Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0077 - Machine Learning-Based Prediction Models for Pancreatic Cancer Risk in New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical/Biochemical and Genetic Indicators
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ahmad Al Homaid, MD
Nazareth Hospital
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Ahmad Alhomaid, MD1, Salma Abdelhafez, MBBCh2, Mariam Abdelhafez, 2, Neha Singh, MD3, Jay Patel, MBBS4, Utkarsh Dayal, MD5, Sindhura Reddy Dadi, MBBS6, Sri Anjali Gorle, 7, Rupak Desai, MBBS8
1Nazareth Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 3NORTH ALABAMA MEDICAL CENTER, Florence, AL; 4B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Saint Vincent Hospital, Worcester, MA; 6Mnr medical college and hospital, Sangareddy, Telangana, India; 7Andhra Medical College, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 8Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Pancreatic cancer progresses silently, often presenting after disease has advanced beyond curative stages. A subset of patients with newly diagnosed diabetes may exhibit early signs of pancreatic malignancy. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have emerged as tools for analyzing complex clinical, biochemical, and genetic markers to identify high-risk individuals. Despite growing popularity, the predictive accuracy and consistency of these models remain unclear.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. Data from 14 studies across PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar (inception to 2025) that developed machine learning models to predict pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes patients were combined. The primary outcome was area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Random-effects meta-analysis pooled diagnostic accuracy measures, with heterogeneity assessed using I² statistics. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis evaluated robustness of findings.
Results: Fourteen studies with over 2.2 million participants from six countries were included. Studies employed various ML approaches including random forest, logistic regression, and neural networks. Data sources included population biobanks and healthcare databases. The pooled AUC was 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82), indicating good discriminative performance. Individual AUCs ranged from 0.71 to 0.93, with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 98.95%, P < 0.01). Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis confirmed robustness with consistent estimates of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82). Studies utilized diverse predictors including biochemical parameters, demographics, genetic variants, and clinical indicators. Models incorporating clinical and genetic data achieved higher performance.
Discussion: Machine learning models demonstrate good diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic cancer risk prediction in new-onset diabetes (pooled AUC 0.77). Despite heterogeneity, sensitivity analyses confirmed robust findings. These models show promise for clinical implementation as risk stratification tools, enabling earlier detection in high-risk populations. Future research should focus on external validation and clinical integration.
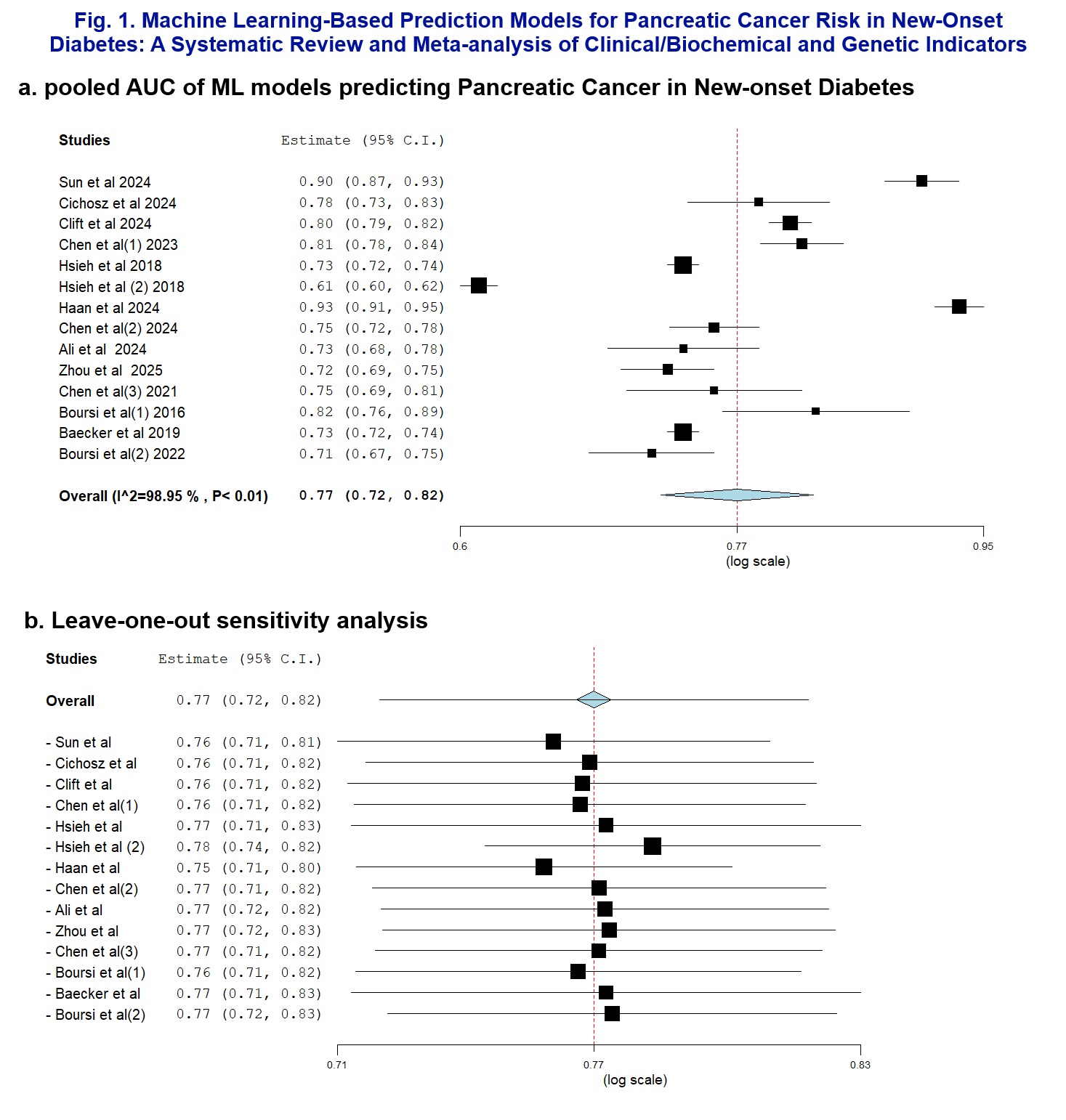
Figure: Figure 1. Machine learning model performance for predicting pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes. (a) Forest plot of pooled AUC from 13 studies showing overall discriminative ability of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82). (b) Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis confirming robustness of the pooled estimate at 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82).
Disclosures:
Ahmad Alhomaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salma Abdelhafez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mariam Abdelhafez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jay Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Utkarsh Dayal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhura Reddy Dadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Anjali Gorle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Alhomaid, MD1, Salma Abdelhafez, MBBCh2, Mariam Abdelhafez, 2, Neha Singh, MD3, Jay Patel, MBBS4, Utkarsh Dayal, MD5, Sindhura Reddy Dadi, MBBS6, Sri Anjali Gorle, 7, Rupak Desai, MBBS8. P0077 - Machine Learning-Based Prediction Models for Pancreatic Cancer Risk in New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical/Biochemical and Genetic Indicators, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Ahmad Alhomaid, MD1, Salma Abdelhafez, MBBCh2, Mariam Abdelhafez, 2, Neha Singh, MD3, Jay Patel, MBBS4, Utkarsh Dayal, MD5, Sindhura Reddy Dadi, MBBS6, Sri Anjali Gorle, 7, Rupak Desai, MBBS8
1Nazareth Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 2Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 3NORTH ALABAMA MEDICAL CENTER, Florence, AL; 4B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Saint Vincent Hospital, Worcester, MA; 6Mnr medical college and hospital, Sangareddy, Telangana, India; 7Andhra Medical College, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India; 8Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Pancreatic cancer progresses silently, often presenting after disease has advanced beyond curative stages. A subset of patients with newly diagnosed diabetes may exhibit early signs of pancreatic malignancy. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have emerged as tools for analyzing complex clinical, biochemical, and genetic markers to identify high-risk individuals. Despite growing popularity, the predictive accuracy and consistency of these models remain unclear.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. Data from 14 studies across PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar (inception to 2025) that developed machine learning models to predict pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes patients were combined. The primary outcome was area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Random-effects meta-analysis pooled diagnostic accuracy measures, with heterogeneity assessed using I² statistics. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis evaluated robustness of findings.
Results: Fourteen studies with over 2.2 million participants from six countries were included. Studies employed various ML approaches including random forest, logistic regression, and neural networks. Data sources included population biobanks and healthcare databases. The pooled AUC was 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82), indicating good discriminative performance. Individual AUCs ranged from 0.71 to 0.93, with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 98.95%, P < 0.01). Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis confirmed robustness with consistent estimates of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82). Studies utilized diverse predictors including biochemical parameters, demographics, genetic variants, and clinical indicators. Models incorporating clinical and genetic data achieved higher performance.
Discussion: Machine learning models demonstrate good diagnostic accuracy for pancreatic cancer risk prediction in new-onset diabetes (pooled AUC 0.77). Despite heterogeneity, sensitivity analyses confirmed robust findings. These models show promise for clinical implementation as risk stratification tools, enabling earlier detection in high-risk populations. Future research should focus on external validation and clinical integration.

Figure: Figure 1. Machine learning model performance for predicting pancreatic cancer in new-onset diabetes. (a) Forest plot of pooled AUC from 13 studies showing overall discriminative ability of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82). (b) Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis confirming robustness of the pooled estimate at 0.77 (95% CI: 0.72-0.82).
Disclosures:
Ahmad Alhomaid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salma Abdelhafez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mariam Abdelhafez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jay Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Utkarsh Dayal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhura Reddy Dadi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Anjali Gorle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Alhomaid, MD1, Salma Abdelhafez, MBBCh2, Mariam Abdelhafez, 2, Neha Singh, MD3, Jay Patel, MBBS4, Utkarsh Dayal, MD5, Sindhura Reddy Dadi, MBBS6, Sri Anjali Gorle, 7, Rupak Desai, MBBS8. P0077 - Machine Learning-Based Prediction Models for Pancreatic Cancer Risk in New-Onset Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical/Biochemical and Genetic Indicators, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

