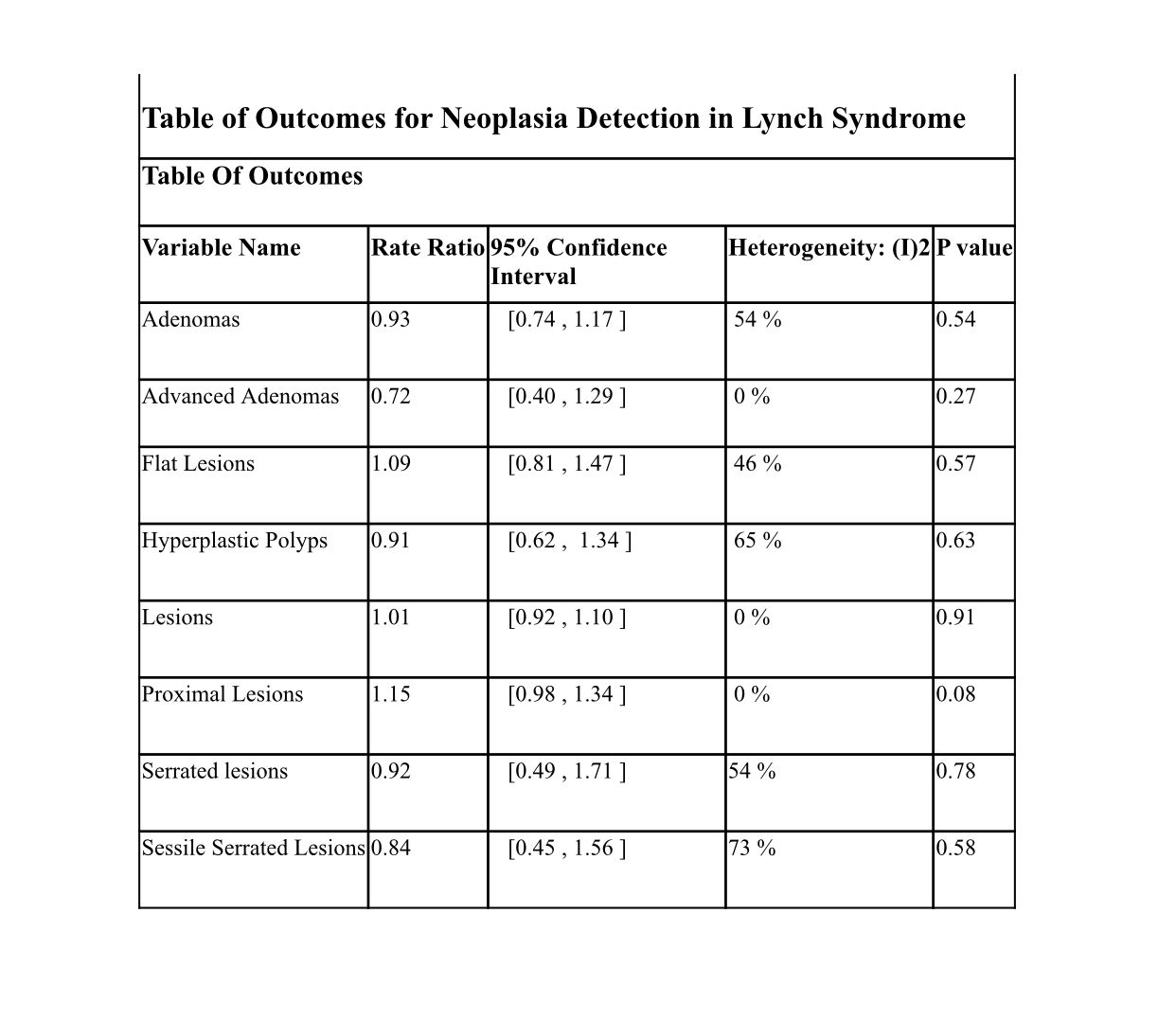
Figure: Table of Outcome for Neoplasia detection in Lynch Syndrome
Disclosures:
Mahnoor Baloch indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zulaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omama Ayatullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asra Amjad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Nazeef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahnoor Baloch, MBBS1, Ahmad Zulaid, MD2, Muhammad A. Kamal, MBBS3, Omama Ayatullah, MBBS4, Allah Dad, MD5, Asra Amjad, MBBS6, Kinza Bakht, MBBS7, Ayesha Nazeef, 1. P0508 - Neoplasia Detection in Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing White Light Endoscopy With Dye-Based and Virtual Chromoendoscopy (Narrow Band Imaging, Intelligent-Scan, Linked Color Imaging), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 2Quaid-e-Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Multan, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Quaid e Azam Medical College, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Dow Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 5Shiekh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan; 6King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Pakistan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Sheikh Zayed Medical College Rahim Yar Khan, Muzaffargarh, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Lynch syndrome (LS) is chracterized by the presence of flat, sessile, and often microsatellite instability (MSI-H) lesions with elevated lifetime risk up to 80% for Colorectal Cancer in affected individuals. These lesions are frequently missed on conventional white light endoscopy (WLE). Chromoendoscopy (ChE), both dye-based and virtual modalities, has been proposed to improve neoplasia detection in LS patients. Therefore, In this meta-analysis, we aim to systematically analyze the comparison of the efficacy of conventional WLE with ChE.
Methods: A systematic search was performed on PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library till May 2025 since the inception, yielding 258 results. After exclusion of studies through deduplication, Title/Abstract and full text screening we finalized 8 studies that met our inclusion criteria. The statistical analysis was performed on RevMan 5 (version 5.4), pooling
Rate Ratios of detection rates (RRs) with 95% Confidence Interval for ChE (dye-based or virtual) and WLE in LS surveillance. The outcomes reported were Lesion Detection Rate (LDR), Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR), and detection of advanced adenomas, flat lesions, serrated lesions, hyperplastic polyps, and proximal lesions.
Results: The analysis encompassed the total of 1469 lesions with 748 lesions that were detected in the ChE group versus 721 in the WLE group.The RR for overall LDR was 1.01 (95% CI: 0.92–1.10), while the ADR was (RR: 0.93, 95% CI: 0.74–1.17). Detection of flat lesions (RR: 1.09, 95% CI: 0.84–1.47) and proximal lesions (RR: 1.15, 95% CI: 0.98–1.34) favored ChE, however the results were non-significant. No significant differences were observed in advanced adenoma (RR: 0.72, 95% CI: 0.40–1.29), serrated lesion (RR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.49–1.71), or sessile serrated lesion (RR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.45–1.56) detection.
Discussion: This ChE, including both dye-based and virtual modalities, yields non-significant, however, slightly better detection rates compared to WLE in LS surveillance and can offer modest benefits in detecting flat and proximal lesions. These findings support the potential for integration of ChE into surveillance protocols to optimize neoplasia detection and outcomes in this high-risk population. Nonetheless, more studies are required to address this comparison in detail.

Figure: Table of Outcome for Neoplasia detection in Lynch Syndrome
Disclosures:
Mahnoor Baloch indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zulaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omama Ayatullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Allah Dad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asra Amjad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kinza Bakht indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Nazeef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahnoor Baloch, MBBS1, Ahmad Zulaid, MD2, Muhammad A. Kamal, MBBS3, Omama Ayatullah, MBBS4, Allah Dad, MD5, Asra Amjad, MBBS6, Kinza Bakht, MBBS7, Ayesha Nazeef, 1. P0508 - Neoplasia Detection in Lynch Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing White Light Endoscopy With Dye-Based and Virtual Chromoendoscopy (Narrow Band Imaging, Intelligent-Scan, Linked Color Imaging), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

