Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0304 - Diagnostic Comparison of Anorectal Manometry and MRI Defecography Using BET as the Gold Standard
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SH
Sahla Hammad, MD
Atrium Health
Charlotte, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Sahla Hammad, MD1, Rachel Moffett, DO1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Jason Baker, MS2, Baha Moshiree, MD3
1Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC; 2Anxrobotics, Foley, AL; 3Atrium Health Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC
Introduction: Defecatory disorders like Chronic Constipation (CC) and Fecal Incontinence (FI), significantly impact quality of life. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management. Balloon Expulsion Test (BET), Anorectal Manometry (ARM) and MRI Defecography (MR-DEF) are commonly used diagnostic tools to evaluate anorectal function. This study aims to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ARM and MR-DEF using BET as a reference.
Methods: A retrospective review of 22 patients seen at a single hybrid academic center from June 2023 to January 2025 underwent ARM, BET, and MR-DEF for evaluation of FI and/or CC refractory to medical therapy. ARM results were categorized per London Classification Part 3 (Rectoanal Coordination Disorders): (1) Abnormal BET and Dyssynergia (Normal = ≥25% reduction in anorectal pressure from baseline during simulated defecation), (2) Abnormal BET with Poor Propulsion (Normal = ≥45 mmHg in intrarectal pressure during simulated defecation), and (3) Abnormal BET with both. BET consisted of the ability to expel a 50 ml balloon in ≤ 60 seconds. MR-DEF was done if either test was abnormal and assessed structural abnormalities (e.g. rectoceles, cystoceles), anorectal angle, portion of contrast or entire contrast expulsion. BET served as index test vs. ARM and MR-DEF. Analysis included sensitivity, specificity and accuracy for identifying dyssynergia.
Results: N = 22 patients, mean age of 52.6 (SD = 11.7; Range: 26 – 72), 86.4% female, 81.8% Caucasian, and mean BMI of 27.6 (SD = 8.3; Range: 19.9 – 50.2) were analyzed. Indication for testing was 77.2% for CC and 22.8% for FI. Minor findings in the London Classification Part 3 Disorders of Recto anal Coordination showed low-to-moderate accuracy compared to BET: Dyssynergia (36.4%), Poor Propulsion (31.6%), and Poor Propulsion and Dyssynergia (31.6%). Dyssynergia sensitivity, 71.4%, is moderate to abnormal BET. [Table 1] Conversely, MR-DEF variables have greater accuracy to BET compared to ARM: Anorectal Angle (52.4%), Portion Contrast Expulsion (47.1%), and Entire Contrast Expulsion (52.6%). [Table 1].
Discussion: Our study suggests that MR-DEF has greater accuracy compared to rectoanal coordination variables (per London Classification) when using BET as a reference. Comparative data using the London classification for BET and MR DEF is limited, and hence large data sets are needed to evaluate further. MRI additionally found structural abnormalities in 77.2% of patients which would not otherwise have been captured on ARM or BET.
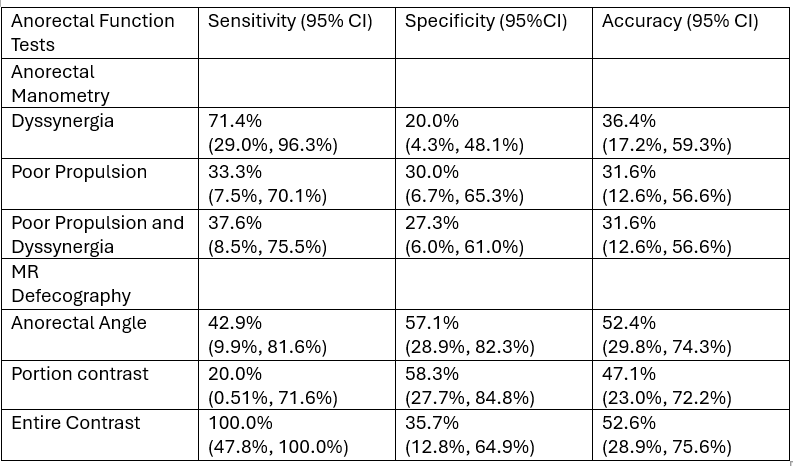
Figure: Table 1
Disclosures:
Sahla Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Moffett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eva Kinzer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Baker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Baha Moshiree indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahla Hammad, MD1, Rachel Moffett, DO1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Jason Baker, MS2, Baha Moshiree, MD3. P0304 - Diagnostic Comparison of Anorectal Manometry and MRI Defecography Using BET as the Gold Standard, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC; 2Anxrobotics, Foley, AL; 3Atrium Health Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC
Introduction: Defecatory disorders like Chronic Constipation (CC) and Fecal Incontinence (FI), significantly impact quality of life. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management. Balloon Expulsion Test (BET), Anorectal Manometry (ARM) and MRI Defecography (MR-DEF) are commonly used diagnostic tools to evaluate anorectal function. This study aims to evaluate the diagnostic performance of ARM and MR-DEF using BET as a reference.
Methods: A retrospective review of 22 patients seen at a single hybrid academic center from June 2023 to January 2025 underwent ARM, BET, and MR-DEF for evaluation of FI and/or CC refractory to medical therapy. ARM results were categorized per London Classification Part 3 (Rectoanal Coordination Disorders): (1) Abnormal BET and Dyssynergia (Normal = ≥25% reduction in anorectal pressure from baseline during simulated defecation), (2) Abnormal BET with Poor Propulsion (Normal = ≥45 mmHg in intrarectal pressure during simulated defecation), and (3) Abnormal BET with both. BET consisted of the ability to expel a 50 ml balloon in ≤ 60 seconds. MR-DEF was done if either test was abnormal and assessed structural abnormalities (e.g. rectoceles, cystoceles), anorectal angle, portion of contrast or entire contrast expulsion. BET served as index test vs. ARM and MR-DEF. Analysis included sensitivity, specificity and accuracy for identifying dyssynergia.
Results: N = 22 patients, mean age of 52.6 (SD = 11.7; Range: 26 – 72), 86.4% female, 81.8% Caucasian, and mean BMI of 27.6 (SD = 8.3; Range: 19.9 – 50.2) were analyzed. Indication for testing was 77.2% for CC and 22.8% for FI. Minor findings in the London Classification Part 3 Disorders of Recto anal Coordination showed low-to-moderate accuracy compared to BET: Dyssynergia (36.4%), Poor Propulsion (31.6%), and Poor Propulsion and Dyssynergia (31.6%). Dyssynergia sensitivity, 71.4%, is moderate to abnormal BET. [Table 1] Conversely, MR-DEF variables have greater accuracy to BET compared to ARM: Anorectal Angle (52.4%), Portion Contrast Expulsion (47.1%), and Entire Contrast Expulsion (52.6%). [Table 1].
Discussion: Our study suggests that MR-DEF has greater accuracy compared to rectoanal coordination variables (per London Classification) when using BET as a reference. Comparative data using the London classification for BET and MR DEF is limited, and hence large data sets are needed to evaluate further. MRI additionally found structural abnormalities in 77.2% of patients which would not otherwise have been captured on ARM or BET.

Figure: Table 1
Disclosures:
Sahla Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Moffett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eva Kinzer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Baker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Baha Moshiree indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahla Hammad, MD1, Rachel Moffett, DO1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Jason Baker, MS2, Baha Moshiree, MD3. P0304 - Diagnostic Comparison of Anorectal Manometry and MRI Defecography Using BET as the Gold Standard, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
