Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0019 - Risk of Biliary Diseases in Patients Treated With GLP-1 vs GLP-1/GI Receptor Agonists: A Real-World Comparative Analysis of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Medora Doris Rodrigues, MD, MPH
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Medora Doris. Rodrigues, MD, MPH1, Jonathan Scott, MD2, Brian T. Lee, MD3, Mena Saad, DO4, Sanya Dhama, MD5, Wichit Srikureja, MD6, Anthony Firek, MD2, Khalid Mumtaz, MBBS, MSc1
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Riverside University Health System, Riverside, CA; 3Hoag Liver Program, Hoag Digestive Health Institute, Hoag Hospital, Newport Beach, CA, Newport Beach, CA; 4Riverside University Health System, Moreno Valley, CA; 5UCR, Riverside, CA; 6Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, WA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), including Semaglutide and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RA Tirzepatide, are increasingly prescribed for diabetes and obesity. However, their role in promoting biliary disease is under-investigated. We aimed to compare the risk of biliary disease between GLP-1 RAs and GLP-1/GIP therapies.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX Research Network (Cambridge, MA), a federated network of de-identified electronic health records. Adults (≥18 years) who initiated and continued subcutaneous Semaglutide or Tirzepatide between 2006 and 2025 were included. Patients with pre-existing biliary disease or prior cholecystectomy were excluded. Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance cohorts by age, sex, BMI, diabetes status, and baseline lipid profile. The primary outcome was new biliary disease (ICD-10 codes for cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, and biliary pancreatitis). Secondary outcomes included cholecystectomy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Cox regression models estimated relative risk.
Results: Baseline characteristics for Tirzepatide (n=63,878) and Semaglutide (n=119,588) users are shown in Table 1. After matching (n=63,057 per group), Tirzepatide users had significantly lower risk of cholelithiasis (0.86% vs. 1.48%; RR 0.58, p< 0.0001), cholecystitis (0.24% vs. 0.45%; RR 0.54, p< 0.0001), choledocholithiasis (0.16% vs. 0.34%; RR 0.47, p< 0.0001), and other gallbladder complications (0.37% vs. 0.65; RR 0.57, p< 0.0001). Biliary pancreatitis was numerically lower (0.04% vs. 0.06%; RR 0.65, p=0.08) but not statistically significant (Table 2a).
Among those with biliary disease, cholecystectomy occurred in 20% of Tirzepatide users versus 21% of Semaglutide users (RR 0.97, p=0.71), and ERCP was performed in 2.72% vs. 3.45% (RR 0.79, p=0.32), with no significant differences (Table 2b).
Discussion: Tirzepatide is associated with a significantly lower risk of biliary disease compared to Semaglutide, including lower rates of cholecystitis and choledocholithiasis. While procedural interventions were numerically reduced in the Tirzepatide group, differences were not statistically significant. These findings suggest a more favorable biliary safety profile for Tirzepatide among GLP-1-based therapies.
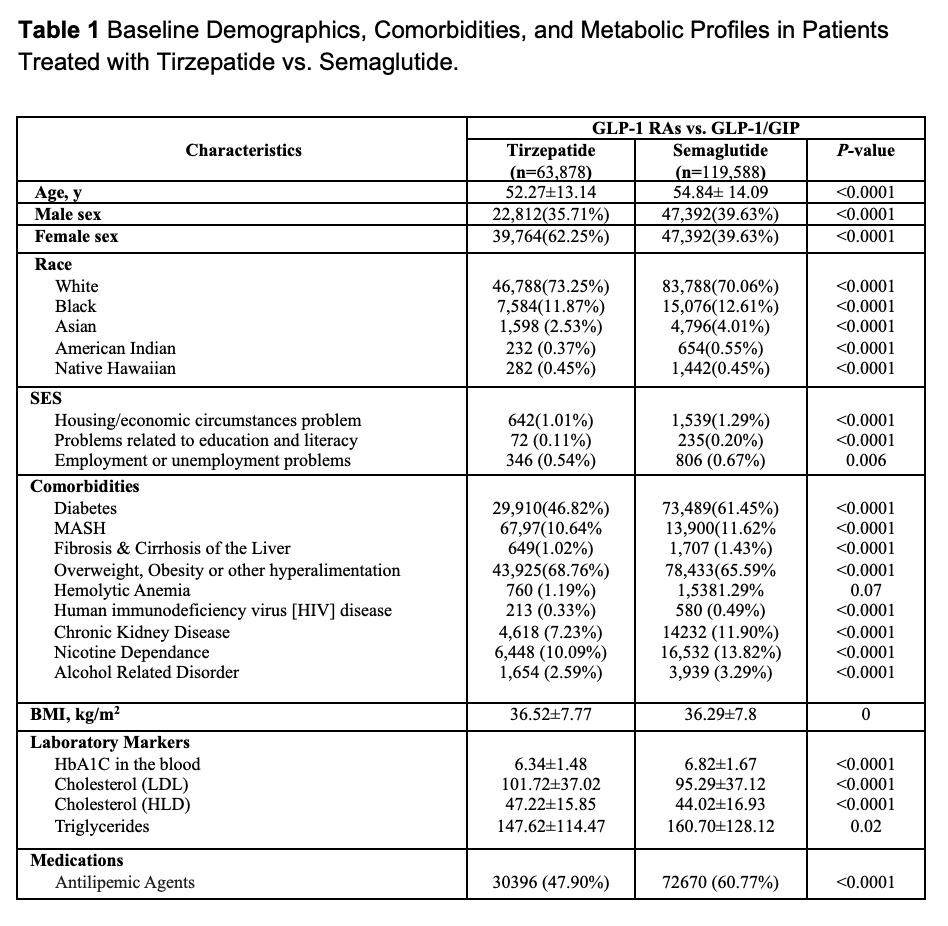
Figure: Baseline Demographics, Comorbidities, and Metabolic Profiles in Patients Treated with Tirzepatide vs. Semaglutide.
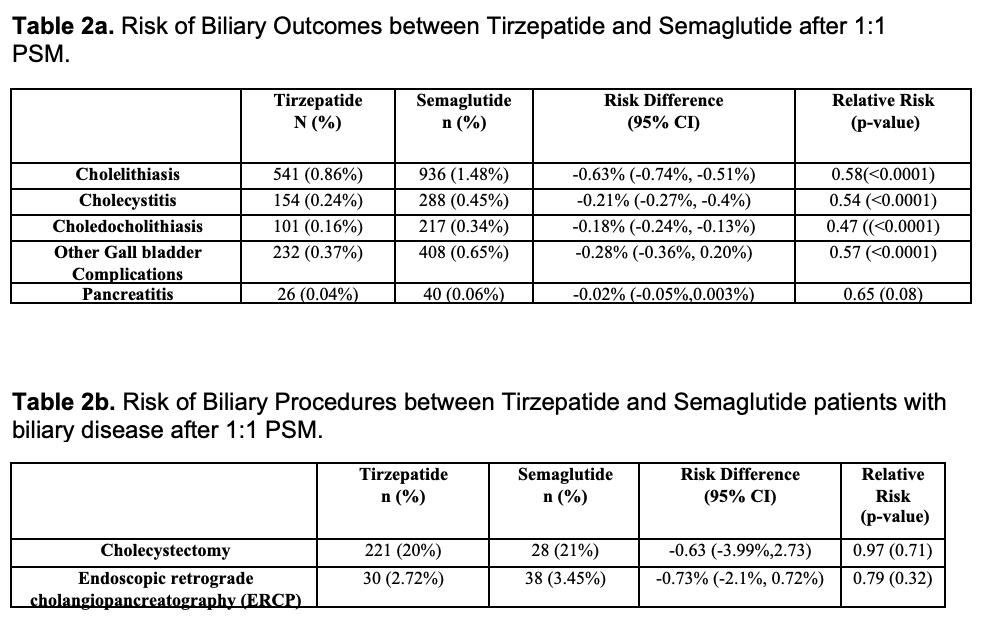
Figure: Table 2a. Risk of Biliary Outcomes between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide after 1:1 PSM.
Table 2b. Risk of Biliary Procedures between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide patients with biliary disease after 1:1 PSM.
Disclosures:
Medora Rodrigues indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathan Scott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Lee: Cook Medical – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Madrigal Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Mena Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanya Dhama indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wichit Srikureja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Firek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Mumtaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Medora Doris. Rodrigues, MD, MPH1, Jonathan Scott, MD2, Brian T. Lee, MD3, Mena Saad, DO4, Sanya Dhama, MD5, Wichit Srikureja, MD6, Anthony Firek, MD2, Khalid Mumtaz, MBBS, MSc1. P0019 - Risk of Biliary Diseases in Patients Treated With GLP-1 vs GLP-1/GI Receptor Agonists: A Real-World Comparative Analysis of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Riverside University Health System, Riverside, CA; 3Hoag Liver Program, Hoag Digestive Health Institute, Hoag Hospital, Newport Beach, CA, Newport Beach, CA; 4Riverside University Health System, Moreno Valley, CA; 5UCR, Riverside, CA; 6Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center, Spokane, WA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), including Semaglutide and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)/GLP-1 RA Tirzepatide, are increasingly prescribed for diabetes and obesity. However, their role in promoting biliary disease is under-investigated. We aimed to compare the risk of biliary disease between GLP-1 RAs and GLP-1/GIP therapies.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX Research Network (Cambridge, MA), a federated network of de-identified electronic health records. Adults (≥18 years) who initiated and continued subcutaneous Semaglutide or Tirzepatide between 2006 and 2025 were included. Patients with pre-existing biliary disease or prior cholecystectomy were excluded. Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance cohorts by age, sex, BMI, diabetes status, and baseline lipid profile. The primary outcome was new biliary disease (ICD-10 codes for cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, and biliary pancreatitis). Secondary outcomes included cholecystectomy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Cox regression models estimated relative risk.
Results: Baseline characteristics for Tirzepatide (n=63,878) and Semaglutide (n=119,588) users are shown in Table 1. After matching (n=63,057 per group), Tirzepatide users had significantly lower risk of cholelithiasis (0.86% vs. 1.48%; RR 0.58, p< 0.0001), cholecystitis (0.24% vs. 0.45%; RR 0.54, p< 0.0001), choledocholithiasis (0.16% vs. 0.34%; RR 0.47, p< 0.0001), and other gallbladder complications (0.37% vs. 0.65; RR 0.57, p< 0.0001). Biliary pancreatitis was numerically lower (0.04% vs. 0.06%; RR 0.65, p=0.08) but not statistically significant (Table 2a).
Among those with biliary disease, cholecystectomy occurred in 20% of Tirzepatide users versus 21% of Semaglutide users (RR 0.97, p=0.71), and ERCP was performed in 2.72% vs. 3.45% (RR 0.79, p=0.32), with no significant differences (Table 2b).
Discussion: Tirzepatide is associated with a significantly lower risk of biliary disease compared to Semaglutide, including lower rates of cholecystitis and choledocholithiasis. While procedural interventions were numerically reduced in the Tirzepatide group, differences were not statistically significant. These findings suggest a more favorable biliary safety profile for Tirzepatide among GLP-1-based therapies.

Figure: Baseline Demographics, Comorbidities, and Metabolic Profiles in Patients Treated with Tirzepatide vs. Semaglutide.

Figure: Table 2a. Risk of Biliary Outcomes between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide after 1:1 PSM.
Table 2b. Risk of Biliary Procedures between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide patients with biliary disease after 1:1 PSM.
Disclosures:
Medora Rodrigues indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathan Scott indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Lee: Cook Medical – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Madrigal Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Mena Saad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanya Dhama indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wichit Srikureja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Firek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khalid Mumtaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Medora Doris. Rodrigues, MD, MPH1, Jonathan Scott, MD2, Brian T. Lee, MD3, Mena Saad, DO4, Sanya Dhama, MD5, Wichit Srikureja, MD6, Anthony Firek, MD2, Khalid Mumtaz, MBBS, MSc1. P0019 - Risk of Biliary Diseases in Patients Treated With GLP-1 vs GLP-1/GI Receptor Agonists: A Real-World Comparative Analysis of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

