Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0013 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Complications in Patients Admitted With Acute Pancreatitis: A Nationwide Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AS
Anmol Singh, MBBS
Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Nashville, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Anmol Singh, MBBS1, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS2, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS3, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Dalbir Sandhu, MD6
1Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 2Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 3Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Sarcopenia, the progressive loss of muscle mass, is a known prognostic factor in various illnesses. Acute pancreatitis (AP), an inflammatory pancreatic disorder, involves significant metabolic stress. While malnutrition is linked to increased mortality and costs in AP, the specific impact of sarcopenia on clinical outcomes in hospitalized AP patients remains underexplored.
Methods: We used the National Inpatient Sample 2016-2022 to identify adult patients ( >18years). Patients with AP were stratified into two groups based on the presence of sarcopenia.. Patients with missing demographics or mortality data were excluded. Multivariate logistic regression model was used to assess the association of sarcopenia with various clinical outcomes, adjusting for patient demographics, comorbidities, etiology of pancreatitis, and hospital-acquired infections.
Results: Out of 2,467,233 patients were admitted with AP, 227,545 (9.2%) diagnosed with sarcopenia. The majority of sarcopenic patients were aged 45-65 years (40.3%), male (53.6%), White (65.2%), and had Medicare insurance (42%). Patients with sarcopenia had a higher incidence of in-hospital mortality (7.3% vs. 2%), sepsis (7.3% vs. 4.6%), shock (14.6% vs 3.6%), acute kidney injury (AKI) (37.9% vs 18%), deep vein thrombosis (DVT) (3.7% vs 0.7%), pulmonary embolism (PE) (1.7% vs 0.5%), portal vein thrombus (PVT) (2.8% vs 0.8%) and ileus (7.6% vs 3.2%) (Figure 1). Patients with sarcopenia had a higher prevalence of infections such as urinary tract infection (13.4% vs 7.6%), pneumonia (11.7% vs 4%), cholangitis (3.1% vs 2.2%), C. Difficile (3.6% vs 1%), and cellulitis (2% vs 0.8%). After adjusting for confounding factors, patients with sarcopenia had higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-1.41, 95% CI-1.34- 1.48,p< 0.001), shock (aOR-1.92, 95% CI-1.85- 2.00, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.41, 95% CI- 1.41-1.49, p< 0.001), intensive care unit admission (aOR-1.79, 95% CI- 1.72-1.87, p< 0.001), PE (aOR-1.60, 95% CI- 1.41-1.82, p< 0.001), DVT (aOR-2.37, 95% CI- 2.21-2.54, p< 0.001), PVT (aOR- 2.57, 95% CI- 2.38-2.77, p< 0.001) and ileus ( aOR-1.70, 95% CI-1.63-1.77, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: Our study notes that AP patients with sarcopenia are at higher risk of worse outcomes compared to those without sarcopenia. Early identification and targeted interventions—such as nutritional support and close monitoring—may help mitigate risks and improve outcomes in this high-risk population.
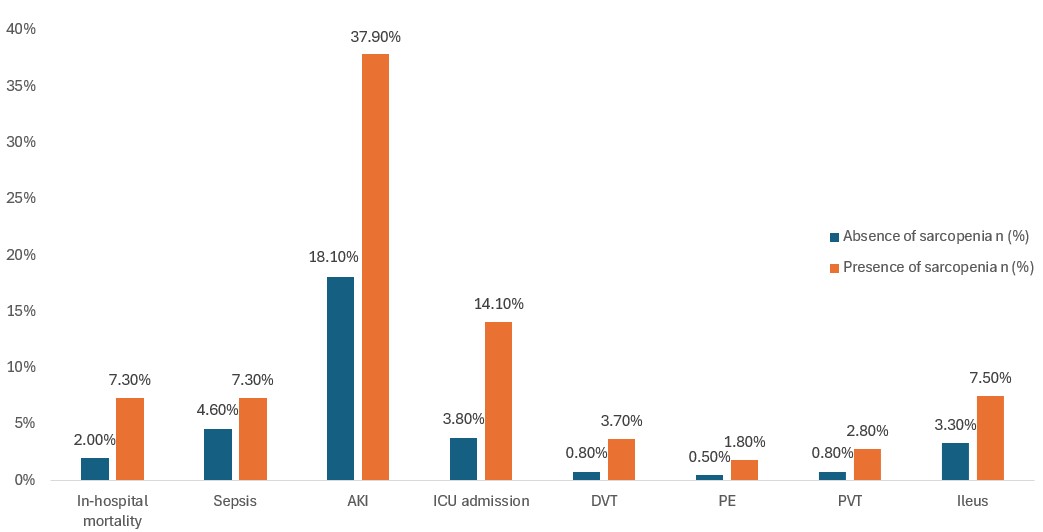
Figure: Figure 1: Clinical outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis with and without Sarcopenia; AKI: Acute Kidney Injury; ICU: Intensive Care Unit; DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis; PE: Pulmonary Embolism; PVT: Portal Vein Thrombosis
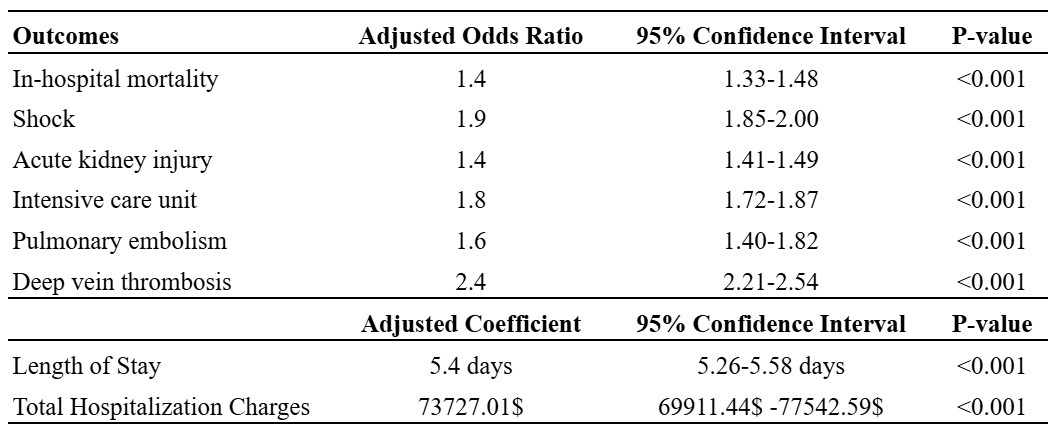
Figure: Table 1: Results of multivariate logistic regression analysis assessing the relationship between sarcopenia and clinical outcomes
Disclosures:
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sampada Bhasker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh, MBBS1, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS2, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS3, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Dalbir Sandhu, MD6. P0013 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Complications in Patients Admitted With Acute Pancreatitis: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Tristar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, TN, Nashville, TN; 2Punjab Institute of Medical Sciences, Jalandhar, Punjab, India; 3Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 4Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India; 5Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, New Jersey, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Sarcopenia, the progressive loss of muscle mass, is a known prognostic factor in various illnesses. Acute pancreatitis (AP), an inflammatory pancreatic disorder, involves significant metabolic stress. While malnutrition is linked to increased mortality and costs in AP, the specific impact of sarcopenia on clinical outcomes in hospitalized AP patients remains underexplored.
Methods: We used the National Inpatient Sample 2016-2022 to identify adult patients ( >18years). Patients with AP were stratified into two groups based on the presence of sarcopenia.. Patients with missing demographics or mortality data were excluded. Multivariate logistic regression model was used to assess the association of sarcopenia with various clinical outcomes, adjusting for patient demographics, comorbidities, etiology of pancreatitis, and hospital-acquired infections.
Results: Out of 2,467,233 patients were admitted with AP, 227,545 (9.2%) diagnosed with sarcopenia. The majority of sarcopenic patients were aged 45-65 years (40.3%), male (53.6%), White (65.2%), and had Medicare insurance (42%). Patients with sarcopenia had a higher incidence of in-hospital mortality (7.3% vs. 2%), sepsis (7.3% vs. 4.6%), shock (14.6% vs 3.6%), acute kidney injury (AKI) (37.9% vs 18%), deep vein thrombosis (DVT) (3.7% vs 0.7%), pulmonary embolism (PE) (1.7% vs 0.5%), portal vein thrombus (PVT) (2.8% vs 0.8%) and ileus (7.6% vs 3.2%) (Figure 1). Patients with sarcopenia had a higher prevalence of infections such as urinary tract infection (13.4% vs 7.6%), pneumonia (11.7% vs 4%), cholangitis (3.1% vs 2.2%), C. Difficile (3.6% vs 1%), and cellulitis (2% vs 0.8%). After adjusting for confounding factors, patients with sarcopenia had higher odds of in-hospital mortality (aOR-1.41, 95% CI-1.34- 1.48,p< 0.001), shock (aOR-1.92, 95% CI-1.85- 2.00, p< 0.001), AKI (aOR-1.41, 95% CI- 1.41-1.49, p< 0.001), intensive care unit admission (aOR-1.79, 95% CI- 1.72-1.87, p< 0.001), PE (aOR-1.60, 95% CI- 1.41-1.82, p< 0.001), DVT (aOR-2.37, 95% CI- 2.21-2.54, p< 0.001), PVT (aOR- 2.57, 95% CI- 2.38-2.77, p< 0.001) and ileus ( aOR-1.70, 95% CI-1.63-1.77, p< 0.001) (Table 1).
Discussion: Our study notes that AP patients with sarcopenia are at higher risk of worse outcomes compared to those without sarcopenia. Early identification and targeted interventions—such as nutritional support and close monitoring—may help mitigate risks and improve outcomes in this high-risk population.

Figure: Figure 1: Clinical outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis with and without Sarcopenia; AKI: Acute Kidney Injury; ICU: Intensive Care Unit; DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis; PE: Pulmonary Embolism; PVT: Portal Vein Thrombosis

Figure: Table 1: Results of multivariate logistic regression analysis assessing the relationship between sarcopenia and clinical outcomes
Disclosures:
Anmol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sampada Bhasker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanisha Sehgal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carol Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aalam Sohal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anmol Singh, MBBS1, Sampada Bhasker, MBBS2, Mohammad Naseem, MBBS3, Tanisha Sehgal, MBBS4, Carol Singh, MBBS5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Aalam Sohal, MD6, Dalbir Sandhu, MD6. P0013 - Impact of Sarcopenia on Complications in Patients Admitted With Acute Pancreatitis: A Nationwide Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
